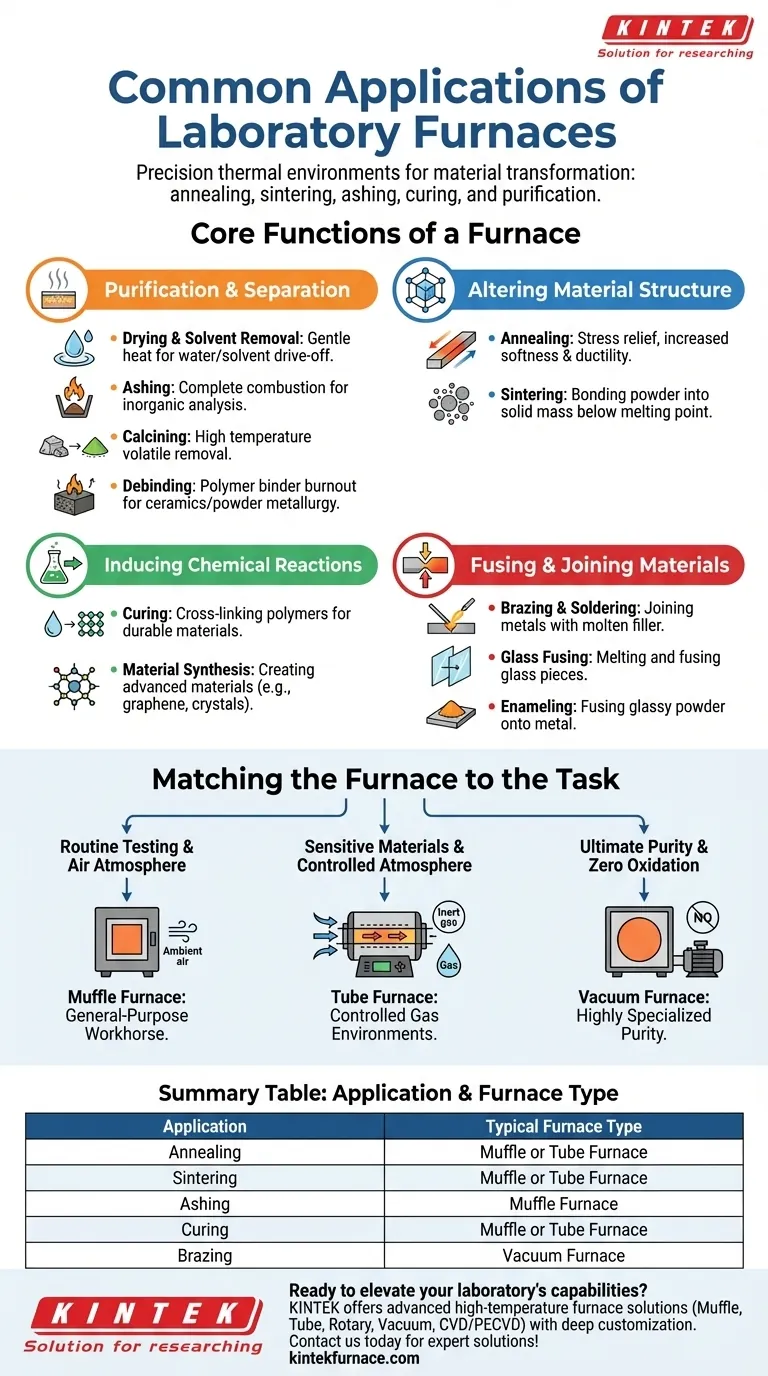
In short, laboratory furnaces are used for a wide range of high-temperature processes that transform materials. Common applications include annealing metals to improve their ductility, sintering powders into solid masses, ashing samples to determine their inorganic content, curing polymers to create durable materials, and purifying compounds through drying or solvent removal.
The core purpose of a laboratory furnace is not just to generate heat, but to precisely control a thermal environment. Understanding this allows you to see them as tools for targeted material transformation, whether you are altering a material's physical structure, driving a chemical reaction, or purifying a sample.

