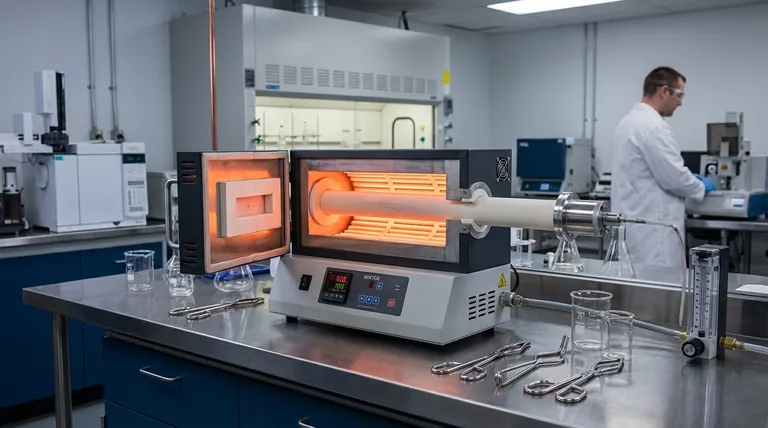
In the laboratory, a tube furnace is a versatile tool primarily used for high-temperature thermal processing of materials under a precisely controlled atmosphere. Common applications range from synthesizing novel materials and purifying compounds to performing critical heat treatments like annealing and calcination.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to create a tightly sealed, uniform thermal environment. This allows for processes that are impossible in open-air furnaces, such as those requiring a vacuum or a specific reactive or inert gas.

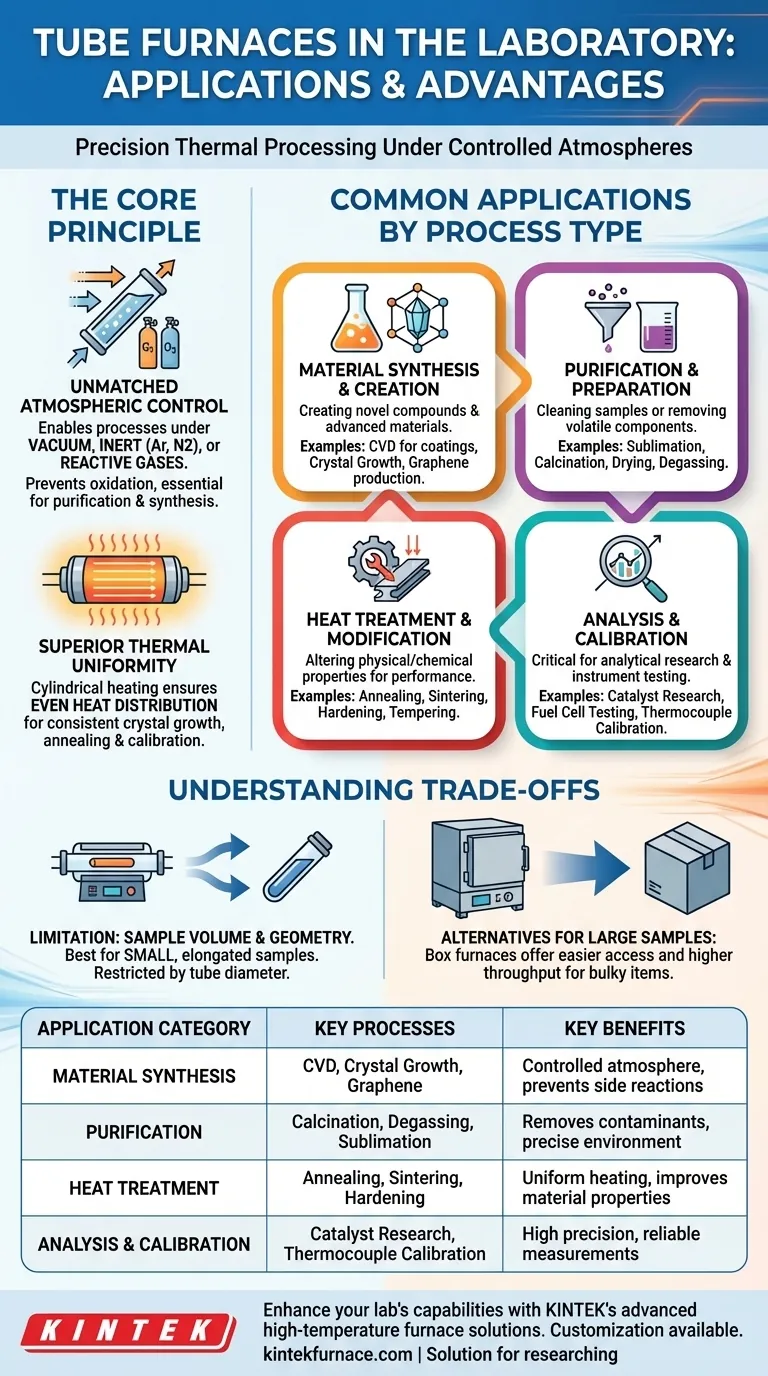
The Core Principle: Why Choose a Tube Furnace?
