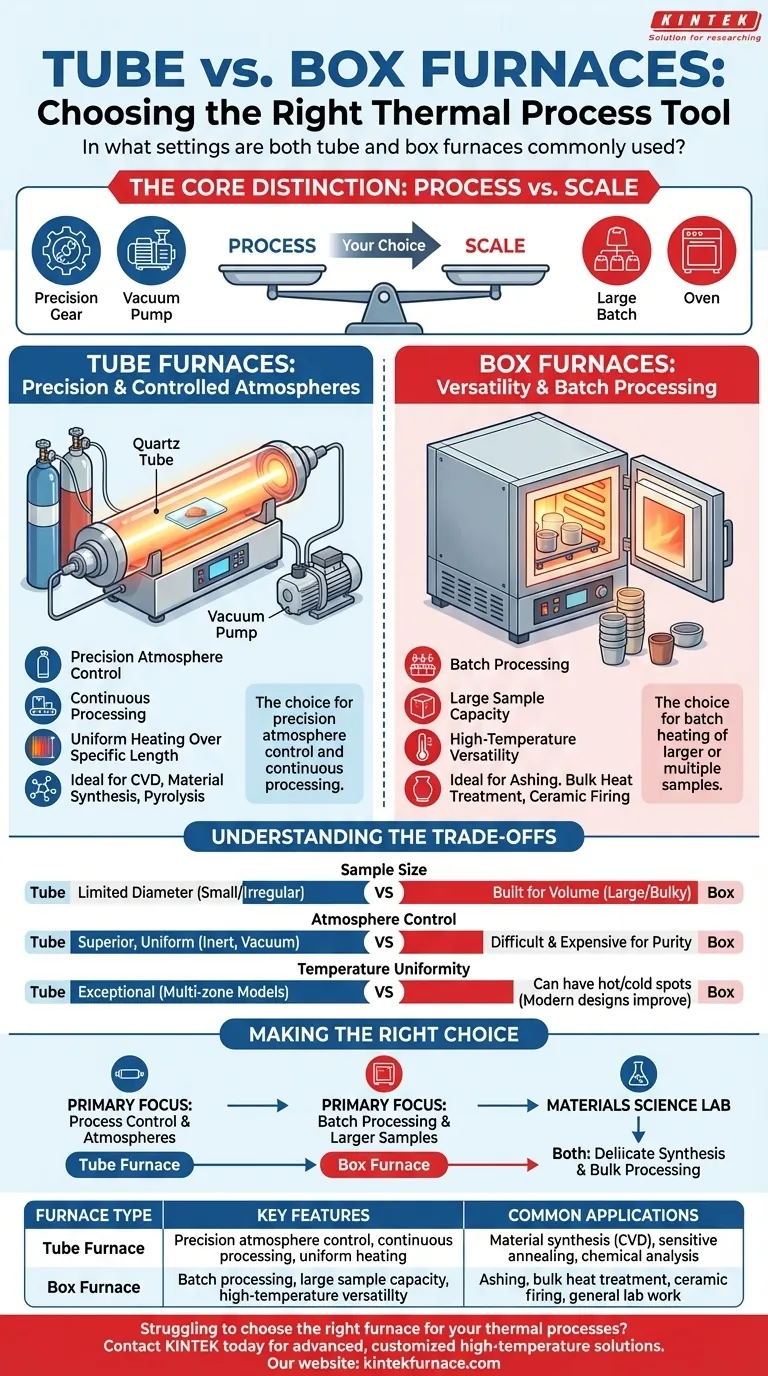
In short, both tube and box furnaces are staple pieces of equipment found in a wide range of industrial, academic, and research settings. They are used for thermal processes like annealing, tempering, sintering, and chemical analysis, but their specific applications are dictated by fundamental differences in their design.
The choice between a tube and a box furnace is not about the industry you are in, but about the process you need to perform. Tube furnaces are chosen for precision atmosphere control and continuous processing, while box furnaces are chosen for batch heating of larger or multiple samples.

The Core Distinction: Process vs. Scale
The key difference between these two furnace types lies in their physical construction, which makes each ideal for different tasks. Understanding this distinction is crucial for selecting the right tool for your work.
