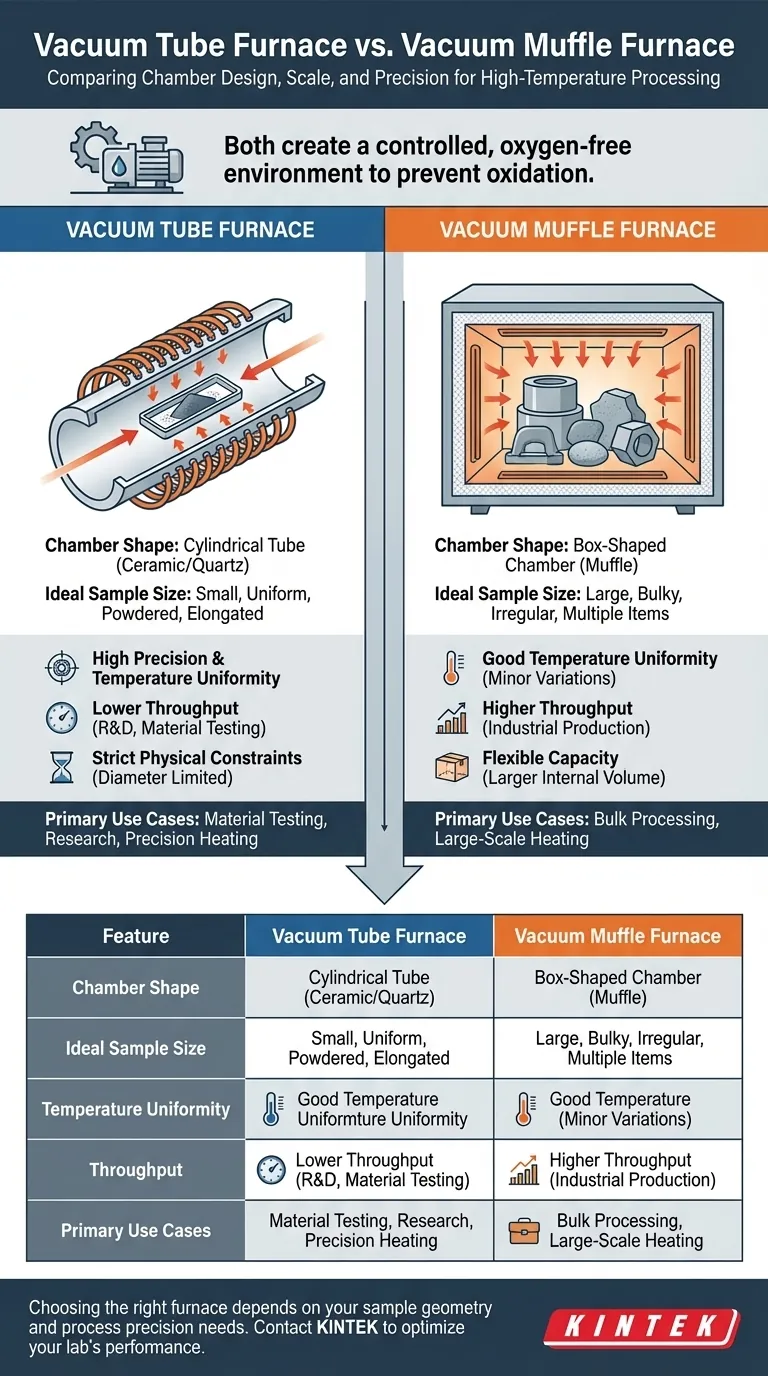
In essence, the difference between a vacuum tube furnace and a vacuum muffle furnace comes down to their internal geometry and the scale of the work they can perform. A vacuum tube furnace uses a long, narrow tube as its heating chamber, making it ideal for precision work on small or uniform samples. In contrast, a vacuum muffle furnace employs a larger, box-shaped chamber, designed to accommodate bulky, numerous, or irregularly shaped materials.
