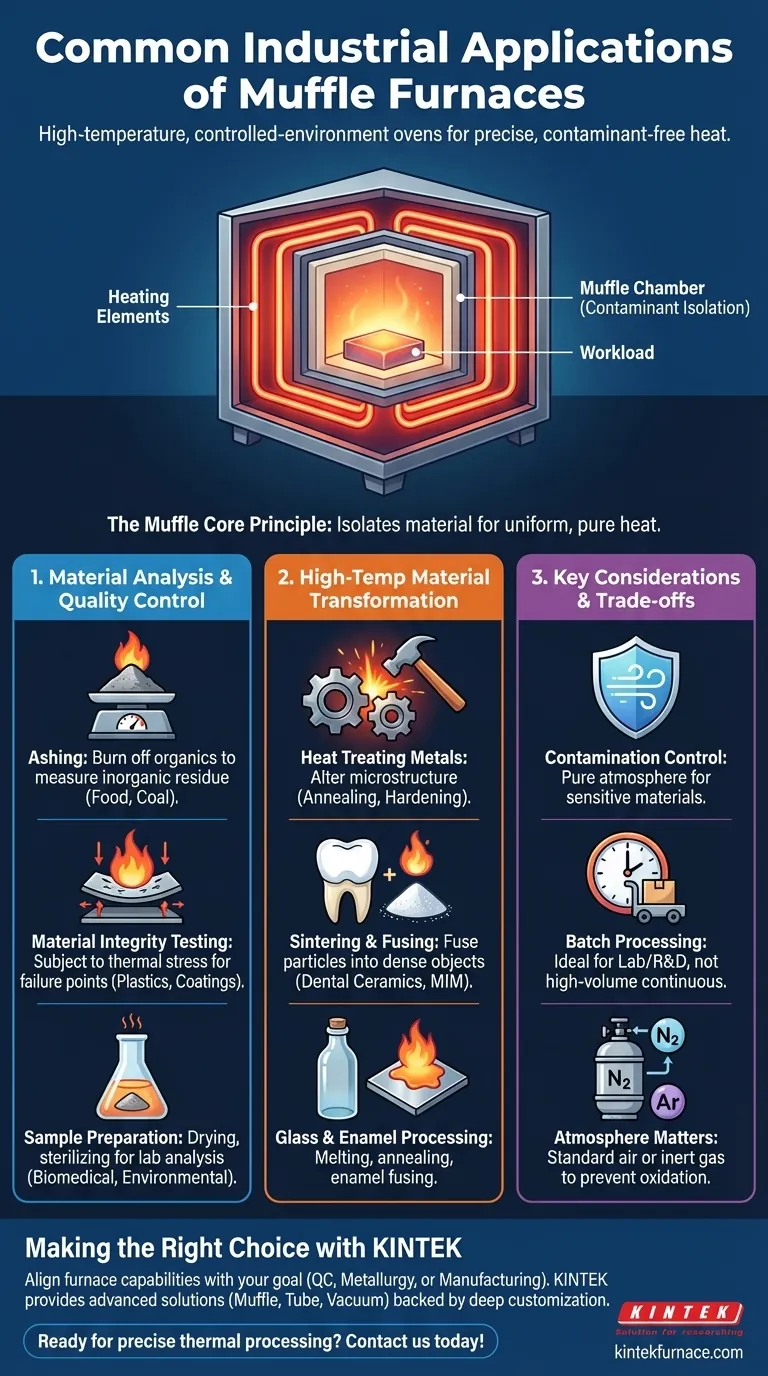
In short, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used across countless industries for processes requiring extreme heat in a controlled environment. Its applications fall into three main categories: material analysis and testing, the heat treatment of metals and ceramics, and specialized manufacturing processes like creating glass or dental crowns. The furnace's key feature is a "muffle," or inner chamber, that isolates the material being heated from contaminants.
At its core, the value of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to get hot. It's the ability to provide precisely controlled, uniform, and contaminant-free heat, which is essential for any process where material purity and predictable thermal transformation are non-negotiable.

