Muffle furnaces are a cornerstone of modern industrial and scientific processes. They are found in nearly any industry that requires precise, high-temperature heating in a controlled environment, including analytical laboratories, metallurgy and metalworking, ceramics and glass manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and various research and development sectors.
A muffle furnace's value is not defined by the industry it serves, but by its core function: providing a highly controlled, contaminant-free environment for high-temperature material analysis and transformation. This universal need is what makes it a vital tool across dozens of seemingly unrelated fields.

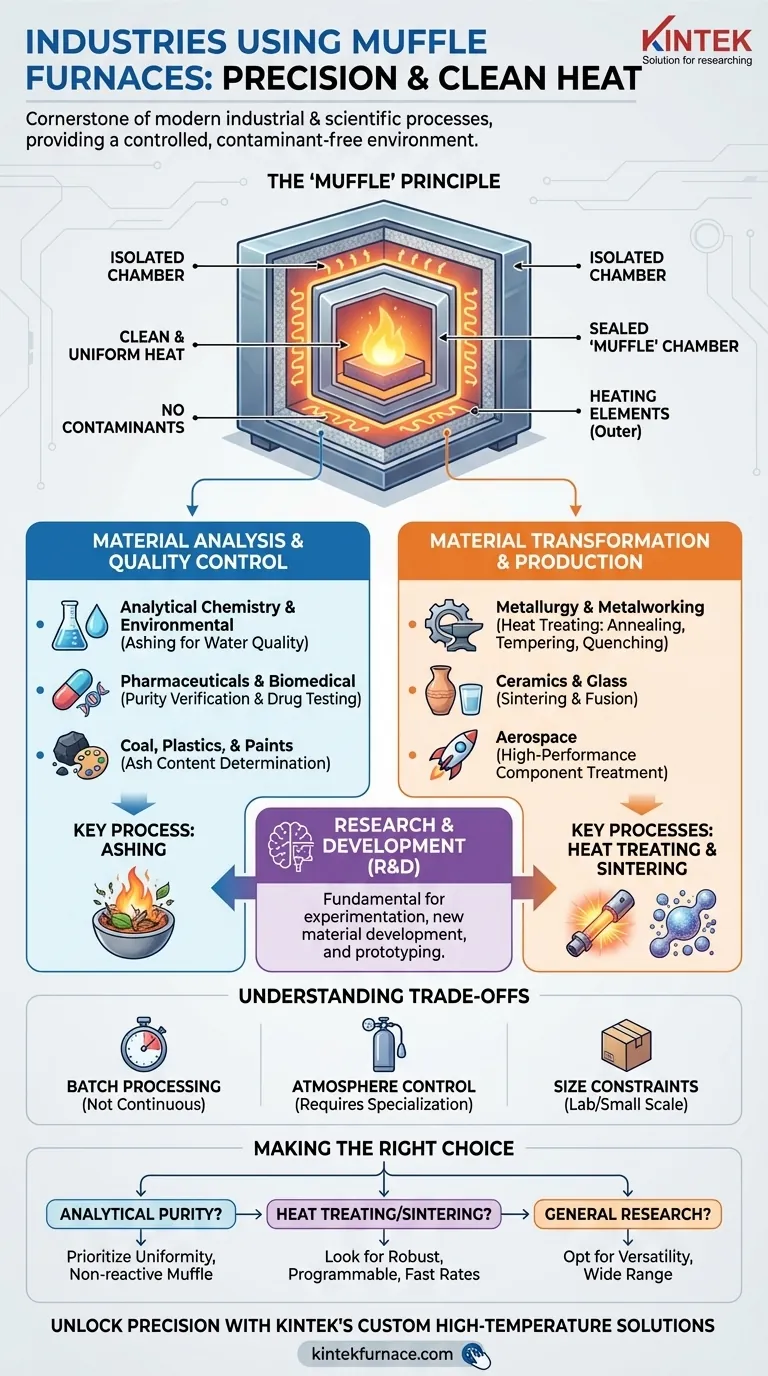
The Core Principle: Why a "Muffle"?
