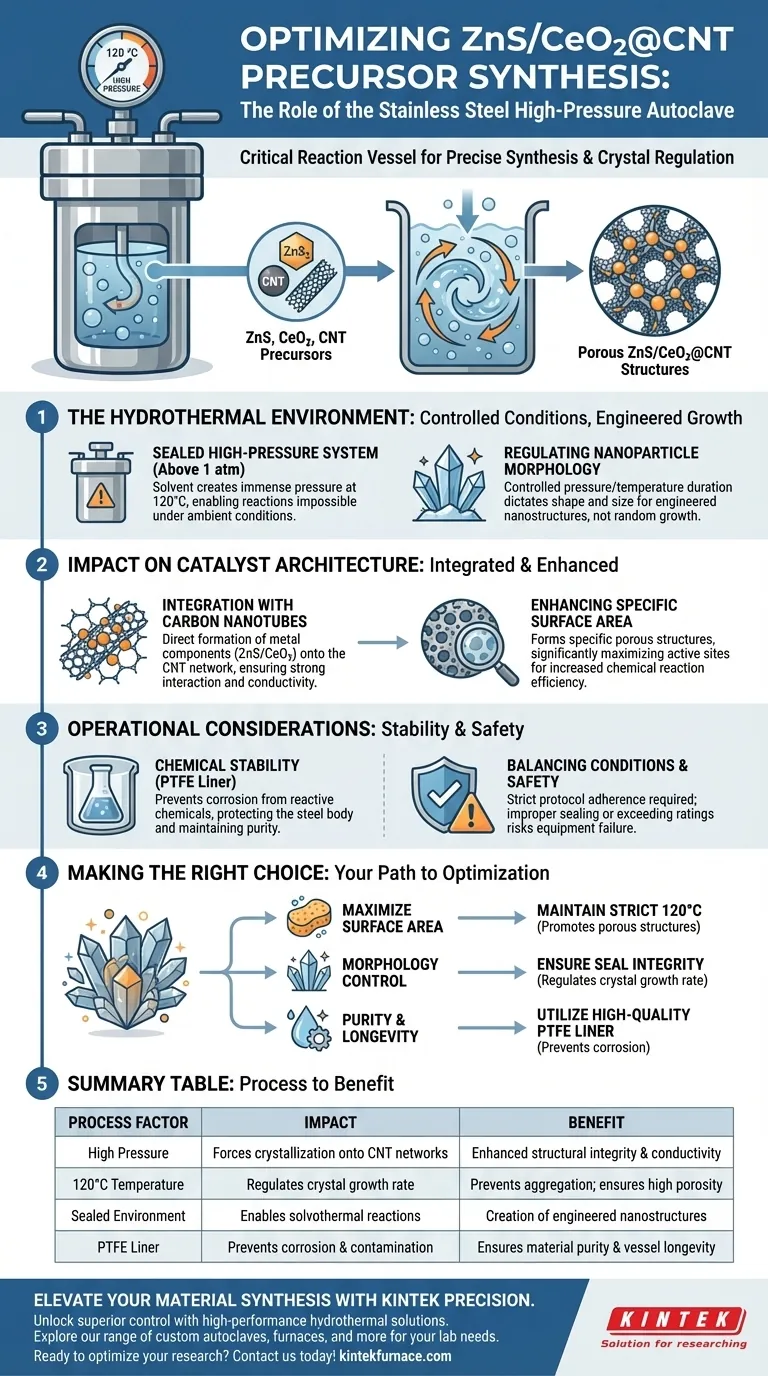
The stainless steel high-pressure autoclave serves as the critical reaction vessel that enables the precise synthesis of ZnS/CeO2@CNT precursors. By maintaining a sealed environment at 120 °C, creates the high-pressure conditions necessary to force metal components to crystallize into specific porous structures directly onto the Carbon Nanotube (CNT) network.
The core function of the autoclave in this process is to provide a stable, high-pressure environment that regulates crystal growth rates. This control is essential for creating high-porosity structures on the CNT network, which significantly maximizes the catalyst's specific surface area.
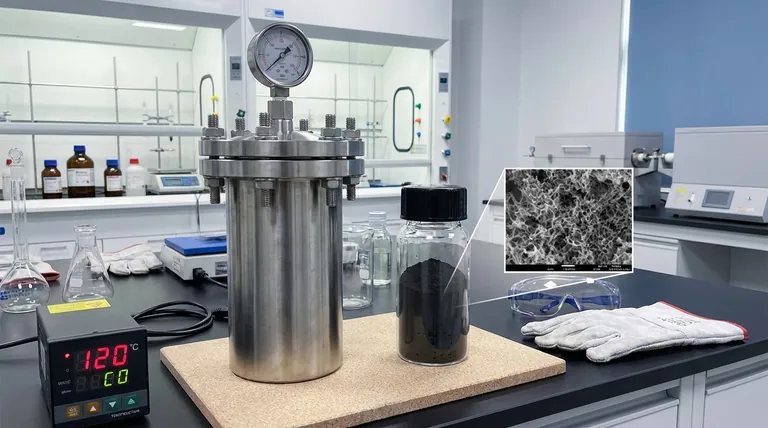

The Role of the Hydrothermal Environment
Creating Controlled Reaction Conditions
The autoclave provides a sealed, high-pressure system.
