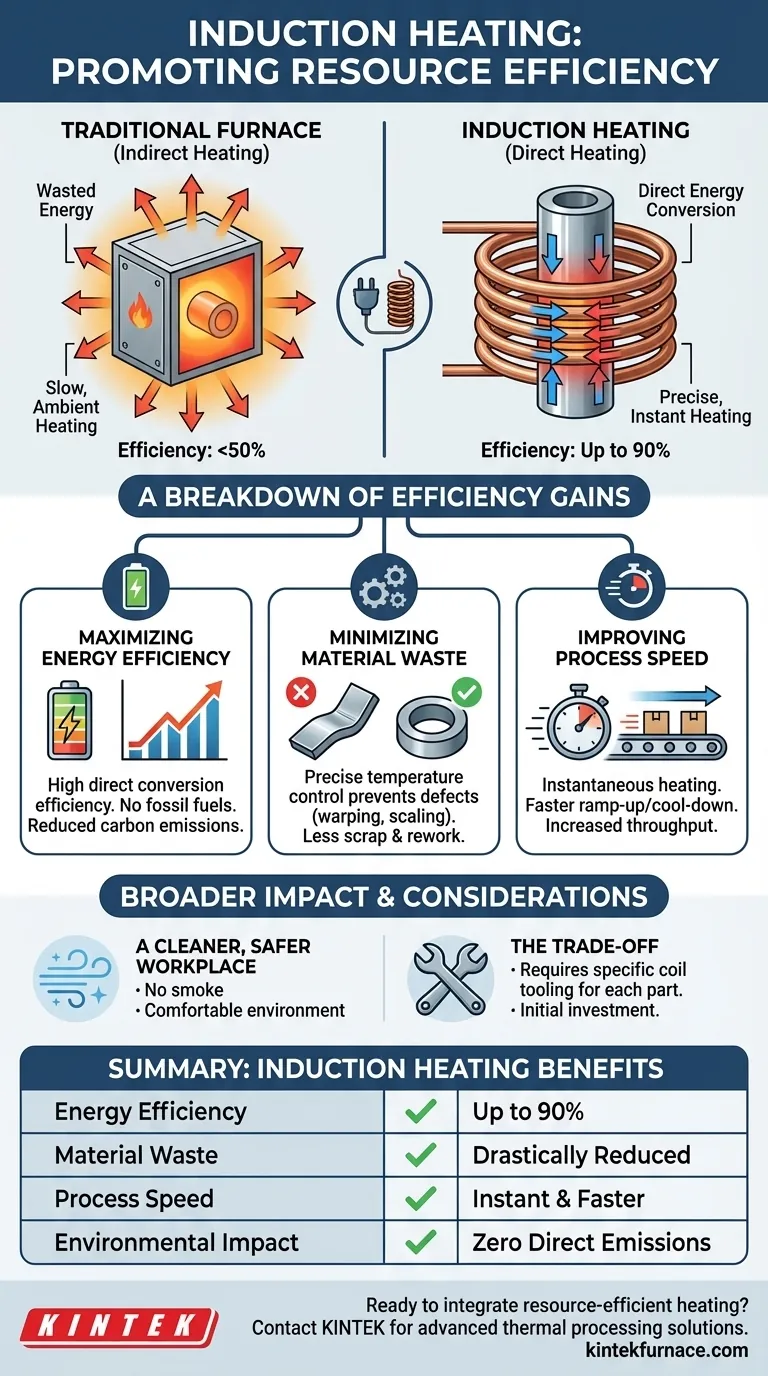
At its core, induction heating promotes resource efficiency in two primary ways: by converting electrical energy into heat with exceptional efficiency and by applying that heat with surgical precision. This combination ensures that energy is not wasted heating the surrounding environment and that material loss from overheating or process errors is dramatically reduced.
The fundamental advantage of induction heating is its shift from brute-force, ambient heating to a highly controlled, direct-to-part energy transfer. This precision is the root cause of its efficiency, impacting everything from energy consumption and material scrap to process speed and workplace safety.

