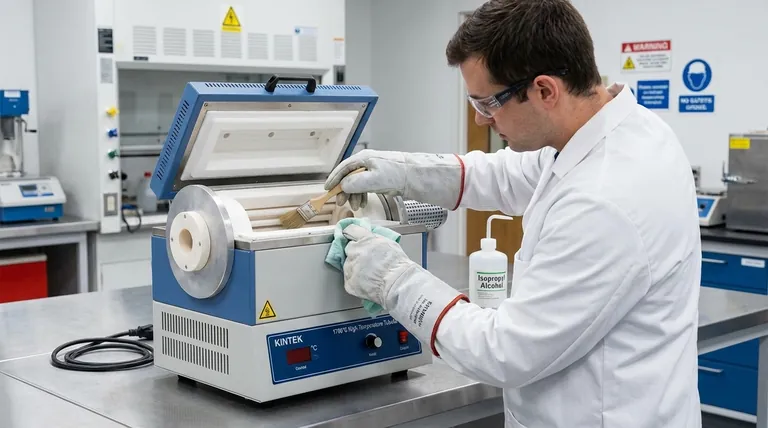
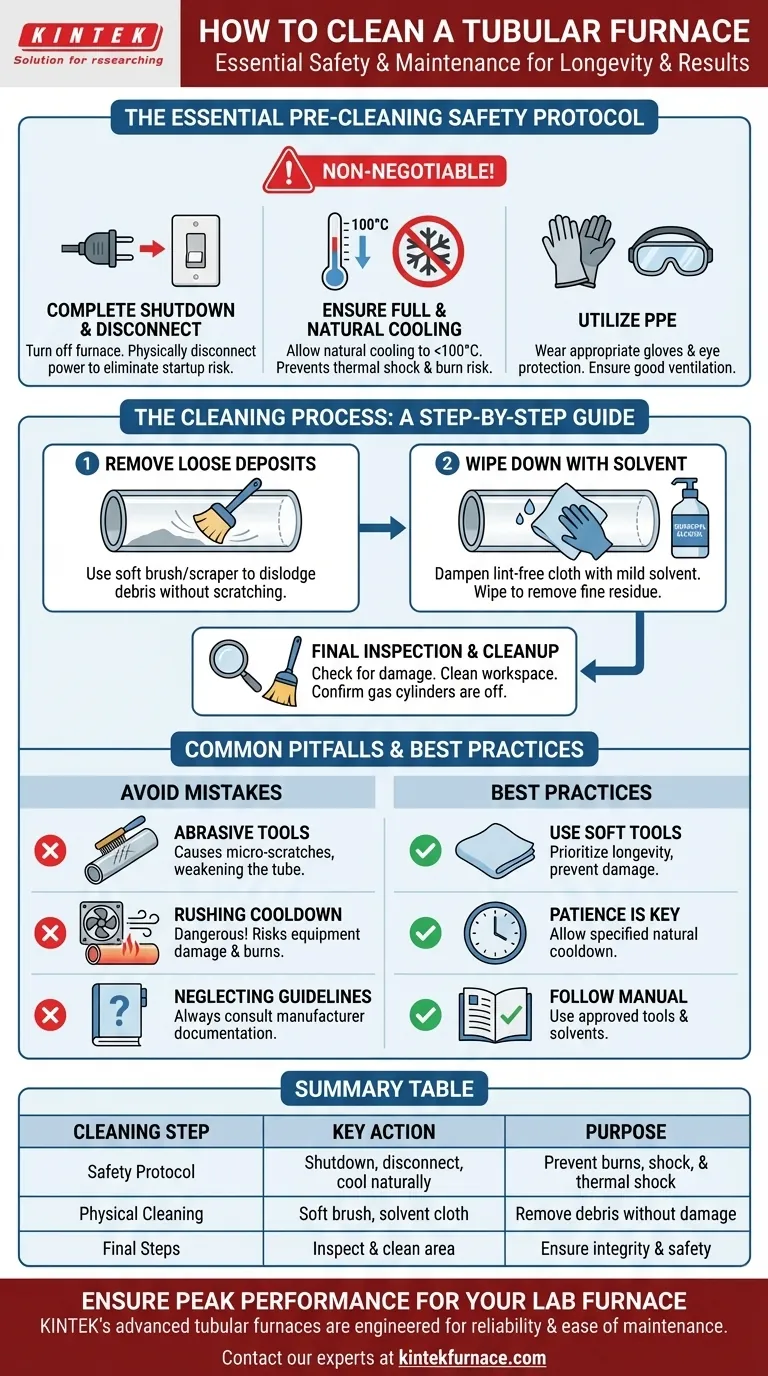
To clean a tubular furnace, you must first execute a complete shutdown by turning off the furnace, disconnecting it from its power source, and allowing the tube to cool completely to a safe temperature. Once cooled, you can physically clean the tube by first removing loose deposits with a soft brush and then wiping away any remaining residue with a cloth dampened with a suitable solvent like alcohol.