When the internal temperature reaches 120 °C, the solvent creates pressure that far exceeds atmospheric levels. This environment allows for solvothermal or hydrothermal reactions that would not occur under standard ambient conditions.
Regulating Nanoparticle Morphology
The high-pressure environment allows for the precise regulation of crystal growth rates.
By controlling the pressure and temperature duration, you dictate the final shape and size of the nanoparticles. This ensures the material does not grow randomly, but rather forms specific, engineered nanostructures.
Impact on Catalyst Architecture
Integration with Carbon Nanotubes
The synthesis process within the autoclave specifically encourages metal components (ZnS/CeO2) to form directly on the Carbon Nanotube network.
The autoclave environment facilitates a strong interaction between the metal precursors and the CNTs. This integration is vital for the structural integrity and electrical conductivity of the final composite material.
Enhancing Specific Surface Area
The primary outcome of this controlled growth is the formation of specific porous structures.
These porous architectures significantly increase the specific surface area of the catalyst. A higher surface area provides more active sites for future chemical reactions, directly improving the efficiency of the material.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of Chemical Stability
While the stainless steel provides structural strength against pressure, it is reactive to certain chemicals.
To prevent corrosion from strong alkaline or acidic solutions, the autoclave typically utilizes a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liner. This liner ensures exceptional chemical stability, protecting the steel body while maintaining the purity of the reaction.
Balancing Conditions and Safety
Operating under high pressure and temperature requires strict adherence to safety protocols.
While extreme conditions can induce unique growths (such as nanowires or nanotubes), failing to properly seal the autoclave or exceeding its rating can lead to equipment failure or inconsistent synthesis results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your ZnS/CeO2@CNT synthesis, consider the following aspects of autoclave usage:
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area: Ensure the temperature is maintained strictly at 120 °C to promote the formation of porous structures rather than dense aggregates.
- If your primary focus is morphology control: Focus on the seal integrity of the autoclave to maintain consistent high pressure, which regulates the crystal growth rate and shape.
- If your primary focus is purity and equipment longevity: Always utilize a high-quality PTFE liner to prevent the reaction solution from corroding the stainless steel shell.
The autoclave is not just a container; it is an active tool that shapes the microscopic architecture of your catalyst through pressure and heat.
Summary Table:
| Process Factor | Impact on ZnS/CeO2@CNT Precursors | Benefit for Catalyst Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| High Pressure | Forces crystallization onto CNT networks | Enhanced structural integrity and conductivity |
| 120°C Temperature | Regulates crystal growth rate | Prevents aggregation; ensures high porosity |
| Sealed Environment | Enables solvothermal reactions | Creation of engineered nanostructures |
| PTFE Liner | Prevents corrosion and contamination | Ensures material purity and vessel longevity |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock superior control over your catalyst morphology with high-performance hydrothermal solutions from KINTEK. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable high-pressure autoclaves designed for your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are developing porous ZnS/CeO2@CNT precursors or advanced nanomaterials, our equipment ensures the chemical stability and thermal precision required for groundbreaking results.
Ready to optimize your research? Contact us today to find the perfect lab high-temp furnace or autoclave solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yulin Luo, Qi-Hui Wu. Carbon Nanotubes-Doped Metal Oxides and Metal Sulfides Heterostructure Achieves 3D Morphology Deposition of Li2S and Stable Long-Cycle Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13060181
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a nitrogen curtain protection system play in copper tube welding? Ensure Peak Joint Integrity
- What is the function of a drying oven in the post-treatment process of Ni and Zn-doped MgO nanoparticles?
- What is the role of high-pressure inert gases in the HPB process? Mastering CZT Crystal Stoichiometry
- Why is a high-pressure autoclave essential for nanomaterials? Unlock Superior Crystallinity and Quantum Yield
- Why is a laboratory blast drying oven necessary for Ni-TiN catalysts? Ensure Precision in Precursor Treatment
- Why is the precision of a temperature control system critical in copper brazing? Ensure Perfect Joints Every Time
- What is the main purpose of annealing? A Guide to Controlling Material Properties
- What is the function of a drying oven for oil shale semi-coke? Achieve Precise Sample Standardization



