Before listing industries, it is critical to understand what makes this furnace unique. The name itself reveals its primary function.
The Isolating Chamber
A muffle furnace contains an insulated outer chamber that holds the heating elements. Inside this, a separate, sealed chamber—the "muffle"—holds the material or sample.
This design is intentional and crucial. It isolates the sample from the direct heat source and any potential contaminants produced by fuel combustion or element degradation. This ensures the heating process is clean and uniform.
Key Applications Across Industries
Industries use muffle furnaces for two primary purposes: analyzing a material's properties or transforming a material's structure. We can group its uses by these functions.
Material Analysis and Quality Control
This is the most common application, where the goal is to test a substance to determine its composition or response to heat.
- Analytical Chemistry & Environmental: Labs use muffle furnaces for ashing, a process that burns off all organic matter to precisely measure the non-combustible inorganic content. This is essential for water quality analysis and sample pretreatment.
- Pharmaceuticals & Biomedical: The industry relies on ashing to perform drug testing and verify the composition of compounds, ensuring they meet strict purity and quality standards.
- Coal, Plastics, & Paints: In these sectors, furnaces determine ash content, a key quality indicator. This data impacts the material's performance, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Material Transformation and Production
Here, the goal is not to analyze a material, but to fundamentally change its physical properties through heat treatment.
- Metallurgy & Metalworking: Muffle furnaces are workhorses for heat-treating small steel parts and other metals. Processes like annealing (softening), tempering (toughening), and quenching (hardening) are performed with high precision.
- Ceramics & Glass: The furnace is essential for sintering, where ceramic powders are heated below their melting point until they fuse into a solid, durable object. It is also used in creating specialized glass and enamel coatings.
- Aerospace: High-performance components often require specialized heat treatments to achieve the necessary strength and thermal resistance. Muffle furnaces provide the controlled environment needed for these critical processes.
Research and Development (R&D)
Across universities and corporate labs, muffle furnaces are a fundamental tool for experimentation. Researchers use them to develop new materials, test the thermal properties of prototypes, and simulate high-temperature industrial processes on a small scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, muffle furnaces are not the solution for every heating task. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Batch Processing, Not Continuous Flow
A standard muffle furnace is designed for batch work. You load a sample, run a heating cycle, and then remove it. They are not suitable for continuous, assembly-line-style production, which requires larger, more specialized tunnel kilns or belt furnaces.
Atmosphere Control Requires Specialization
A basic muffle furnace operates with ambient air. While the muffle isolates the sample from direct contamination, creating a specific atmosphere (such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon) requires more advanced and costly models equipped with gas ports and vacuum seals.
Size and Scale Constraints
Muffle furnaces are generally intended for laboratory benchtops or small-scale industrial applications. They are perfect for treating small parts, crucibles of powder, or analytical samples, but are not designed for processing very large workpieces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" furnace depends entirely on the task you need to accomplish.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity and ash content: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional temperature uniformity and a high-quality, non-reactive muffle material to prevent cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is heat treating metals or sintering ceramics: Look for models with robust construction, programmable controllers, and fast heating and cooling rates to execute precise thermal profiles.
- If your primary focus is general research and materials testing: Opt for a versatile furnace with a wide temperature range and user-friendly programming to accommodate a diverse array of future experiments.
Ultimately, understanding the core function of the muffle—providing clean, controlled heat—is the key to deploying it effectively in any industry.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry & Environmental | Material Analysis | Ashing for water quality analysis |
| Pharmaceuticals & Biomedical | Material Analysis | Ashing for drug testing and purity verification |
| Coal, Plastics, & Paints | Material Analysis | Ash content determination |
| Metallurgy & Metalworking | Material Transformation | Annealing, tempering, quenching |
| Ceramics & Glass | Material Transformation | Sintering, glass production |
| Aerospace | Material Transformation | Heat treatment for high-performance components |
| Research & Development | Material Analysis & Transformation | Prototype testing, thermal property studies |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Custom High-Temperature Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, or R&D, we deliver reliable, contaminant-free heating for superior material analysis and transformation. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnaces can enhance your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















