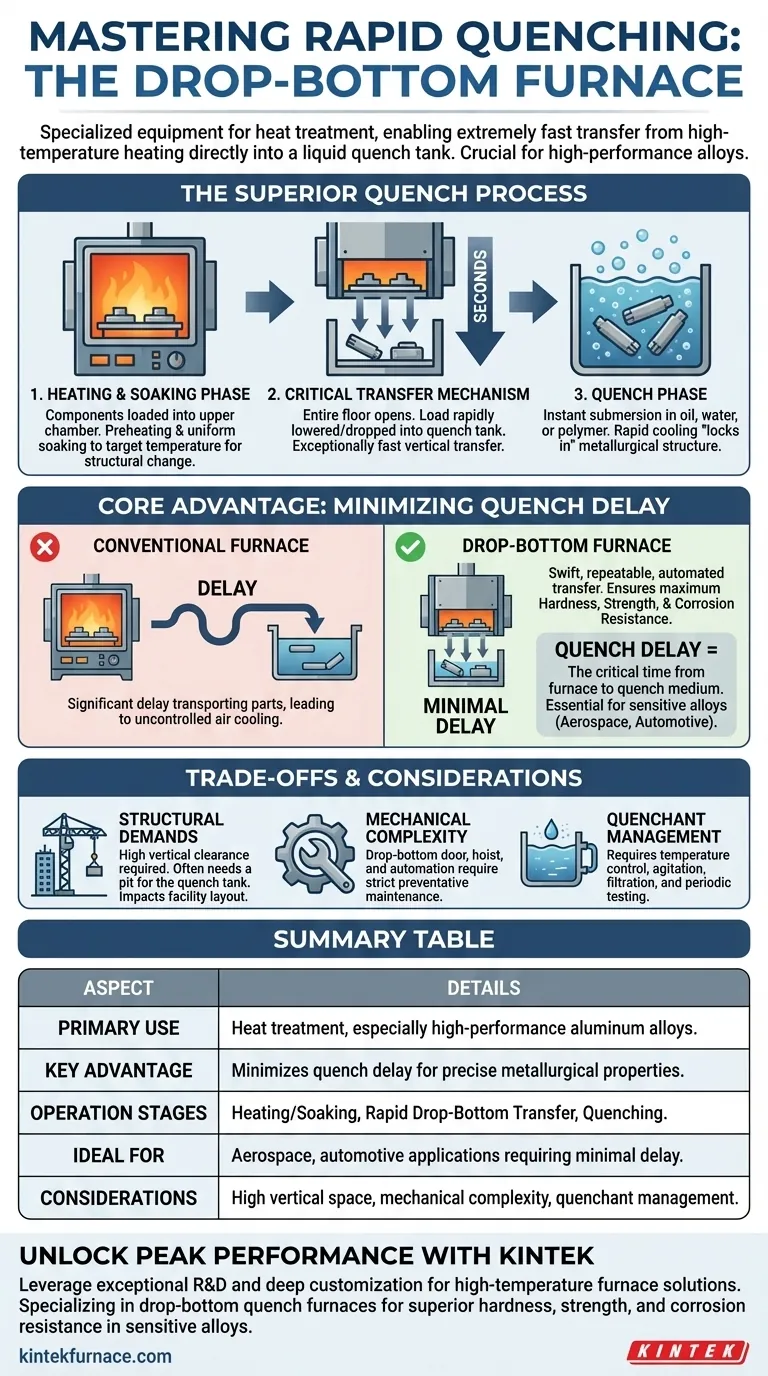
At its core, a drop-bottom quench furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment designed for the heat treatment of metal components. Its primary function is to enable an extremely fast transfer from a high-temperature heating chamber directly into a liquid quench tank, a process critical for developing specific mechanical properties in materials like aluminum alloys.
The defining advantage of a drop-bottom furnace is not just heat treatment, but the minimization of quench delay. This design ensures components are quenched almost instantaneously after heating, which is the only way to achieve the desired metallurgical structure in many high-performance alloys.
