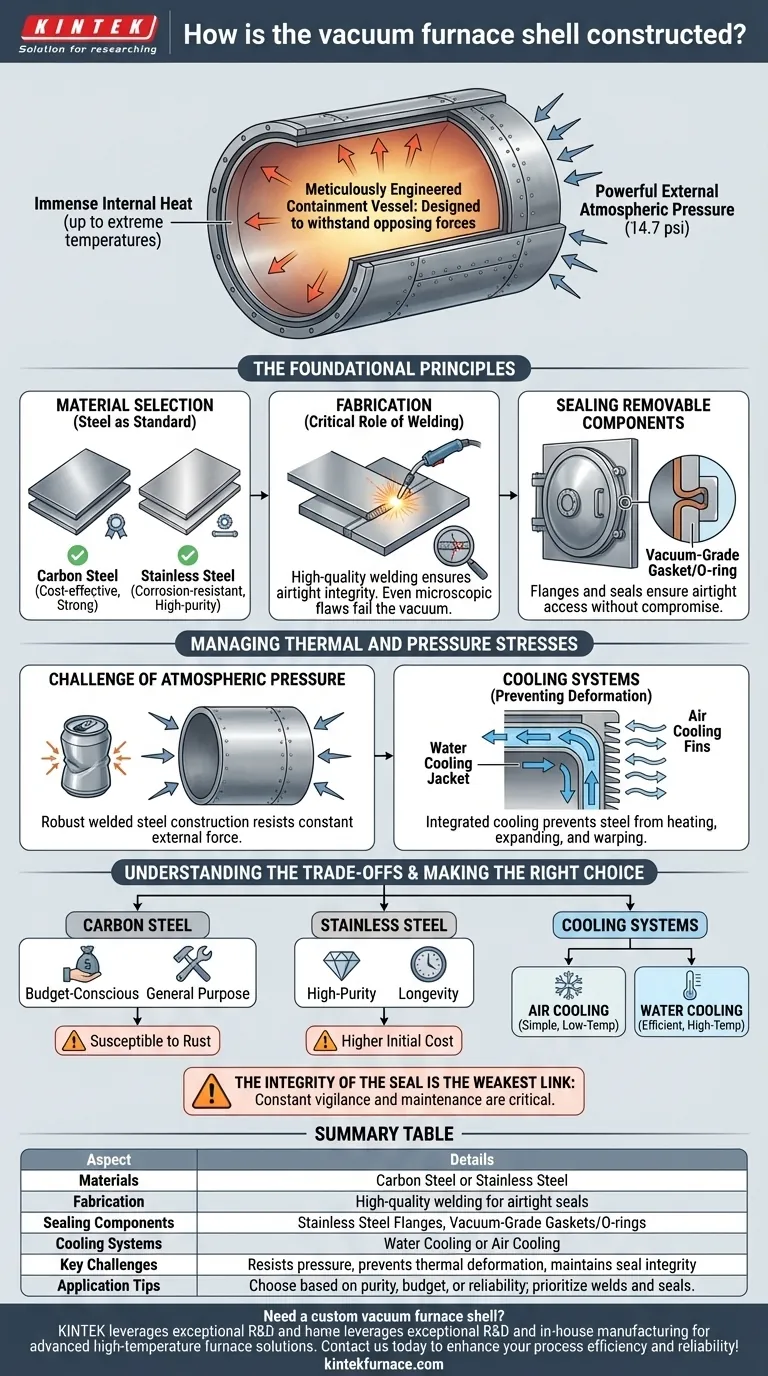
At its core, a vacuum furnace shell is a meticulously engineered containment vessel designed for two opposing forces: immense internal heat and powerful external atmospheric pressure. It is constructed by welding together plates of carbon steel or stainless steel, with any removable components like doors or ports secured with specialized vacuum-sealing materials to ensure an airtight chamber.
The construction of the shell is not just about building a box; it's about creating a stable and impermeable barrier. Its primary purpose is to withstand the crushing force of the atmosphere while remaining cool and rigid enough to maintain a perfect vacuum seal, even as temperatures inside reach extreme levels.
