In essence, you calibrate a muffle furnace by comparing its displayed temperature to the actual internal temperature, which is measured using an independent, calibrated thermometer system. You then use the difference, or "error," to either adjust the furnace's controller settings or create a correction chart. This process ensures your furnace achieves the precise temperature required for accurate and repeatable results.
The core principle of calibration is not just setting a temperature, but verifying it. You are using a trusted, external measurement device to confirm that the temperature shown on your furnace's display accurately reflects the true thermal conditions inside the chamber.

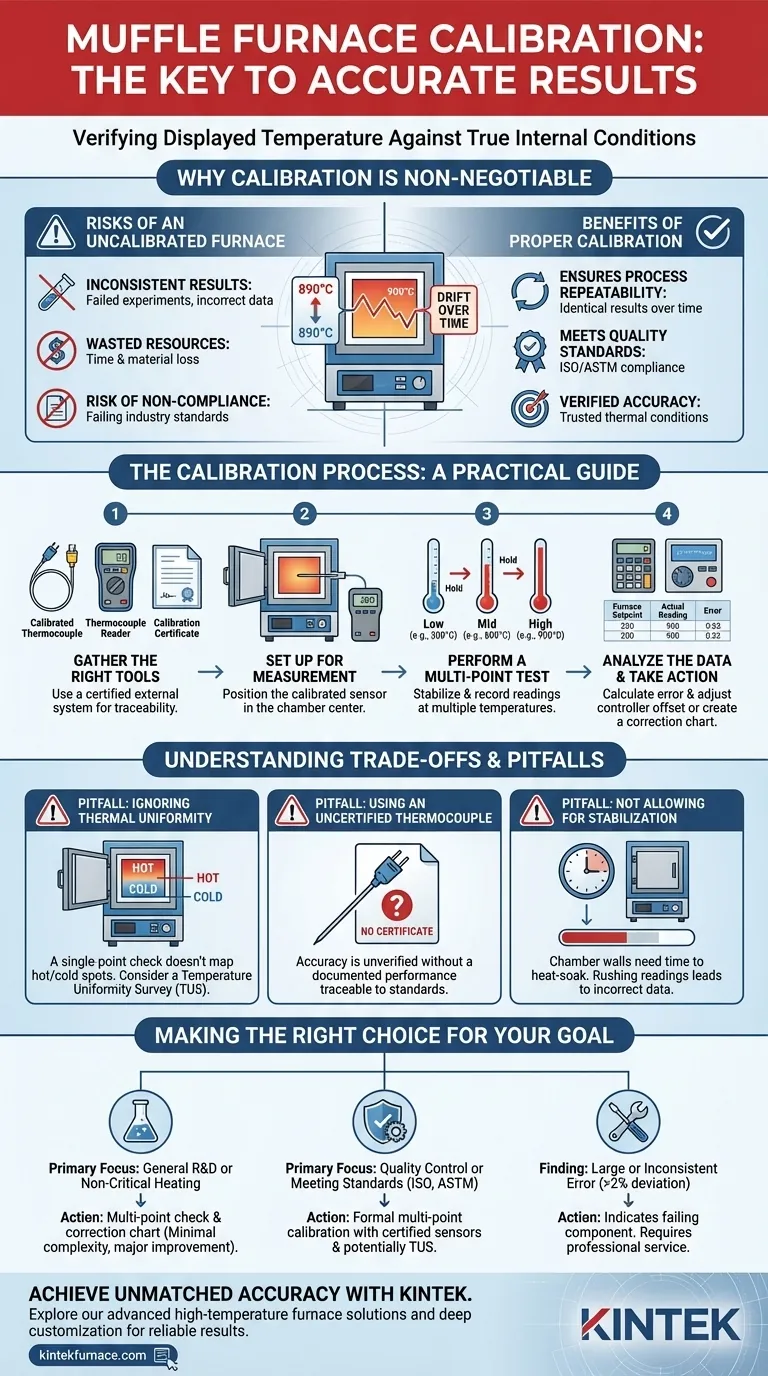
Why Furnace Calibration is Non-Negotiable
A muffle furnace is a precision instrument, but its accuracy can drift over time due to aging components like the internal thermocouple or controller electronics. Relying on an unverified temperature display is a significant risk.
The Cost of an Uncalibrated Furnace
An inaccurate furnace leads to inconsistent results. This can mean failed experiments, materials that don't meet specifications, or incorrect data for research, wasting both time and resources.
Meeting Quality and Industry Standards
For many industries, including aerospace, medical, and manufacturing, temperature accuracy is not optional. Processes governed by standards like ISO or ASTM require documented proof that the equipment used is calibrated and accurate.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
Calibration is the only way to ensure that a process run at 900°C today is identical to one run at 900°C six months from now. This repeatability is the foundation of reliable scientific and industrial work.
