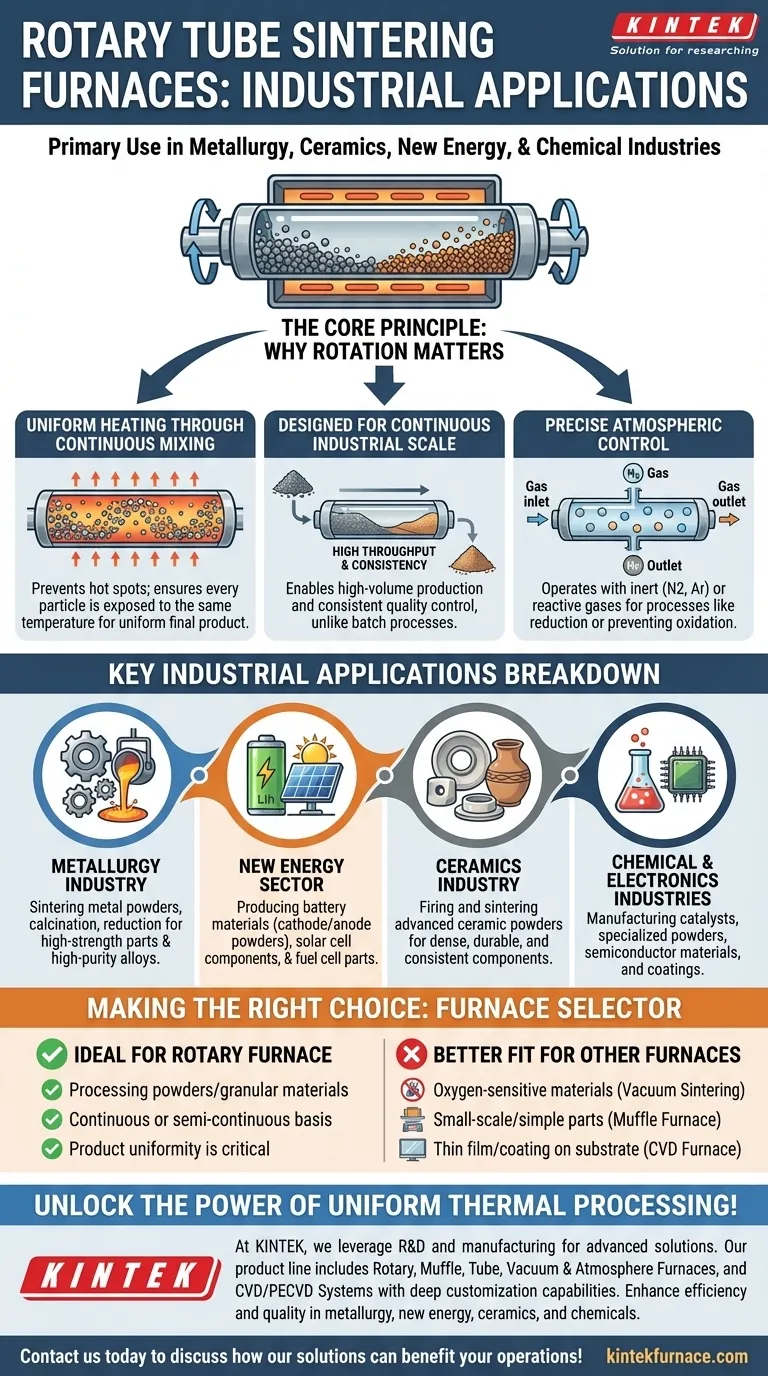
In short, rotary tube sintering furnaces are primarily used in the metallurgy, ceramics, new energy, and chemical industries. Their core function is to uniformly heat and process granular or powder-like materials at high temperatures, making them indispensable for manufacturing advanced materials.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace isn't just its high heat, but its ability to continuously mix materials during processing. This ensures exceptional uniformity, a critical requirement for producing the high-performance powders and components demanded by modern industry.
