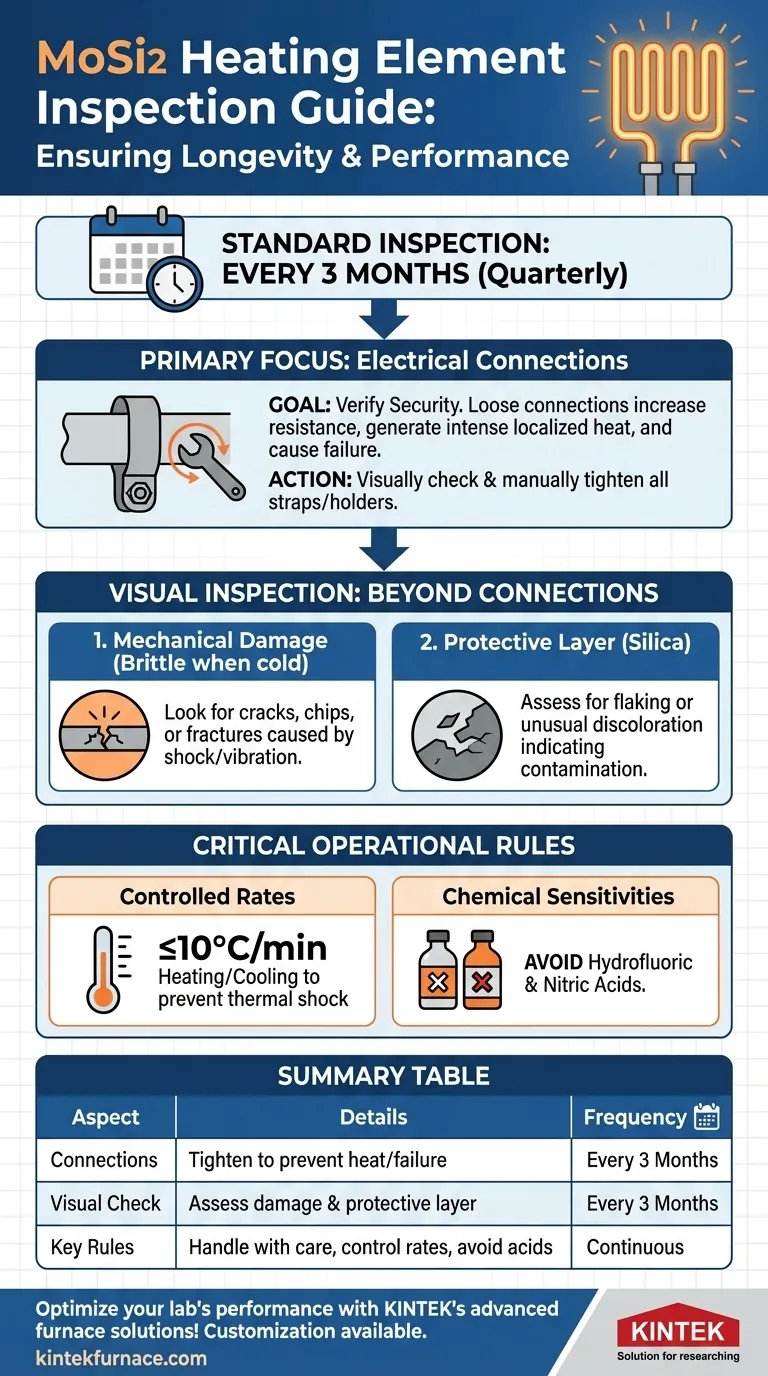
As a general rule, MoSi2 (Molybdenum Disilicide) heating elements require a standard inspection every 3 months. The primary goal of this check is to verify that all electrical connections are secure. If any connections are found to be loose, they must be tightened to prevent operational failure.
The core principle of MoSi2 element maintenance is not just adhering to a schedule, but understanding the element's unique characteristics. Proactive checks prevent failures caused by loose electrical contacts, while proper handling and operational practices are essential to manage their inherent brittleness and maximize their long service life.
