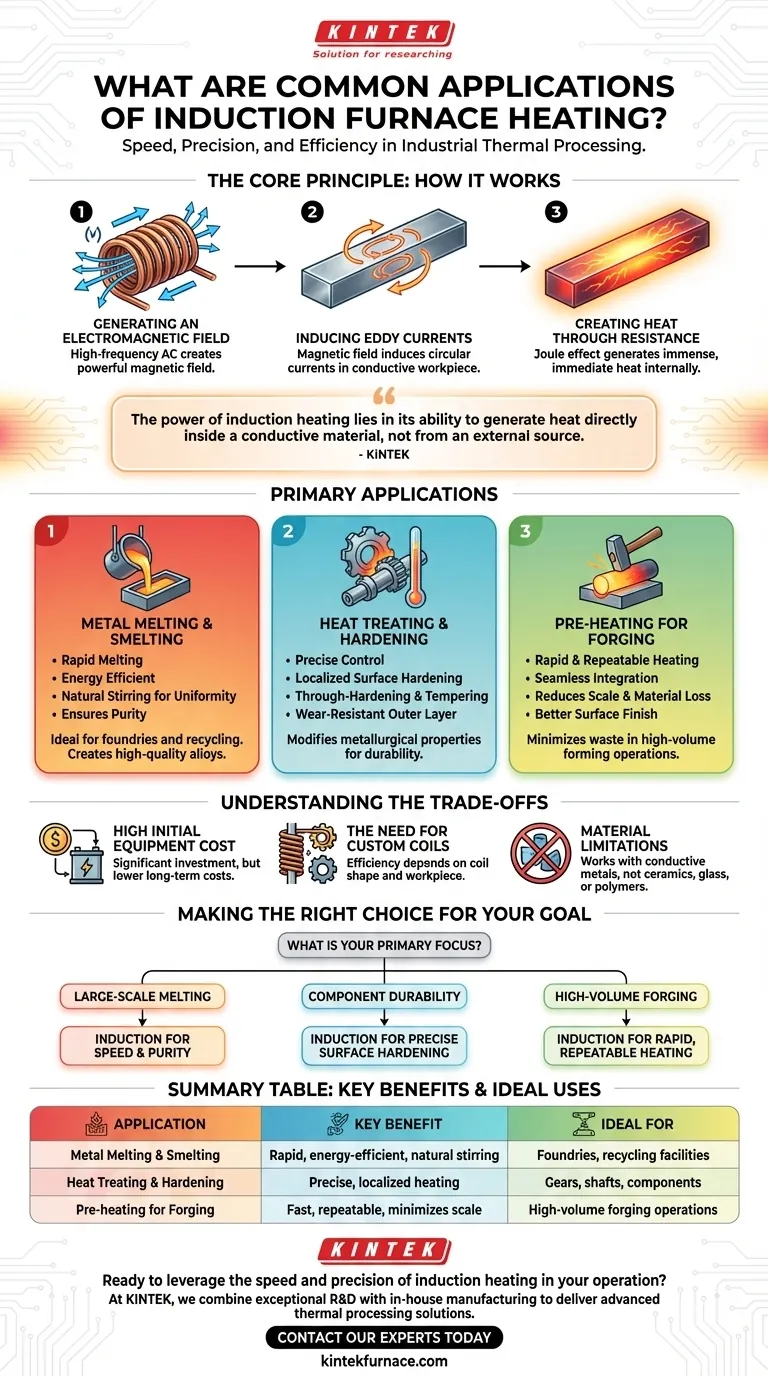
In industrial thermal processing, induction furnace heating is a cornerstone technology prized for its speed, precision, and efficiency. Its most common applications are the high-volume melting and smelting of metals, the precise heat treatment of components for hardening, and the rapid pre-heating of billets for forging and forming operations.
The power of induction heating lies in its ability to generate heat directly inside a conductive material, not from an external source. This internal heating method provides unparalleled speed, precision, and cleanliness, making it the preferred choice for processes ranging from large-scale melting to highly localized surface hardening.