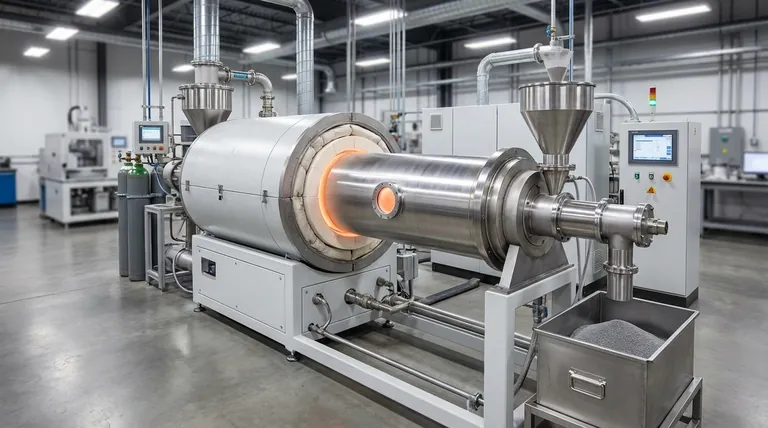

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
A rotary tube furnace is designed for dynamic thermal processing. Understanding its fundamental mechanism explains its widespread adoption across multiple high-tech fields.
Uniform Heating Through Continuous Mixing
The furnace consists of a cylindrical tube that slowly rotates while being heated externally. As the material—typically a powder or granule—is fed into the tube, the rotation causes it to tumble and mix continuously.
This constant agitation ensures that every particle is exposed to the same temperature for the same duration. This prevents hot spots and inconsistencies, leading to a highly uniform final product.
Designed for Continuous Industrial Scale
Unlike "batch" furnaces where material is loaded and unloaded in discrete cycles, many rotary furnaces are designed for continuous operation. Raw material is fed into one end and the processed material is discharged from the other.
This continuous workflow is essential for large-scale industrial manufacturing, enabling high throughput and consistent quality control.
Precise Atmospheric Control
These furnaces can operate with controlled atmospheres, such as inert gases (nitrogen, argon) or reactive gases. This is critical for processes like reduction (removing oxygen from metal oxides) or preventing oxidation in sensitive materials.
Key Industrial Applications Breakdown
The combination of uniform heating, continuous processing, and atmospheric control makes the rotary tube furnace a vital tool in several key sectors.
The Metallurgy Industry
In metallurgy, these furnaces are a cornerstone of powder metallurgy. They are used for sintering metal powders below their melting point to create dense, high-strength parts.
They also play a critical role in producing high-purity metals and alloys through processes like calcination (thermal decomposition) and reduction.
The New Energy Sector
This is a rapidly growing area of application. Rotary furnaces are essential for producing materials for lithium-ion batteries, where the chemical composition and particle structure of cathode and anode powders must be precisely controlled through roasting.
They are also used in the manufacturing of components for solar cells and fuel cells, which rely on advanced materials with specific properties.
The Ceramics Industry
The furnace is used for firing and sintering advanced ceramic powders. The uniform heating ensures the creation of dense, durable ceramic components with consistent mechanical and thermal properties, avoiding cracks or weaknesses.
The Chemical and Electronics Industries
In chemical processing, rotary furnaces are used to produce catalysts, zinc oxide, and other specialized chemical powders.
In electronics, they are used for preparing specific semiconductor materials and coatings that require precise thermal treatment to achieve their desired electrical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not the universal solution for all high-temperature applications.
When a Rotary Furnace Is Ideal
This furnace excels when you are processing powders or granular materials on a continuous or semi-continuous basis, and where product uniformity is the most critical factor.
When Other Furnaces Are a Better Fit
For materials highly sensitive to oxygen, a dedicated vacuum sintering furnace provides a purer environment. For small-scale lab research or simple heat treatment of solid parts, a less complex muffle furnace is often more practical. For creating thin films or coatings on a substrate, a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) furnace is the appropriate tool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and your manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, uniform processing of powders (e.g., battery materials, metal powders): A rotary tube sintering furnace is the industry-standard solution for its efficiency and consistency.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-high-purity parts in an oxygen-free environment: A vacuum furnace is better suited to protect your material from atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is small-batch lab work or heat-treating a solid object: A simpler and more cost-effective muffle furnace is likely the superior choice.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capabilities to your process requirements is the key to achieving a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Sintering metal powders, calcination, reduction for high-strength parts and alloys |
| Ceramics | Firing and sintering ceramic powders for durable, consistent components |
| New Energy | Producing lithium-ion battery materials, solar cell components, and fuel cell parts |
| Chemical | Manufacturing catalysts, zinc oxide, and specialized chemical powders |
| Electronics | Preparing semiconductor materials and coatings with precise thermal treatment |
Unlock the power of uniform thermal processing for your industry! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, new energy, ceramics, or chemicals, we can enhance your efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