Beyond Heating: The Core Functions of a Furnace
While applications like "annealing" or "curing" seem distinct, they are all built on a few fundamental thermal processes. Understanding these core functions helps clarify what a furnace actually does to a sample.
Function 1: Purification and Separation
Many furnace applications are designed to remove unwanted substances from a sample by heating it until the volatile components vaporize.
- Drying & Solvent Removal: The gentle application of heat to drive off water or organic solvents.
- Ashing: The complete combustion of a sample (like coal or oil) in air to burn away all organic material, leaving only the inorganic ash for analysis.
- Calcining: Heating a material to a high temperature to drive off volatile components, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone to produce lime.
- Debinding: A critical step in powder metallurgy and ceramic manufacturing where heat is used to burn out a polymer "binder" that temporarily holds a part's shape.
Function 2: Altering Material Structure
Heat provides the energy needed to physically rearrange the atomic or crystalline structure of a material, fundamentally changing its properties without changing its chemical composition.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a metal to relieve internal stresses, increase its softness and ductility, and refine its grain structure. This makes the metal easier to work with.
- Sintering: Heating a compressed powder (like ceramic or metal powder) to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles to bond together and form a solid, dense object.
Function 3: Inducing Chemical Reactions
In many cases, heat acts as the catalyst or energy source required to initiate or accelerate a chemical reaction, creating entirely new materials or compounds.
- Curing: Using heat to trigger chemical cross-linking in polymers (like epoxies or polyimides), transforming a liquid or soft material into a hard, stable solid.
- Material Synthesis: Providing the high-energy environment needed to create advanced materials, such as producing graphene or growing specific types of crystals.
Function 4: Fusing and Joining Materials
This function relies on using heat to melt materials so they can be joined, coated, or reshaped.
- Brazing & Soldering: Joining two pieces of metal by melting a filler metal into the joint. Brazing occurs at higher temperatures than soldering.
- Glass Fusing: Heating pieces of glass until they melt and fuse together.
- Enameling: Fusing a glassy powder onto a substrate (usually metal) to form a hard, protective, and decorative coating.
Matching the Furnace to the Task
The specific application dictates the type of furnace required. The primary difference between furnace types is their ability to control the atmosphere surrounding the sample.
Muffle Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven that heats the sample in ambient air. Its insulated chamber protects the heating elements from contamination.
This is the go-to choice for straightforward processes like ashing, basic metal heat treatment, and firing ceramics where an air atmosphere is acceptable or required.
Tube Furnaces: For Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace contains the sample within a cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz. This design allows you to purge the air and replace it with a controlled gas.
These are essential for processes where the sample cannot be exposed to oxygen. This includes annealing sensitive metals, synthesizing air-sensitive materials, and running reactions under inert (argon, nitrogen) or reactive gas flows.
Vacuum Furnaces: For Ultimate Purity
A vacuum furnace is a highly specialized unit that removes nearly all atmospheric gases from the chamber before heating.
This is critical for the highest-purity applications, such as vacuum brazing aerospace components or heat-treating reactive metals like titanium, where even trace amounts of oxygen would cause catastrophic oxidation.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The right furnace is the one that provides the precise environment your process demands.
- If your primary focus is routine testing like ashing or simple heat treatment: A standard muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If you are working with sensitive materials that react with air: You need a tube furnace to control the atmosphere with inert or reactive gases.
- If your goal is to join high-strength alloys or process materials with zero oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the only tool that can provide the necessary level of atmospheric purity.
Ultimately, selecting a furnace is about defining the exact thermal transformation you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Application | Core Function | Typical Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Altering Material Structure | Muffle or Tube Furnace |
| Sintering | Altering Material Structure | Muffle or Tube Furnace |
| Ashing | Purification and Separation | Muffle Furnace |
| Curing | Inducing Chemical Reactions | Muffle or Tube Furnace |
| Brazing | Fusing and Joining Materials | Vacuum Furnace |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—offers deep customization to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you're in material science, R&D, or industrial processing, our furnaces ensure superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with cutting-edge technology and expert solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















