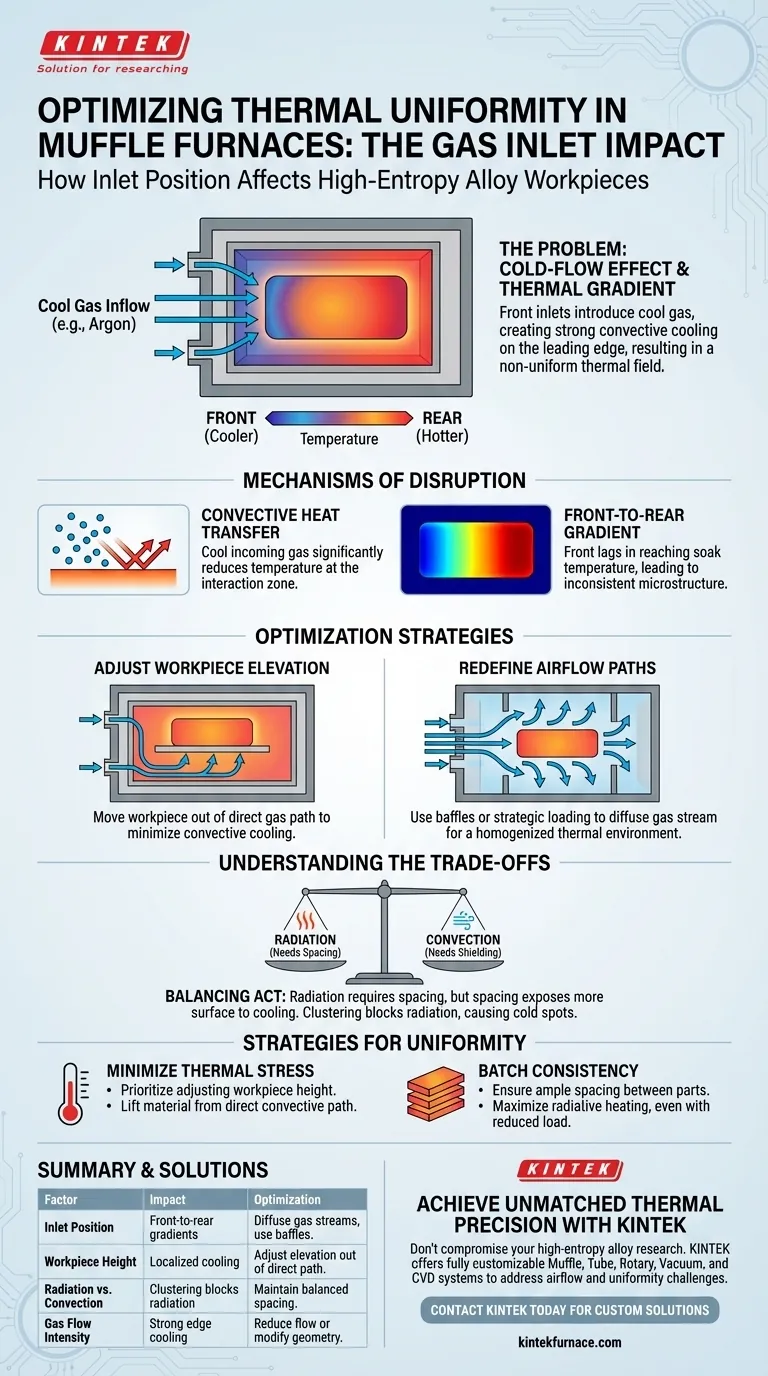
The positioning of gas inlets directly dictates the thermal uniformity of your workpiece. specifically, placing inlets symmetrically at the front of a muffle furnace introduces a flow of cool gas (typically argon) that creates strong convective heat transfer. This dynamic consistently results in a temperature gradient where the front of the high-entropy alloy workpiece remains cooler than the rear.
The "cold-flow effect" caused by inlet positioning disrupts the furnace's thermal equilibrium. While the gas is necessary for atmospheric control, its entry point creates an active cooling zone that must be managed through structural optimization.
