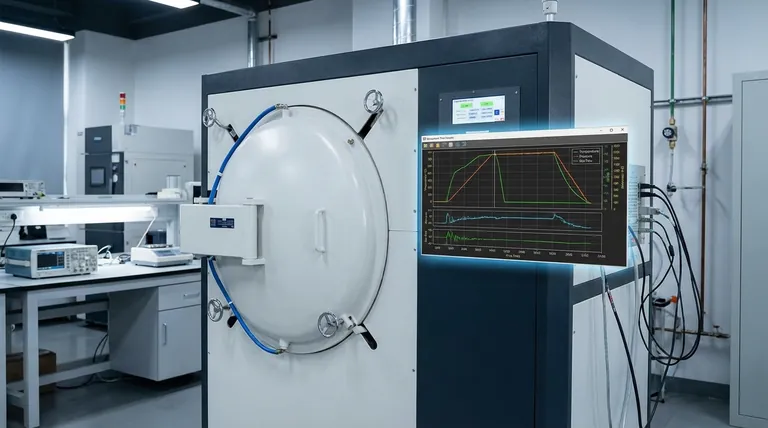
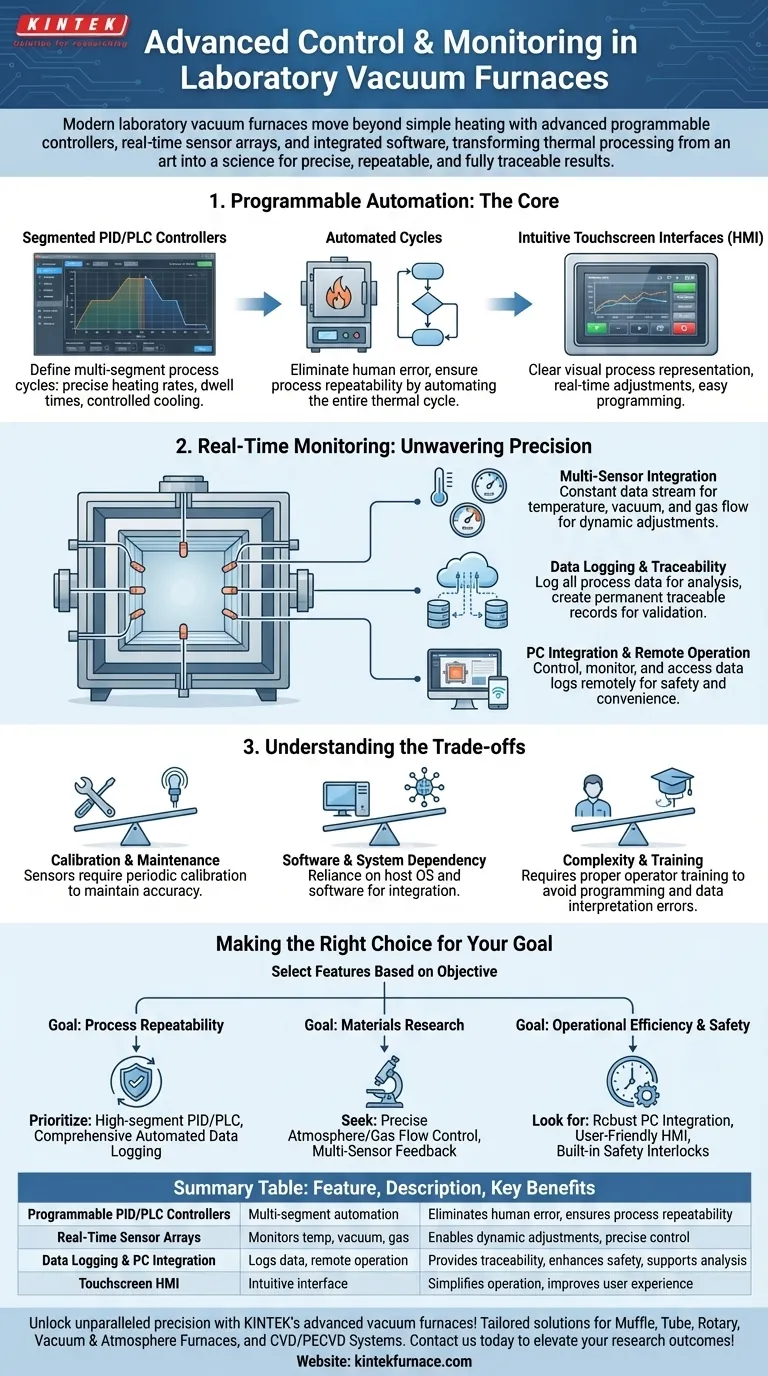
In short, modern laboratory vacuum furnaces are equipped with advanced programmable controllers, real-time sensor arrays, and integrated software for remote operation. These systems move beyond simple heating elements to offer precise, automated, and data-rich control over the entire thermal process, from heating and dwelling to cooling and atmospheric management.