Material Analysis and Quality Control
One of the most common uses for a muffle furnace is to analyze the fundamental properties of a material. This is a critical step in quality control, research, and regulatory compliance.
Determining Ash Content
Ashing is a primary application. A sample (like a food product, polymer, or coal) is heated to a high temperature to completely burn off all organic substances.
What remains is the ash, or the non-combustible inorganic residue. Measuring the weight of this ash is a critical quality metric in industries from food science to petrochemicals. The muffle's isolation ensures the result is not skewed by contaminants.
Testing Material Integrity
Muffle furnaces are used to subject materials to extreme thermal stress. This can include testing the strength of plastics, the durability of paint coatings, or the properties of fibers after heat exposure.
By using precise temperature profiles, researchers and engineers can determine a material's failure points and performance characteristics under specific conditions.
Sample Preparation
In biomedical and environmental labs, muffle furnaces prepare samples for further analysis. This can involve drying biological tissues, sterilizing equipment, or removing organic matter from water samples before testing for mineral content.
High-Temperature Material Transformation
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are workhorses for fundamentally changing a material's physical properties. These metallurgical and ceramic processes rely on exact temperature control.
Heat Treating Metals
Heat treatment alters the microstructure of metals to change their properties. A muffle furnace provides the clean, controlled environment needed for these processes.
Common treatments include annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility), hardening (to increase strength), brazing, and soldering.
Sintering and Fusing Materials
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse particles together without melting them. This is fundamental to creating dense, solid objects from powders.
Applications include creating advanced dental ceramics, producing components via metal injection molding (MIM), and processing materials in the aerospace and nuclear sectors.
Glass and Enamel Processing
Muffle furnaces are used to melt raw materials to create glass. They are also used for glass annealing, a crucial step where finished glass is slowly cooled to remove internal stresses and prevent it from shattering.
Similarly, they are used to fuse enamel coatings onto metal surfaces, creating durable and decorative finishes.
Understanding the Core Principle and Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace involves understanding its primary advantage and its limitations.
The "Muffle" Advantage: Contamination Control
The defining feature is the muffle itself—an inner chamber that separates the workload from the heating elements. In older fuel-fired furnaces, this prevented byproducts of combustion from contaminating the material.
While most modern furnaces are electric, the principle of isolation remains critical. It ensures that the heated atmosphere is pure, which is vital for sensitive materials that could be altered by oxidation or other reactions.
Key Limitation: Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are almost always used for batch processing. You load a sample, run a heating cycle, and then unload it.
This makes them ideal for labs, R&D, and small-scale or specialized production, but less suitable for high-volume, continuous manufacturing, which often requires larger industrial kilns or conveyor belt furnaces.
Atmosphere Matters
A basic muffle furnace operates with a standard air atmosphere. However, many advanced applications, especially in metallurgy, require an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent the metal from oxidizing at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right thermal process, align the furnace's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control and analysis: You need a furnace that provides repeatable, accurate, and contaminant-free heating to ensure your test results (like ash content) are reliable.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy or materials science: You need a furnace with precise temperature programming and, potentially, the ability to control the atmosphere to prevent oxidation during annealing or sintering.
- If your primary focus is specialized manufacturing: You need a furnace that delivers exceptionally uniform heat distribution to ensure consistent product quality, whether you are creating dental crowns or annealing glass.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a foundational tool for anyone who needs to apply clean, precise heat to transform or analyze a material.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Industries Benefited |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis & Quality Control | Ashing, thermal stress testing, sample preparation | Food science, petrochemicals, biomedical, environmental labs |
| High-Temperature Material Transformation | Heat treating metals, sintering, glass annealing | Metallurgy, ceramics, aerospace, dental, nuclear sectors |
| Specialized Manufacturing | Glass melting, enamel fusing, custom production | Manufacturing, art, electronics |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in material analysis, metallurgy, or specialized manufacturing, we can help you achieve contaminant-free, uniform heating for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your processes and drive innovation in your lab or production line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