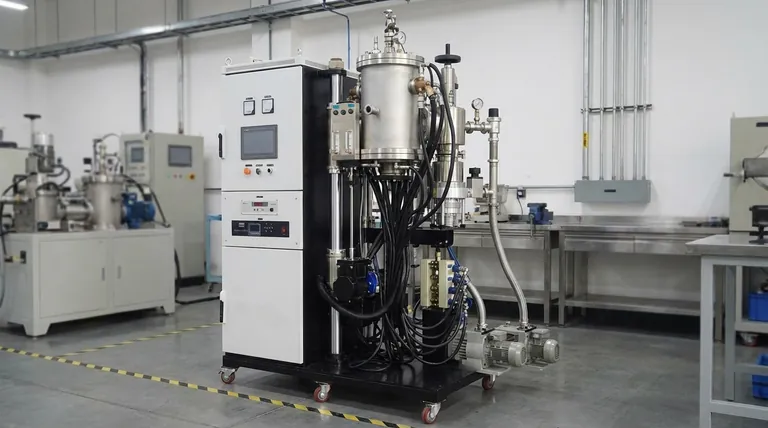

How a Drop-Bottom Furnace Delivers a Superior Quench
The furnace operates in distinct, sequential stages, with its physical design directly optimized for the most critical transition: the quench itself.
The Heating and Soaking Phase
First, metal components are loaded into the upper heating chamber. The furnace brings the material to a precise, uniform temperature in a process known as preheating and then holds it there during the soaking phase. This ensures the entire part, regardless of its geometry, reaches the target temperature needed to alter its crystalline structure.
The Critical Transfer Mechanism
This is where the "drop-bottom" design proves its value. The entire floor of the heating chamber opens, and the load is rapidly lowered or dropped directly into the quench tank positioned immediately below it. This vertical transfer is exceptionally fast, often taking only a few seconds.
The Quench Phase
Once submerged in the quench tank, the components are cooled with extreme rapidity. The quenching medium is typically oil, water, or a polymer solution, chosen based on the material and the desired final properties. This rapid cooling "locks in" the metallurgical structure achieved during the soaking phase.
The Core Advantage: Minimizing Quench Delay
Understanding why this speed is so vital is key to understanding the furnace's purpose. The entire design exists to solve the problem of quench delay.
What is Quench Delay?
Quench delay is the time that elapses from the moment a hot component leaves the furnace's heating chamber to the moment it is fully submerged in the quenching medium. During this brief interval, the part is exposed to open air and begins to cool prematurely.
The Impact of Delay on Material Properties
For many alloys, particularly those used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications, even a few seconds of delay are unacceptable. Uncontrolled cooling in the air allows the metal's internal structure to change in undesirable ways, preventing it from reaching its maximum potential hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Why the Drop-Bottom Design Excels
A conventional furnace might require parts to be moved by a forklift or conveyor to a separate quench tank. This introduces significant and often inconsistent quench delays. The drop-bottom furnace integrates the heating and quenching stages vertically, making the transfer a swift, repeatable, and automated process that guarantees minimal delay.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, this design comes with specific operational and facility requirements.
Structural and Space Demands
Drop-bottom furnaces are inherently tall structures. They require significant vertical clearance and often need a pit excavated below the floor to house the quench tank, impacting facility layout and installation costs.
Mechanical Complexity
The drop-bottom door, hoist mechanism, and associated automation are complex systems. They require a strict regimen of preventative maintenance, including lubrication of moving parts and inspection of seals and lifting components, to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Quenchant Management
The quenching medium itself requires careful management. Its temperature must be controlled, and it must be agitated, filtered, and periodically tested and replaced to ensure consistent cooling rates from batch to batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heat treatment furnace depends entirely on the metallurgical requirements of your components.
- If your primary focus is processing high-performance aluminum alloys: A drop-bottom furnace is the industry standard, as the need for minimal quench delay is non-negotiable for solution heat treating.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness and strength in sensitive alloys: The near-instantaneous quench provided by this design is essential for locking in the desired metallurgical properties before they can degrade.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment of less-sensitive steels: Other designs, such as batch or continuous belt furnaces, may offer a more cost-effective solution if a slightly longer quench delay is acceptable for the material.
Ultimately, the choice of a drop-bottom furnace is a decision driven by the uncompromising need for metallurgical precision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Heat treatment of metal components, especially high-performance aluminum alloys, for rapid quenching. |
| Key Advantage | Minimizes quench delay to ensure precise metallurgical properties like hardness and strength. |
| Operation Stages | Heating/soaking, rapid drop-bottom transfer, quenching in oil/water/polymer. |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, automotive applications requiring minimal quench delay. |
| Considerations | High vertical space, mechanical complexity, quenchant management needs. |
Unlock Peak Performance for Your High-Performance Alloys with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. If you're working with sensitive alloys that demand minimal quench delay, our drop-bottom quench furnaces can deliver the rapid, precise heat treatment you need for superior hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- How do vacuum furnaces contribute to long-term cost savings? Reduce Costs with Efficiency and Quality
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