The purpose of advanced controls is not just automation, but the transformation of thermal processing from an art into a science. By providing granular control and detailed data, these features ensure that experimental results are precise, repeatable, and fully traceable.

The Core of Modern Control: Programmable Automation
The foundational element of an advanced furnace is its ability to execute complex recipes without manual intervention. This capability is built on intelligent controllers that serve as the brains of the operation.
Segmented PID/PLC Controllers
Most advanced furnaces use PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems.
These controllers allow you to program multi-segment process cycles. You can define precise heating rates, specific dwell times at target temperatures, and controlled cooling rates.
The Power of Automated Cycles
By automating the entire thermal cycle, you eliminate the variability and human error associated with manual adjustments. This ensures that every sample is processed under identical conditions.
The result is a dramatic increase in process repeatability, which is critical for both research and quality control applications.
Intuitive Touchscreen Interfaces (HMI)
Modern furnaces feature a Human-Machine Interface (HMI), typically a touchscreen panel. This interface provides a clear visual representation of the process, allowing for real-time parameter adjustments and easy programming of thermal cycles.
Real-Time Monitoring for Unwavering Precision
What cannot be measured cannot be controlled. Advanced furnaces are outfitted with a network of sensors that provide a constant stream of data, enabling the control system to make dynamic adjustments.
Multi-Sensor Integration
Key parameters are monitored in real-time. This universally includes temperature, but also extends to vacuum pressure and gas flow.
Embedded sensors, such as thermocouples, are placed in strategic zones to ensure that the reported temperature is accurate and uniform across the entire chamber.
Data Logging and Traceability
A critical feature is the ability to log all process data. This information can be exported for analysis, creating a permanent, traceable record of the exact conditions your material was exposed to.
This is invaluable for validating results, troubleshooting failures, and fulfilling quality assurance requirements.
PC Integration and Remote Operation
Many furnaces now offer optional PC integration. This allows an operator to control the furnace, monitor its status, and access data logs remotely from a computer.
This capability not only enhances convenience but also improves safety by allowing for the remote supervision of high-temperature or long-duration processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced features offer significant benefits, they also introduce complexities that must be managed.
Calibration and Maintenance
Sensors for temperature, pressure, and gas flow can drift over time and require periodic calibration to maintain accuracy. Relying on uncalibrated sensors negates the core benefit of a precision system.
Software and System Dependency
Integration with a PC introduces a dependency on software and the host operating system. Future OS updates or computer failures can potentially disrupt furnace operations if not managed properly.
Complexity and Training
A highly programmable, multi-sensor system is inherently more complex than a manual furnace. Proper operator training is essential to leverage its full capabilities and avoid errors in programming or interpretation of data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The most "advanced" furnace is the one that best matches your specific application. Evaluate features based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with a high-segment PID/PLC controller and comprehensive, automated data logging.
- If your primary focus is materials research: Seek a system with precise atmosphere and gas flow control, along with multi-sensor feedback for temperature, pressure, and gas composition.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and safety: Look for robust PC integration for remote monitoring, a user-friendly HMI, and built-in safety interlocks like over-temperature protection.
Ultimately, these control and monitoring features empower you to dictate the precise thermal environment for your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable PID/PLC Controllers | Multi-segment automation of heating, dwelling, and cooling cycles | Eliminates human error, ensures process repeatability |
| Real-Time Sensor Arrays | Monitors temperature, vacuum pressure, and gas flow with embedded sensors | Enables dynamic adjustments and precise environmental control |
| Data Logging and PC Integration | Logs process data for export and allows remote operation via software | Provides traceability, enhances safety, and supports analysis |
| Touchscreen HMI | Intuitive interface for programming and real-time adjustments | Simplifies operation and improves user experience |
Unlock unparalleled precision in your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met with reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can elevate your research and quality control outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