The Principle: Precision Over Power
Traditional heating methods, like furnaces, operate by creating a hot environment and waiting for the part to absorb that heat. Induction heating works on an entirely different principle, making it inherently more efficient.
How It Works
Induction heating uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a powerful, oscillating magnetic field around the coil. When a conductive material, like a metal part, is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents (known as eddy currents) directly within the part itself. The resistance of the metal to these currents generates instantaneous, localized heat.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A furnace heats the air, the furnace walls, and everything else inside it just to warm up the target part—a process known as indirect heating. This leads to significant thermal loss.
Induction is a form of direct heating. It heats only the material placed inside the coil, turning the part into its own heat source. No energy is wasted heating the surrounding air.
Localized and Controllable Heat
The heat is generated only within the portion of the material inside the magnetic field. This allows for an incredible level of control. You can heat a specific section of a shaft for hardening or a precise joint for welding, leaving the rest of the component unaffected.
A Breakdown of Efficiency Gains
This precise, direct heating mechanism translates into several distinct areas of resource efficiency that are critical for modern industrial operations.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
Because induction converts energy directly into heat within the workpiece, it can achieve energy efficiency ratings of up to 90%. Traditional fossil-fuel-fired furnaces often lose more than half their energy to the environment.
By using electricity instead of combustible fuels, induction also helps organizations reduce direct carbon emissions and move closer to carbon neutrality goals.
Minimizing Material Waste
Precise temperature control prevents common manufacturing defects like warping, scaling, or distortion caused by overheating. This accuracy, regardless of batch size, is crucial when working with specialty metals or in critical heat-treating applications.
Fewer rejected parts means less material scrap, less energy wasted on rework, and a direct reduction in the cost of raw materials.
Improving Process Speed
Induction heating is known for its speed. Heat is generated instantly within the part, eliminating the long ramp-up and cool-down times associated with furnaces. This speed increases throughput, making the entire production line more efficient.
Understanding the Broader Impact
The efficiency of induction heating extends beyond just energy and materials, creating a positive ripple effect on operations and the work environment.
A Cleaner, Safer Workplace
Induction is a clean process. Unlike combustion-based heating, it produces no smoke, waste heat, or harmful byproducts.
This significantly improves workplace air quality and reduces the ambient temperature, creating a safer and more comfortable environment for employees.
The Trade-off: Tooling and Application Specificity
While highly versatile, induction heating is not a universal solution. The efficiency of the process depends heavily on the design of the induction coil, which must be properly matched to the geometry of the part being heated.
This means an initial investment in engineering and tooling is often required for each unique application, a trade-off for its exceptional control and efficiency once operational.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating induction heating, consider how its specific benefits align with your highest priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: The combination of lower energy consumption and drastically reduced material scrap provides a clear and compelling return on investment.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and ESG goals: Induction heating offers a direct path to decarbonization by eliminating fossil fuels from the process and significantly lowering overall energy use.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: The unparalleled speed, accuracy, and repeatability of induction heating ensure every part meets exact specifications, eliminating process variability.
Ultimately, adopting induction heating is a strategic decision to invest in a more precise, clean, and fundamentally efficient manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Efficiency Metric | Induction Heating Benefit |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Up to 90% direct energy conversion, versus <50% for traditional furnaces. |
| Material Waste | Precise control drastically reduces scrap from overheating and rework. |
| Process Speed | Instantaneous heating increases throughput and overall production line efficiency. |
| Environmental Impact | Zero direct emissions and a cleaner, safer workplace. |
Ready to integrate resource-efficient heating into your process?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal processing solutions. Whether your goal is to reduce energy costs, minimize material scrap, or achieve carbon neutrality, our team can help.
We specialize in developing precisely controlled heating systems for diverse laboratory and industrial applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can design a solution to meet your unique efficiency and sustainability requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















