At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a manufacturing process that creates a high-performance, solid thin film on a substrate from a chemical reaction in a gaseous state. A mixture of reactive gases, known as precursors, are introduced into a reaction chamber where they decompose and react on or near a heated object, depositing the desired material layer by layer.
The challenge in advanced manufacturing is not just coating an object, but creating a perfectly uniform, high-purity film with precisely controlled properties. CVD achieves this by building the film atom-by-atom from a gaseous phase, offering unparalleled control over the final material.
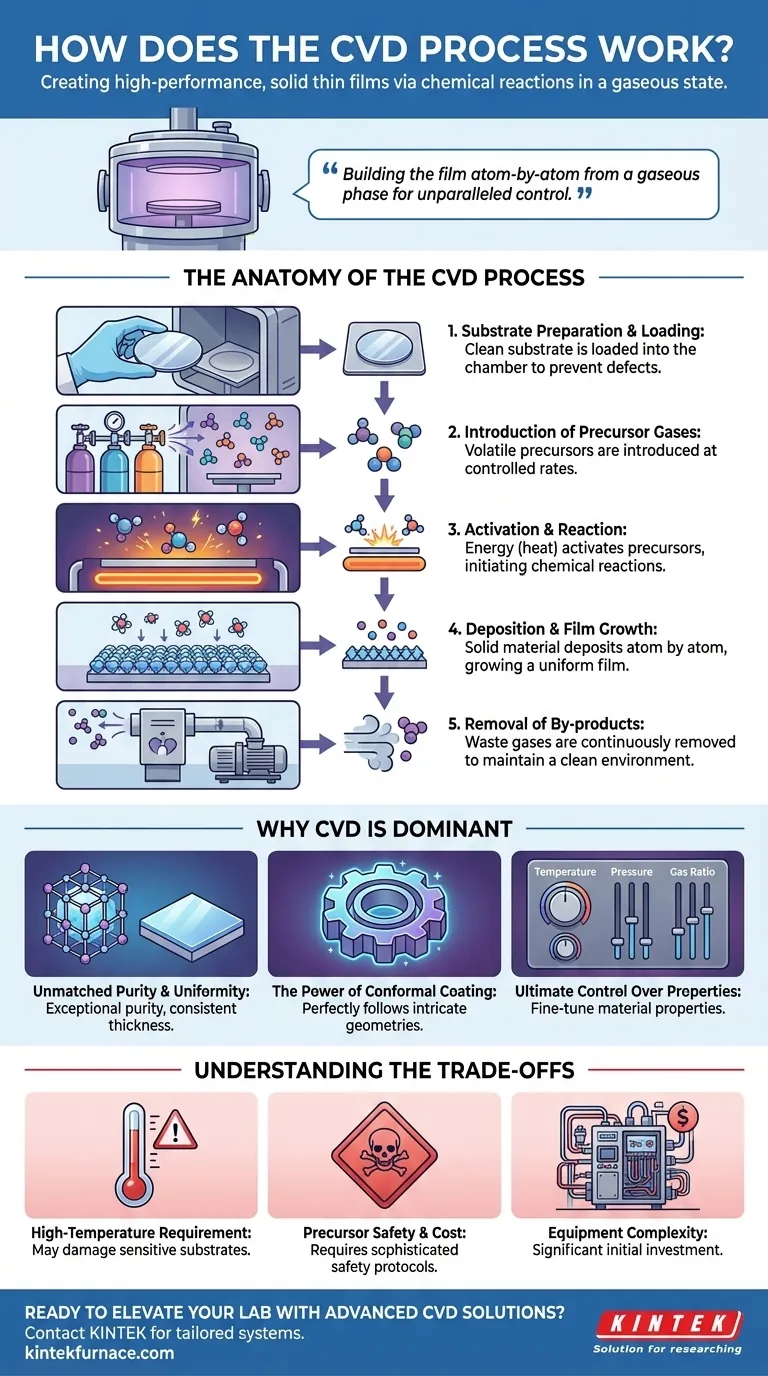
The Anatomy of the CVD Process
To truly understand CVD, it's best to view it as a sequence of carefully controlled events. Each step is critical for the formation of a high-quality film.