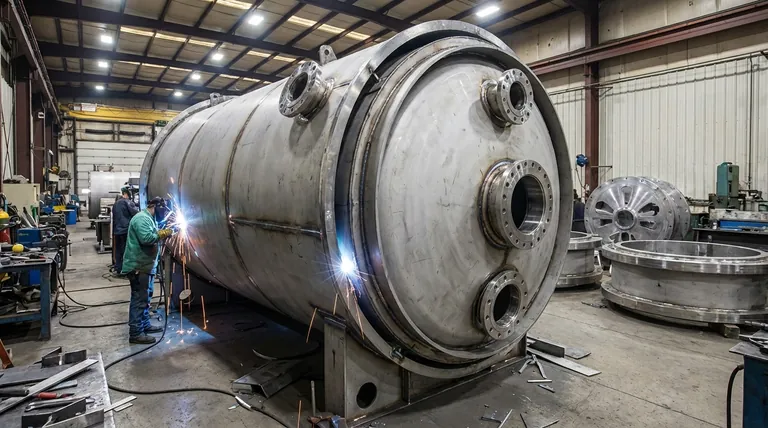

The Foundational Principles of Shell Construction
To achieve its purpose, the furnace shell relies on specific material choices and fabrication methods. Every element is designed to guarantee the integrity of the vacuum.
Material Selection: Steel as the Standard
The shell is almost universally built from either carbon steel or stainless steel. The choice is dictated by strength, weldability, and resistance to thermal stress. These materials provide the necessary structural rigidity to prevent the shell from collapsing under atmospheric pressure when a vacuum is pulled inside.
Fabrication: The Critical Role of Welding
The steel plates are joined using high-quality welding. The integrity of these welds is paramount. Even a microscopic flaw or pinhole leak will prevent the furnace from achieving or holding the required vacuum level, rendering the entire system ineffective. The quality of the welding directly translates to the performance of the furnace.
Sealing Removable Components
Since a furnace must be loaded and unloaded, it includes doors and ports for access and instrumentation. These openings are sealed using components like stainless steel flanges and vacuum-grade gaskets or O-rings. This ensures that these removable parts can be opened and closed repeatedly without compromising the airtightness of the chamber.
Managing Thermal and Pressure Stresses
A vacuum furnace shell operates in a demanding environment. It must manage both the pressure differential and the heat generated by the process without failing.
The Challenge of Atmospheric Pressure
Creating a vacuum doesn't "suck" the air out; it pumps it out, leaving very little pressure inside. The result is that the full force of Earth's atmosphere—about 14.7 pounds per square inch—is constantly pushing in on every surface of the shell. The shell's robust, welded steel construction is engineered specifically to resist this immense and constant external force.
Cooling Systems: Preventing Deformation
While the inside of the furnace gets incredibly hot, the shell itself must remain relatively cool. To achieve this, a cooling system is integrated into the shell's design, typically a jacket through which water or air circulates. This cooling prevents the steel from heating up, expanding, and warping. Any deformation would compromise the seals and could lead to catastrophic structural failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The specific design of a shell involves balancing cost, performance, and operational requirements.
Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel
Carbon steel is a strong and cost-effective choice. However, it is susceptible to rust, and any corrosion can threaten the integrity of the vacuum seals over time. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and is often preferred for high-purity processes or humid environments, though it comes at a higher initial cost.
Air Cooling vs. Water Cooling
Water cooling is far more efficient at removing heat and is the standard for most industrial, high-temperature, or high-duty-cycle furnaces. Air cooling is simpler and less expensive to implement but is only suitable for smaller laboratory furnaces or those operating at lower temperatures where the heat load is minimal.
The Integrity of the Seal: The Weakest Link
The single most common point of failure in a vacuum furnace system is the seal. Whether it's a microscopic crack in a weld or a degraded O-ring on a door, the entire process depends on a perfect seal. Constant vigilance and maintenance of these sealing surfaces are critical for reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the shell's construction allows you to evaluate a furnace based on its fundamental design.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing and longevity: Prioritize a stainless steel shell with a robust water-cooling system to ensure maximum cleanliness and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is a budget-conscious, general-purpose application: A well-fabricated carbon steel shell can provide excellent performance, provided it is properly maintained to prevent corrosion.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Pay the most attention to the quality of the welds and the design of the seals on doors and ports, as these are the most likely sources of vacuum leaks.
Ultimately, the furnace shell is the unsung hero of the vacuum heat-treating process, providing the stable and secure environment required for a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Materials | Carbon steel (cost-effective, strong) or stainless steel (corrosion-resistant, high-purity) |
| Fabrication | High-quality welding for airtight seals, critical for vacuum integrity |
| Sealing Components | Stainless steel flanges with vacuum-grade gaskets or O-rings for doors and ports |
| Cooling Systems | Water cooling (efficient for high-temp/industrial use) or air cooling (for low-temp/lab use) |
| Key Challenges | Resists atmospheric pressure (14.7 psi), prevents thermal deformation, maintains seal integrity |
| Application Tips | Choose based on purity, budget, or reliability needs; prioritize welds and seals for leak prevention |
Need a custom vacuum furnace shell tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for your experiments. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- What is the significance of porcelain furnaces in academic and scientific research? Unlock Innovation with Precise High-Temperature Control
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab



