Cleaning a tubular furnace is more than a simple housekeeping task; it is a critical safety and maintenance procedure that ensures the longevity of the equipment and prevents cross-contamination between experimental runs.

The Essential Pre-Cleaning Safety Protocol
Before any cleaning can begin, a strict safety protocol is non-negotiable. The high operating temperatures of these furnaces present significant risks if procedures are not followed precisely.
Step 1: Complete Shutdown and Disconnect
The first step is to turn off the furnace controls. For absolute safety, you must then physically disconnect the unit from its power source to eliminate any risk of accidental startup or electrical shock.
Step 2: Ensure Full and Natural Cooling
Never attempt to clean a hot furnace. Allow the furnace tube to cool naturally to below 100°C. Forcibly cooling the furnace or opening the chamber prematurely can cause thermal shock, potentially cracking the tube, and poses a severe burn risk.
Step 3: Utilize Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Even with a cooled furnace, residual heat or chemical residues can be a hazard. Always wear appropriate heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses or goggles. Ensure the area is well-ventilated, especially when working with solvents.
The Cleaning Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
With the furnace safely shut down and cooled, you can proceed with the physical cleaning of the tube.
Removing Loose Deposits
Begin by using a soft brush or a gentle scraper to remove any loose debris, dust, or sample residue from the inner walls of the furnace tube. The goal is to dislodge material without scratching the tube's surface.
Wiping Down with a Solvent
After brushing, dampen a clean, lint-free cloth with a mild solvent such as isopropyl alcohol. Carefully wipe the interior of the tube to remove any fine particulate matter or chemical films left behind.
Final Inspection and Area Cleanup
Once the tube is clean, perform a quick visual inspection for any scratches or damage that may have occurred. Clean the area around the furnace to ensure the entire workspace is tidy. If you used process gases, confirm the gas cylinders are turned off.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of your furnace.
Using Abrasive Tools
Aggressive scraping with hard or sharp tools can create micro-scratches on the tube's interior. These scratches can become stress points that weaken the tube over time and can trap contaminants, affecting future experiments. Always opt for the softest tool that can get the job done.
Rushing the Cooldown Process
Patience is a critical part of the safety protocol. Forcibly opening the furnace door to speed up cooling is dangerous and risks damaging the equipment. Always allow for a natural cooldown period as specified by the manufacturer.
Neglecting Manufacturer Guidelines
Your furnace manufacturer provides the definitive guide for maintenance. Always consult their documentation for specific recommendations regarding approved cleaning tools and chemical solvents for your particular model and tube material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to cleaning should align with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is safety: Always prioritize a complete, verified shutdown and natural cooldown before any physical contact with the furnace.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Use only soft, non-abrasive tools and manufacturer-approved solvents to prevent damage to the furnace tube.
- If your primary focus is experimental integrity: Ensure all residue is thoroughly removed after every run to prevent cross-contamination that could invalidate your results.
Consistent and careful maintenance is the key to reliable results and a long operational life for your tubular furnace.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Protocol | Shutdown, disconnect power, cool naturally. | Prevent burns, electrical shock, and thermal shock. |
| Physical Cleaning | Use a soft brush and solvent-dampened cloth. | Remove debris and residue without damaging the tube. |
| Final Steps | Inspect for damage and clean the workspace. | Ensure equipment integrity and a safe lab environment. |
Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity for Your Lab Furnace
Proper maintenance is critical, but so is having the right equipment for your unique research needs. KINTEK's advanced tubular furnaces are engineered for reliability and ease of maintenance.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can enhance your lab's safety, efficiency, and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