While both furnaces create a controlled, oxygen-free environment, your choice represents a direct trade-off. A vacuum tube furnace offers superior temperature uniformity for small-scale applications, whereas a vacuum muffle furnace prioritizes capacity and the flexibility to handle larger processing volumes.

Deconstructing the Terminology
To understand the difference, it's crucial to separate the two parts of each name: the environment ("vacuum") and the chamber type ("tube" or "muffle").
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Both furnace types are first and foremost vacuum furnaces. Their primary function is to heat materials in a low-pressure environment, effectively removing air and other reactive gases.
This vacuum is critical for preventing oxidation, contamination, and unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface during high-temperature processing.
The Role of the Chamber: Tube vs. Muffle
The terms "tube" and "muffle" describe the shape and design of the physical chamber where the sample is placed.
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz. Heating elements are positioned around the outside of this tube, creating a highly uniform temperature zone along its central axis.
A muffle furnace uses a box-shaped chamber (the "muffle") that sits inside a larger insulated cabinet. The heating elements are typically located within the cabinet but outside the muffle, or sometimes embedded in the muffle walls, to heat the internal volume.
Key Differentiating Factors
The difference in chamber design leads to several practical distinctions that will guide your choice.
Sample Size and Geometry
This is the most significant differentiator. The narrow diameter of a tube furnace inherently limits it to small, elongated, or powdered samples that can fit inside.
A muffle furnace, with its box-like chamber, offers far more internal volume. It is the clear choice for processing large components, multiple items at once, or materials with irregular shapes.
Temperature Uniformity and Control
Due to their cylindrical geometry and external heating, tube furnaces excel at creating a precise and highly uniform thermal zone. This makes them ideal for scientific research and processes where exact temperature control is paramount.
While modern muffle furnaces have excellent temperature control, heating a large, rectangular volume perfectly evenly is more challenging. They are better suited for bulk heating where minor temperature variations across the chamber are acceptable.
Operational Use and Throughput
Tube furnaces are generally used for batch processes involving smaller quantities. Their setup is well-suited for R&D, material testing, and specialized small-scale production.
Muffle furnaces are built for higher throughput. Their larger doors and chambers make it easier to load and unload bulky materials, making them a staple in industrial production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two furnaces requires acknowledging their inherent limitations. Neither is universally superior; they are simply designed for different tasks.
The Limits of the Tube Furnace
The primary trade-off is scale. The strict physical constraints of the tube's diameter mean that if your sample doesn't fit, the furnace is not an option, regardless of its precision. They are ill-suited for any form of bulk processing.
The Compromises of the Muffle Furnace
The main compromise is a potential reduction in absolute temperature uniformity compared to a tube furnace. While excellent for most applications, processes demanding the highest level of precision across a sample might be better served by the focused heating of a tube design. It also heats a larger volume, which can lead to lower energy efficiency for very small samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific material and processing goal will dictate the correct choice. Base your decision on the physical nature of your sample and the precision your process demands.
- If your primary focus is high-precision treatment of small, uniform, or powdered samples: The vacuum tube furnace is the superior choice for its exceptional temperature control and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is processing large parts, bulky materials, or multiple items simultaneously: The vacuum muffle furnace is the only practical option due to its significantly larger internal capacity.
- If your primary focus is simply preventing surface oxidation on any sample: Both furnaces achieve this, so the decision should revert back to the physical size and shape of your material.
By understanding that the choice hinges on sample geometry versus process precision, you can confidently select the furnace that aligns perfectly with your technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Tube Furnace | Vacuum Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Shape | Cylindrical tube | Box-shaped chamber |
| Ideal Sample Size | Small, uniform, or powdered | Large, bulky, or irregular |
| Temperature Uniformity | High precision and uniformity | Good, with minor variations |
| Throughput | Lower, suited for R&D and small batches | Higher, ideal for industrial production |
| Primary Use Cases | Material testing, research, precision heating | Bulk processing, large-scale heating |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need precision for small samples or capacity for large volumes. Don't let furnace selection hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your lab's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