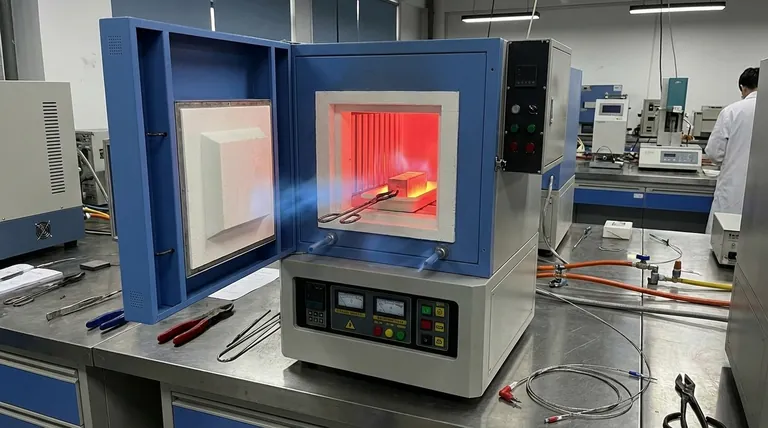
Mechanisms of Thermal Disruption
The Impact of Convective Heat Transfer
When gas enters the furnace, it is significantly cooler than the internal operating temperature.
The position of the inlets determines exactly where this cooler medium interacts with the hot zone.
In a front-loading muffle furnace with front inlets, this creates a distinct convective current that strikes the leading edge of the workpiece first.
The Front-to-Rear Gradient
This convective action strips heat away from the front of the material more aggressively than the rear.
The result is a non-uniform thermal field across the high-entropy alloy.
While the rear of the workpiece may reach the target soak temperature, the front may lag behind, leading to inconsistent microstructure evolution across the sample.
Optimizing the Thermal Field
Adjusting Workpiece Elevation
To counteract the cooling effect of the gas inlet, you must reconsider where the workpiece sits within the chamber.
Changing the placement height can move the alloy out of the direct path of the strongest gas currents.
This simple adjustment helps minimize direct convective cooling on the front face of the material.
Redefining Airflow Paths
The geometry of the furnace structure itself plays a role in stabilizing the temperature.
By modifying how the air flows—either through baffles or strategic loading—you can diffuse the incoming gas stream.
This reduces the intensity of the "cold spot" at the front of the furnace, allowing for a more homogenized thermal environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Radiation vs. Convection
While managing gas flow is critical, you cannot ignore the fundamentals of furnace heating.
Heating in these environments relies heavily on radiation, not just the gas atmosphere.
If you attempt to block gas flow by clustering workpieces too closely, you will inhibit radiative heat transfer, causing cold spots between the parts.
The Density Dilemma
There is a distinct tension between shielding the workpiece and ensuring uniform heating.
You need the gas to protect the high-entropy alloy from oxidation, but the gas flow introduces thermal instability.
Similarly, you need distance between workpieces to allow for radiative heating, but this spacing exposes more surface area to the cooling effects of the gas inlet.
Strategies for Thermal Uniformity
To achieve the best results with high-entropy alloys, you must balance the need for protective gas atmospheres with the physics of heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is minimizing thermal stress: Prioritize the adjustment of workpiece height to lift the material out of the direct convective path of the front gas inlets.
- If your primary focus is batch consistency: Ensure ample spacing between individual workpieces to maximize radiative heating, even if this requires reducing the total load size.
Mastering the airflow path is the only way to turn a protective atmosphere into a thermally neutral variable.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Thermal Distribution | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet Position | Creates front-to-rear temperature gradients due to cool gas inflow. | Implement baffles or diffuse gas streams. |
| Workpiece Height | Direct exposure to convective currents causes localized cooling. | Adjust elevation to move material out of direct airflow paths. |
| Radiation vs. Convection | Clustering blocks radiation; spacing exposes parts to cold-flow effects. | Maintain balanced spacing to ensure uniform radiative heating. |
| Gas Flow Intensity | Strong convection strips heat from the workpiece's leading edge. | Reduce flow rate or modify furnace geometry to stabilize the field. |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Precision for Your Alloys
Don't let convective heat loss compromise your high-entropy alloy research. KINTEK provides industry-leading lab high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all precision-engineered to provide the stable thermal environments your work demands.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to address your specific airflow and temperature uniformity challenges.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and ensure every workpiece achieves consistent microstructure evolution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yuchen Wang, Haisheng Fang. Research and optimization of temperature uniformity of high-precision muffle furnace. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/3009/1/012076
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a Muffle Furnace in the heat treatment of beryl? Master Gemstone Color Modification
- How does high-temperature calcination functionalize ZnO and KCC-1? Optimize Nanopowder Architecture and Performance
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors
- How does a vacuum tube furnace differ from a vacuum muffle furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why is a muffle furnace considered a versatile piece of equipment? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace facilitate the modification of dolomite? Engineering Superior Adsorbents
- What is a box type resistance furnace and how does it work? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What is a box type electric furnace and its main components? Discover Precision Heating for Your Lab



















