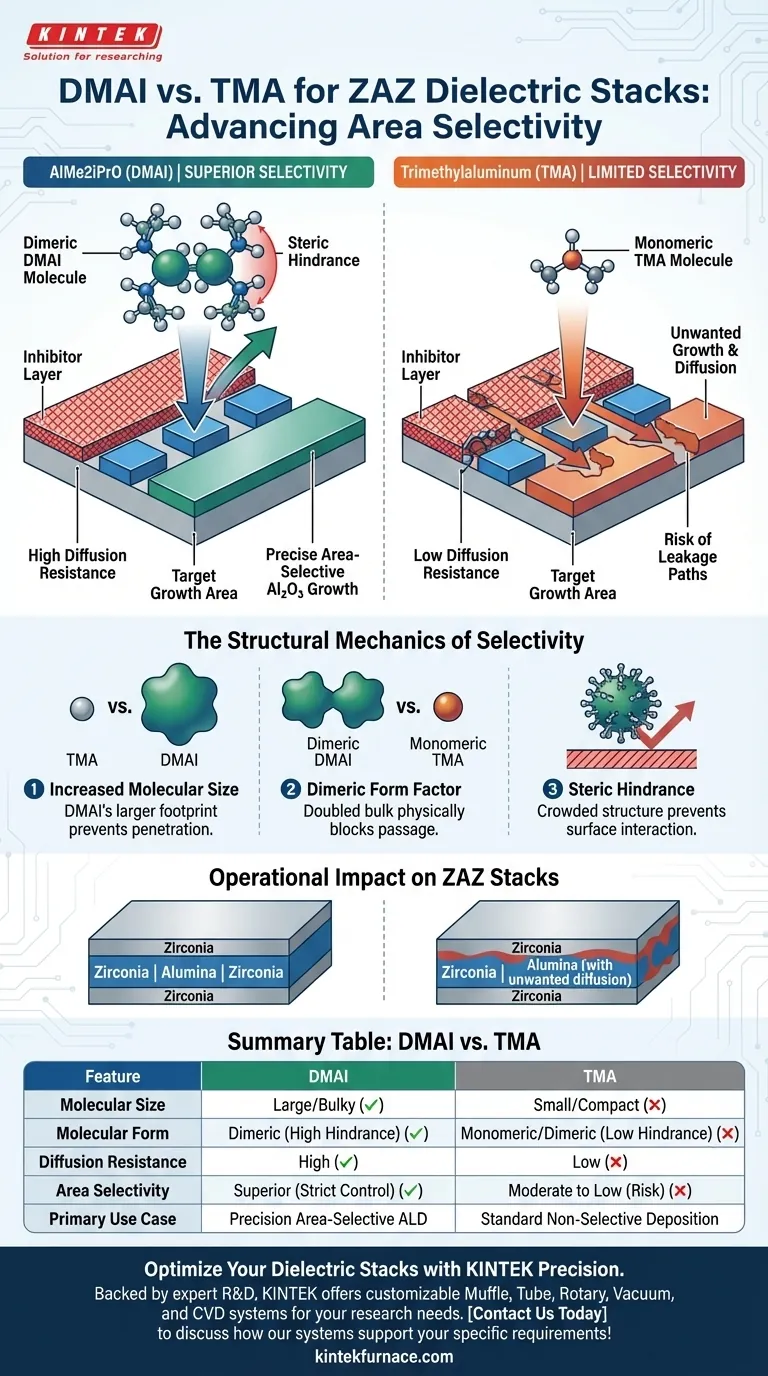
AlMe2iPrO (DMAI) provides superior area selectivity compared to the standard Trimethylaluminum (TMA) precursor. Its primary advantage is the ability to strictly confine aluminum oxide growth to intended locations, significantly reducing the risk of unwanted deposition in areas protected by inhibitors.
The core difference lies in physical chemistry: DMAI’s larger, dimeric structure creates sufficient steric hindrance to block it from diffusing into inhibited regions, a common failure point when using the smaller TMA molecule.
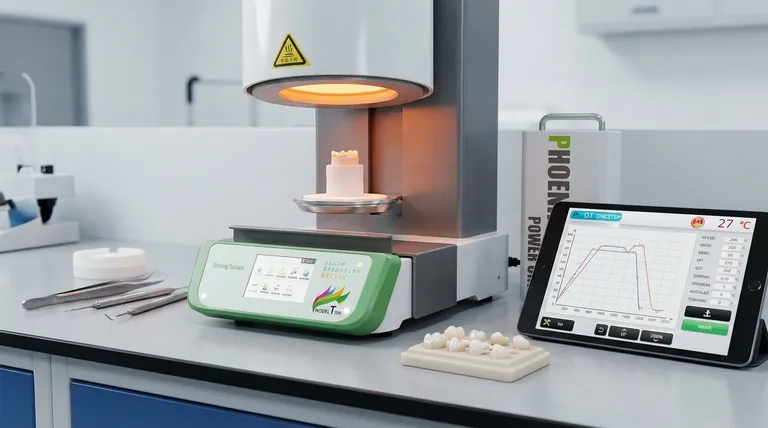

The Structural Mechanics of Selectivity
To understand why DMAI outperforms TMA in selective Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), you must look at the molecular architecture of the precursors.