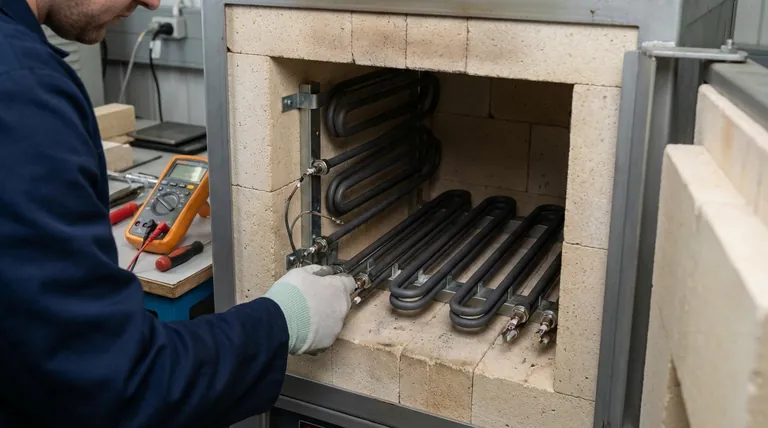

The Primary Focus of Inspection: Electrical Connections
The single most critical maintenance task for MoSi2 elements is ensuring the integrity of their electrical connections. This simple check is fundamental to furnace reliability.
Why Loose Connections Cause Failure
When a connection becomes loose, it increases electrical resistance at that point. This resistance generates intense localized heat, which can lead to the strap or holder burning out and causing a complete element failure. A regular quarterly check prevents this common issue.
The Inspection and Tightening Process
The process is straightforward. Power down and cool the furnace according to safe operating procedures. Visually and manually check each element's connection straps for tightness. If any movement is detected, use the appropriate tools to tighten the connection securely.
Visual Inspection: Beyond the Connections
While connections are the primary checkpoint, a thorough visual inspection can reveal early signs of other potential issues, helping you extend element life and prevent unexpected downtime.
Identifying Mechanical Damage
MoSi2 elements are extremely brittle at room temperature. Damage can occur from mechanical shock or vibration. During your inspection, look for any visible cracks, chips, or fractures on the elements themselves. Damaged elements should be scheduled for replacement.
Assessing the Protective Layer
During operation at high temperatures, MoSi2 elements form a protective outer layer of silica (glass). This layer is what gives them their excellent longevity. Look for any signs of this layer flaking off or showing unusual discoloration, which could indicate contamination or an overly aggressive furnace atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brittleness vs. Longevity
MoSi2 elements offer exceptional performance, but this comes with specific operational requirements. Understanding their core trade-offs is key to successful long-term use.
The Challenge of Brittleness
The primary drawback is their fragility when cold. This necessitates careful handling during installation and inspection. More importantly, it requires controlled heating and cooling rates during furnace operation, typically not exceeding 10°C per minute, to prevent thermal shock and breakage.
The Benefit of a Long Service Life
When handled and operated correctly, MoSi2 elements have an exceptionally long and stable service life. The protective silica layer allows them to withstand continuous high-temperature use, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs over time compared to other element types.
Chemical Sensitivities
While resistant to most acids and alkalis, it is important to know that MoSi2 elements will be attacked and damaged by hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid. Ensure your process does not introduce these chemicals into the furnace atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align with your operational priorities. A quarterly inspection is the baseline, but your focus may vary.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: The non-negotiable quarterly check of electrical connections is your most critical task to prevent sudden, avoidable failures.
- If your primary focus is extending element lifespan: Emphasize strict adherence to controlled heating/cooling rates and careful visual inspection for early signs of mechanical or chemical degradation.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Always ensure the furnace is properly cooled and de-energized before any hands-on inspection or maintenance.
Ultimately, proactive and informed maintenance is the key to unlocking the full performance and longevity of your MoSi2 heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Inspection Frequency | Every 3 months (quarterly) |
| Primary Focus | Check and tighten electrical connections to prevent localized heat and failure |
| Visual Checks | Look for cracks, chips, or damage due to brittleness; assess protective silica layer for flaking or discoloration |
| Key Considerations | Handle with care (brittle when cold), control heating/cooling rates (≤10°C/min), avoid hydrofluoric and nitric acids |
| Benefits | Maximizes uptime, extends service life, ensures operational safety |
Optimize your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior efficiency and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your maintenance goals and enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