Tube Furnaces: Precision and Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace is designed around a long cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz, which contains the sample. This geometry is its defining advantage.
Its narrow, enclosed shape makes it exceptionally easy to purge with a gas or pull into a vacuum. This gives you precise control over the chemical environment your sample is heated in.
This control is essential for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), material synthesis under inert gas, or heat-treating sensitive alloys that would oxidize in air.
Box Furnaces: Versatility and Batch Processing
A box furnace, sometimes called a muffle furnace, is essentially a high-temperature oven with a larger, cubical chamber.
Its primary advantage is space. The larger chamber allows for the heating of bulky items or multiple samples at once in a single batch.
Box furnaces are the workhorses for general-purpose applications like ashing materials for analysis, firing ceramics, or performing standard heat treatments where the atmosphere (typically air) is not a critical variable.
Common Applications by Furnace Type
While both appear in the same labs, their specific uses rarely overlap. The process dictates the furnace.
Typical Tube Furnace Applications
The need for a controlled atmosphere or uniform heating over a specific length defines tube furnace applications.
- Material Synthesis: Used for producing advanced materials like semiconductors, graphene, and polymer composites, often via chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
- Material Processing: Essential for annealing, hardening, sintering, and calcination where exposure to oxygen must be prevented.
- Specialized Analysis: Applied in oil and gas analysis, pyrolysis, and testing materials for aerospace, where samples are processed under specific gas flows.
- Continuous Flow Processes: The tubular design is ideal for heating materials as they pass through, common in industrial production and gas preheating.
Typical Box Furnace Applications
The need for capacity and simple, high-temperature heating defines box furnace applications.
- Material Analysis: Widely used for sample preparation, such as ashing coal, paper, or agricultural products to determine their inorganic content.
- Bulk Heat Treatment: The go-to tool for annealing, tempering, or hardening multiple metal parts simultaneously.
- High-Temperature Firing: Used extensively in firing ceramics, smelting metals, and creating ceramic-metal seals.
- General Lab Work: Functions as a robust, all-purpose oven for drying glassware or performing basic thermal decomposition tests.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing one furnace over the other involves clear trade-offs in capability and flexibility.
Sample Size and Throughput
Tube furnaces are inherently limited by the diameter of their process tube, making them unsuitable for large or irregularly shaped objects.
Box furnaces, by contrast, are built for volume. They easily accommodate crucibles, trays of parts, or bulky components that would never fit in a tube.
Atmosphere Control
This is the most critical trade-off. Tube furnaces provide superior, uniform atmosphere control. It is simple to achieve a pure inert gas environment or a consistent vacuum.
While vacuum box furnaces exist, achieving the same level of atmospheric purity and laminar gas flow as in a tube furnace is significantly more difficult and expensive.
Temperature Uniformity
Tube furnaces, especially multi-zone models, offer exceptional temperature uniformity along the length of the tube. This is critical for growing crystals or performing sensitive chemical reactions.
Box furnaces can be prone to hot and cold spots, although modern designs with advanced heating elements and insulation have greatly minimized this issue for most general-purpose applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be based on the non-negotiable requirements of your specific thermal process.
- If your primary focus is process control with specific atmospheres: The tube furnace is your only viable choice for applications like CVD, pyrolysis, or sensitive annealing.
- If your primary focus is batch processing or larger samples: The box furnace provides the capacity and versatility for general heat treatment, ashing, or firing multiple items at once.
- If you are running a materials science lab: You will likely need both; the tube furnace for delicate synthesis and the box furnace for subsequent bulk processing.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace comes down to matching the tool's core strengths to the demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Furnace | Precision atmosphere control, continuous processing, uniform heating | Material synthesis (e.g., CVD), sensitive annealing, chemical analysis |
| Box Furnace | Batch processing, large sample capacity, high-temperature versatility | Ashing, bulk heat treatment, ceramic firing, general lab work |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your thermal processes? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise solutions for industries like materials science, research, and manufacturing. Enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can meet your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