Increased Molecular Size
TMA is a relatively small molecule. While this makes it reactive, it also allows it to penetrate or slip past chemical inhibitors meant to mask specific areas of the substrate.
DMAI possesses a significantly larger molecular footprint. This increased physical size is the first line of defense against unwanted diffusion.
The Dimeric Form Factor
Beyond its base molecular weight, DMAI tends to exist in a dimeric form.
This means molecules associate in pairs, effectively doubling the size of the active unit during key transport phases. This bulky structure makes it physically difficult for the precursor to navigate the small potential gaps in an inhibitor layer.
Utilizing Steric Hindrance
The ligand structure of DMAI introduces steric hindrance.
In simple terms, the arrangement of atoms in DMAI creates a crowded spatial environment. This "bulkiness" prevents the molecule from interacting with or adsorbing onto surfaces that have been treated with inhibitors, ensuring the reaction only occurs on the exposed, targeted surfaces.
Operational Impact on Dielectric Stacks
When preparing Zirconia-Alumina-Zirconia (ZAZ) stacks, the integrity of the layers is paramount.
Resistance to Diffusion
The primary operational benefit of DMAI is its resistance to diffusion.
Because of the structural factors listed above, DMAI cannot easily migrate into protected regions. TMA, by contrast, is prone to diffusing into these protected zones, which compromises the definition of the dielectric stack.
Improved Area Selectivity
The direct result of this resistance is significantly improved area selectivity.
By using DMAI, you ensure that Al2O3 growth is strictly confined to the desired regions. This precision is critical for maintaining the performance characteristics of the ZAZ stack without introducing leakage paths or parasitic capacitance in the inhibited areas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While DMAI offers clear advantages for selectivity, it is important to understand the context of this choice relative to TMA.
The Limitation of TMA
TMA is often the default choice for aluminum deposition due to its high reactivity and well-understood behavior. However, its small size becomes a liability in area-selective processes.
If your process relies heavily on inhibitors to block growth, TMA introduces a high risk of failure because it can bypass the inhibitor barrier. DMAI is specifically advantageous when the success of the device relies on the integrity of the inhibition, rather than just the growth rate of the film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct precursor depends on the specific constraints of your ZAZ stack fabrication process.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Selectivity: Choose DMAI. Its bulky, dimeric structure provides the necessary steric hindrance to prevent growth in inhibited areas.
- If your primary focus is Standard, Non-Selective Growth: TMA remains a viable option, but be aware that it lacks the geometric bulk required to respect complex inhibition patterns.
DMAI transforms the physical limitations of the molecule into a processing asset, turning molecular bulk into precise spatial control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | AlMe2iPrO (DMAI) | Trimethylaluminum (TMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Size | Large / Bulky | Small / Compact |
| Molecular Form | Dimeric (Higher steric hindrance) | Monomeric/Dimeric (Lower hindrance) |
| Diffusion Resistance | High (Resists inhibitor penetration) | Low (Prone to diffusion) |
| Area Selectivity | Superior (Strict growth control) | Moderate to Low (Risk of unwanted growth) |
| Primary Use Case | Precision Area-Selective ALD | Standard Non-Selective Deposition |
Optimize Your Dielectric Stacks with KINTEK Precision
Choosing the right precursor like DMAI is essential for the precision required in advanced ZAZ stack fabrication. At KINTEK, we understand that high-performance materials demand high-performance equipment.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of laboratory solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. All our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs, ensuring your ALD processes achieve maximum selectivity and efficiency.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact us today to discuss how our customizable systems can support your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Moo‐Yong Rhee, Il‐Kwon Oh. Area‐Selective Atomic Layer Deposition on Homogeneous Substrate for Next‐Generation Electronic Devices. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202414483
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra-High Vacuum Flange Aviation Plug Glass Sintered Airtight Circular Connector for KF ISO CF
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in NiWO4/GO preparation? Master High-Performance Composite Synthesis
- What process problems are addressed by using a walking-beam furnace model? Solve Clad Plate Thermal Stress Challenges
- What is the purpose of employing Ozone (O3) treatment following the AS-ALD of Al2O3? Boost Film Purity and Density
- What advantages does peat char offer compared to traditional charcoal? Boost Your Furnace Efficiency by 22%
- How does an industrial high-temperature resistance furnace ensure borosilicate fiber quality? Master Thermal Precision
- What are the advantages of using a batch furnace? Achieve Unmatched Process Flexibility and Precision
- Why is an incubator required for VP-FSCM? Master Curing Controls for Superior Soil Solidification Results
- How does the structure of a shaft furnace facilitate the reduction of iron ore? Mastering High-Temp Heat Exchange