While many furnaces can reach high temperatures, the unique design of a tube furnace—a cylindrical chamber—offers distinct advantages that make it essential for specific scientific and industrial tasks.
Unmatched Atmospheric Control
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its ability to control the atmosphere surrounding the sample. The tube can be sealed at both ends, allowing you to create a specific environment.
This is critical for applications like purification, synthesis, or degassing, where exposure to oxygen or moisture would compromise the results. It enables processes under vacuum or with a continuous flow of inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or reactive gases.
Superior Thermal Uniformity
The cylindrical heating elements surrounding the work tube provide exceptionally even heat distribution along the length of the sample. Many models feature multiple heating zones for programming precise temperature gradients.
This uniformity is vital for processes like crystal growth, thermocouple calibration, and annealing, where even slight temperature variations can lead to defects or inaccurate measurements.
Ideal for Specific Sample Forms
The tubular shape is perfectly suited for processing small sample volumes, powders, wires, and thin films. It is also ideal for continuous-flow experiments where gases react with a solid catalyst inside the tube.
Materials like shafts and strips can be easily inserted and subjected to a consistent thermal profile, a task that is more difficult in a standard box furnace.
Common Applications by Process Type
The applications of a tube furnace can be grouped into four main categories, highlighting its role in creating, refining, testing, and analyzing materials.
Material Synthesis and Creation
This involves creating new materials or compounds from precursors. The controlled environment prevents unwanted side reactions.
Examples include synthesis of novel compounds, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for coatings, crystal growth, and the production of advanced materials like graphene and polymer composites.
Purification and Preparation
These processes aim to clean a sample or prepare it for subsequent steps by removing volatile components or inducing chemical changes.
Common applications are purification through sublimation, calcination (decomposing materials with heat), drying under vacuum, and degassing samples to remove trapped contaminants.
Heat Treatment and Modification
Heat treatment alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material to improve its performance.
This includes annealing to increase ductility, hardening or tempering to optimize strength, sintering to fuse powders into a solid mass, and accelerated aging to test material longevity.
Analysis and Calibration
The furnace's precision makes it a critical tool for analytical research and instrument calibration.
Key uses here are catalyst research, where reaction efficiency is tested under controlled conditions, fuel cell testing, polymer analysis, and the precise calibration of thermocouples against known temperature points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Limitation: Sample Volume and Throughput
Tube furnaces are inherently designed for small-volume samples and low-throughput operations. The diameter of the work tube physically restricts the size of the object you can process.
For heat-treating large, bulky components or processing large batches of material, a box furnace or chamber furnace is a more practical choice.
Limitation: Sample Geometry and Accessibility
The tubular design, while excellent for uniformity, can make loading and unloading irregularly shaped samples difficult. Samples must fit within the tube's diameter and be placed carefully to reside in the uniform hot zone.
Box furnaces, with their large front-opening doors and flat hearth plates, offer much easier access for a wider variety of sample shapes and sizes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing tool depends entirely on your specific experimental needs.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or reactions in a controlled atmosphere: The tube furnace is your indispensable tool for work under vacuum or with specific reactive or inert gases.
- If your primary focus is uniform heat treatment of small or elongated samples: Use a tube furnace for its superior thermal uniformity when annealing wires, testing material strips, or sintering powders.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky samples or maximizing throughput: A tube furnace is likely the wrong choice; a box or chamber furnace will better suit your needs.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the expert's choice for precision thermal processing where control over the sample's environment is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | CVD, crystal growth, graphene production | Controlled atmosphere, prevents side reactions |
| Purification | Calcination, degassing, sublimation | Removes contaminants, precise environment |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, sintering, hardening | Uniform heating, improves material properties |
| Analysis & Calibration | Catalyst research, thermocouple calibration | High precision, reliable measurements |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're working on material synthesis, purification, or precise analysis, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