The Calibration Process: A Practical Guide
Calibration involves comparing your furnace's reading to a known, traceable standard. Here is the equipment and process required.
Step 1: Gather the Right Tools
Your furnace's built-in sensor is the Unit Under Test (UUT). To test it, you need a separate, reliable measurement system. This typically consists of:
- A Calibrated Thermocouple: This is a high-temperature sensor (often Type K, S, or R) that has been professionally calibrated against known standards. It must come with a calibration certificate that shows its error at various temperatures. Using an uncalibrated thermocouple to perform a calibration is pointless.
- A Thermocouple Reader or Datalogger: This is a high-accuracy digital meter that the calibrated thermocouple plugs into. It displays the temperature measured by the external sensor.
Step 2: Set Up for the Measurement
Position the tip of the calibrated thermocouple inside the furnace chamber. Ideally, it should be in the geometric center of the chamber or at the specific location where your samples will be placed.
Carefully close the furnace door, allowing the thermocouple wire to pass through the opening with minimal gap. Some furnace doors have a small port for this purpose.
Step 3: Perform a Multi-Point Test
A single-point check is good, but a multi-point calibration across your typical operating range is far better.
- Set a Low Temperature: Set the furnace controller to your first test point (e.g., 300°C).
- Wait for Stabilization: Allow the furnace to heat up and stabilize. This is critical. Wait until the furnace's display and your external reader have both held a steady temperature for at least 15-20 minutes.
- Record Both Readings: Write down the temperature from the furnace display and the temperature from your calibrated external reader.
- Repeat at Other Temperatures: Repeat this process for mid-range and high-range temperatures that you typically use (e.g., 600°C and 900°C).
Step 4: Analyze the Data and Take Action
You now have a set of data comparing the setpoint to the actual temperature.
- Calculate the Error: For each test point, the error is
(Actual Temperature from Reader) - (Furnace Display Temperature). - Adjust the Controller Offset: Many modern digital controllers have a calibration or offset parameter in their settings menu. If your furnace is reading low by 8°C, you can enter an offset to correct the display. Consult your furnace manual for instructions on this.
- Create a Correction Chart: If the controller cannot be adjusted, create a simple chart. This chart will tell you what temperature to set on the furnace to achieve a desired true temperature. For example: "To achieve 900°C, set furnace to 908°C."
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Proper calibration requires attention to detail. Avoiding these common mistakes is essential for a meaningful result.
Pitfall: Ignoring Thermal Uniformity
The temperature in the center of the furnace may be different from the temperature in the corners. A single-point calibration tells you the accuracy at that one spot. A more advanced Temperature Uniformity Survey (TUS) involves placing multiple thermocouples throughout the chamber to map out these hot and cold spots.
Pitfall: Using an Uncertified Thermocouple
Using a brand-new but uncalibrated thermocouple for this task provides no guarantee of accuracy. The entire principle rests on comparing your furnace to a sensor with a known, documented performance traceable to national standards.
Pitfall: Not Allowing for Stabilization (Soak Time)
Furnaces, especially large ones, have significant thermal mass. The air temperature may reach the setpoint quickly, but the chamber walls and insulation take much longer to become fully heat-soaked and stable. Rushing the readings will lead to incorrect data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your calibration strategy depends on your accuracy requirements.
- If your primary focus is general R&D or non-critical heating: Performing a single or multi-point check and creating a correction chart provides a major improvement in accuracy with minimal complexity.
- If your primary focus is quality control or meeting industry standards (ISO, ASTM): A formal, multi-point calibration performed with a certified thermocouple is required, and a full Temperature Uniformity Survey may be necessary.
- If you find a large or inconsistent error: A significant deviation (e.g., >2% of the setpoint) or a non-linear error may indicate a failing controller or a degraded internal thermocouple, which requires professional service.
By taking the time to calibrate your furnace, you are taking direct control over the accuracy and repeatability of your thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Calibration Step | Key Action | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Gather Tools | Use a calibrated thermocouple & reader with a certificate. | Ensures measurement is traceable to a known standard. |
| 2. Set Up | Position the thermocouple in the chamber's geometric center. | Measures temperature where your samples will be. |
| 3. Multi-Point Test | Test at low, mid, and high-range temperatures after stabilization. | Verifies accuracy across your entire operating range. |
| 4. Analyze & Act | Calculate error and adjust the controller offset or create a correction chart. | Corrects the furnace's display to reflect the true temperature. |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Processing Accuracy with KINTEK
Calibration is key to reliable results, but it starts with a precision-engineered furnace. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions.
Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is built for accuracy and durability. Coupled with our strong deep customization capability, we can precisely engineer a solution to meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring consistent performance and simplifying your calibration process.
Stop risking inconsistent results. Let's discuss how a KINTEK furnace can enhance your lab's capabilities and reliability.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