The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Works
To understand its applications, you must first understand its unique mechanism. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats the air around an object, an induction furnace turns the object into its own heat source.
Generating an Electromagnetic Field
An induction system uses a copper coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece, such as a steel bar, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Creating Heat Through Resistance
The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates immense and immediate heat. This phenomenon, known as the Joule effect, heats the workpiece from the inside out with exceptional speed.
Primary Application: Metal Melting and Smelting
For foundries and recycling facilities, induction is often the technology of choice for turning solid metal into a liquid state.
The Advantage of Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the metal charge, melting occurs far more rapidly than in fuel-fired furnaces. This reduces energy loss to the environment and increases throughput.
Ensuring Purity and Stirring
The electromagnetic field naturally stirs the molten metal bath. This action ensures alloys are mixed thoroughly and uniformly, and it helps bring impurities to the surface to be skimmed off. With no combustion byproducts, the process is inherently cleaner.
Precision Application: Heat Treating and Hardening
Induction heating’s control makes it ideal for modifying the metallurgical properties of finished or semi-finished parts. This includes the "quenching and tempering" mentioned in steel processing.
Localized Surface Hardening
Perhaps the most powerful application is case hardening. The induction coil can be shaped to heat only the surface of a part, like the teeth of a gear or the bearing surface of a shaft. When rapidly cooled (quenched), this creates an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer layer while the core remains softer and more ductile to absorb shock.
Through-Hardening and Tempering
For smaller components, the entire part can be heated uniformly and then quenched for full hardness. The part can then be placed back in an induction system for a second, lower-temperature heating cycle known as tempering, which reduces brittleness and improves toughness.
High-Volume Application: Pre-heating for Forging
Before a metal billet can be pressed or hammered into a new shape (forging), it must be heated to a specific, uniform temperature to make it malleable.
Rapid and Repeatable Heating
Induction can heat a steel bar to forging temperature in a matter of seconds or minutes. This allows for seamless integration into an automated production line, ensuring each part is heated to the exact same temperature every time.
Reducing Scale and Material Loss
Because the heating is so fast, the workpiece spends very little time at a high temperature where it can react with oxygen in the air. This drastically reduces the formation of oxide scale on the surface, minimizing material waste and leading to a better surface finish on the final forged part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to its proper application.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Induction power supplies and their associated cooling systems represent a significant capital investment compared to simpler gas-fired furnaces. However, this is often offset by lower energy costs and higher productivity over time.
The Need for Custom Coils
The efficiency of induction heating is highly dependent on the shape and position of the coil relative to the workpiece. For complex parts, a custom-designed coil is often required, which adds engineering cost and complexity.
Material Limitations
The fundamental principle relies on electrical conductivity. This means induction heating works exceptionally well for metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum but cannot be used to heat non-conductive materials like ceramics, glass, or most polymers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use induction heating should be driven by the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is large-scale melting: Induction offers unmatched speed and purity, especially when creating specific alloys that require thorough mixing.
- If your primary focus is component durability: Use induction for precise surface hardening to create wear-resistant parts without making the entire component brittle.
- If your primary focus is high-volume forging or forming: Induction provides rapid, repeatable heating that minimizes material waste from oxidation and maximizes production throughput.
By understanding its principle of internal heating, you can leverage induction technology to achieve superior control and efficiency in your thermal processing applications.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Melting & Smelting | Rapid, energy-efficient melting with natural stirring for alloy uniformity. | Foundries, recycling facilities creating high-purity metals and alloys. |
| Heat Treating & Hardening | Precise, localized heating for surface hardening or through-hardening of parts. | Manufacturing gears, shafts, and components requiring wear resistance and durability. |
| Pre-heating for Forging | Fast, repeatable heating that minimizes scale (oxide) formation and material loss. | High-volume forging operations needing consistent billet temperatures for forming. |
Ready to leverage the speed and precision of induction heating in your operation? At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced thermal processing solutions. Whether you need a system for high-volume melting, precision hardening, or rapid forging pre-heats, our team can provide a robust induction furnace tailored to your unique requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing for maximum efficiency and quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies



