Step 1: Substrate Preparation and Loading
Before any deposition can occur, the object to be coated, known as the substrate, must be meticulously cleaned. Any surface contaminants will lead to defects in the final film. The clean substrate is then placed inside the CVD reaction chamber.
Step 2: Introduction of Precursor Gases
The chamber is typically brought to a specific pressure, often a vacuum, and heated. Volatile precursor gases, which contain the elements of the desired film, are then introduced into the chamber at a controlled rate.
Step 3: Activation and Reaction
Energy, most commonly heat, is applied within the chamber. This energy "activates" the precursors, causing them to become chemically reactive. Reactions can occur in the gas phase above the substrate or directly on the hot substrate surface itself.
Step 4: Deposition and Film Growth
The chemical reactions produce a solid material that deposits onto the substrate's surface. This process occurs atom by atom, allowing the film to grow in a highly uniform and controlled manner.
Step 5: Removal of By-products
The chemical reactions also create gaseous by-products that are not part of the final film. These waste gases are continuously removed from the chamber by a vacuum system, ensuring a clean deposition environment.
Why CVD is a Dominant Technology
The meticulous nature of the CVD process gives it several powerful advantages that make it essential for industries from semiconductors to aerospace.
Unmatched Purity and Uniformity
Because the film is built from a highly pure gaseous state inside a controlled environment, the final product can achieve exceptional purity levels. This gas-phase transport ensures the material is deposited evenly across the entire substrate, resulting in a film with consistent thickness.
The Power of Conformal Coating
Unlike line-of-sight processes like spray painting or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the precursor gases in a CVD process can reach every exposed surface of a complex, three-dimensional object. This results in a conformal coating that perfectly follows even the most intricate geometries.
Ultimate Control Over Material Properties
By precisely adjusting the process parameters—such as temperature, pressure, and the ratio of precursor gases—engineers can fine-tune the film's properties. This allows for the creation of customized materials with specific characteristics like hardness, electrical conductivity, or optical transparency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is without its limitations. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging the challenges associated with CVD.
The High-Temperature Requirement
Traditional thermal CVD often requires very high temperatures (several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius). This can damage or destroy thermally sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain electronic components.
Precursor Safety and Cost
The precursor gases used in CVD can be highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates sophisticated safety protocols, handling systems, and exhaust management, which adds to the operational complexity and cost.
Equipment Complexity
CVD reactors are complex machines that require precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow. The need for vacuum systems, heating elements, and safety interlocks makes the initial equipment investment significant.
Is CVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Your decision to use CVD should be based on a clear understanding of your primary technical goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film quality and purity: CVD is the gold standard for applications like semiconductor manufacturing and high-performance optical coatings where material perfection is non-negotiable.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates: You must consider lower-temperature variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) or explore alternative methods entirely.
- If your goal is to coat complex, 3D shapes uniformly: The conformal nature of CVD makes it a vastly superior choice over line-of-sight deposition methods.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can make an informed decision about whether Chemical Vapor Deposition aligns with your project's technical and operational requirements.
Summary Table:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Substrate Preparation | Clean and load the object to be coated into the chamber to prevent defects. |
| 2. Gas Introduction | Introduce precursor gases at controlled rates under specific pressure and temperature. |
| 3. Activation | Apply energy (e.g., heat) to make gases reactive for chemical reactions. |
| 4. Deposition | Solid material deposits atom by atom, growing a uniform film on the substrate. |
| 5. By-product Removal | Remove waste gases via vacuum to maintain a clean environment. |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with advanced CVD solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior film quality, purity, and conformal coatings. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















