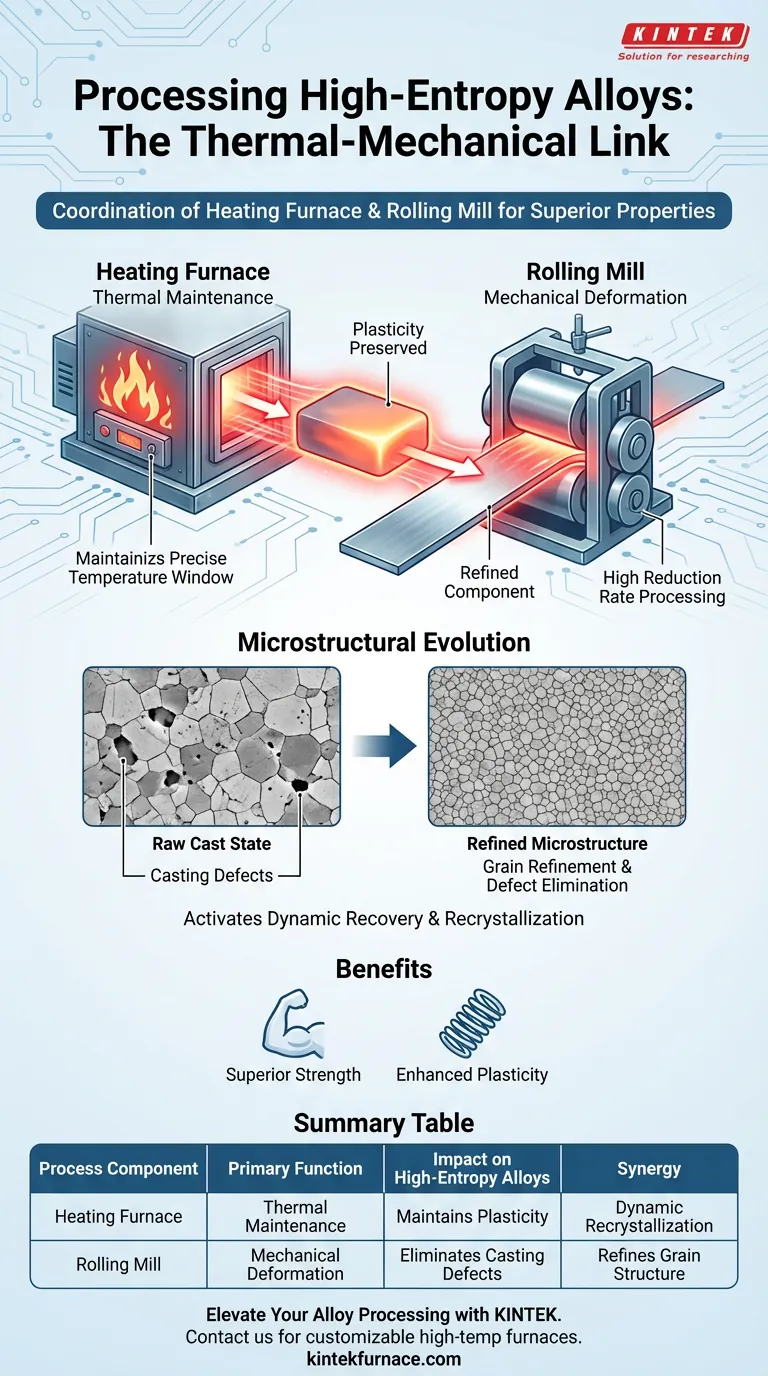
The coordination between a heating furnace and a rolling mill acts as the foundational thermal-mechanical link in processing high-entropy alloys. The furnace is responsible for holding the alloy within a precise temperature window to maintain necessary plasticity, while the rolling mill exploits this thermal state to apply high reduction rate processing. Together, they transform the material from a raw cast state into a refined, high-performance structural component.
This synchronized process does more than simply shape the metal; it fundamentally alters its microstructure. By triggering dynamic recovery and recrystallization, this coordination eliminates casting defects and refines grain structures, resulting in a material that exhibits both superior strength and enhanced plasticity.

The Mechanics of the Coordination
To understand how high-entropy alloys achieve their superior properties, one must look at how thermal energy and mechanical force interact during the rolling process.
The Critical Role of the Heating Furnace
The primary function of the heating furnace is thermal maintenance. It is not enough to simply heat the alloy; the furnace must keep the material within a specific temperature range.
By maintaining this precise thermal environment, the furnace preserves the alloy's plasticity. This ensures the material is soft enough to undergo significant deformation without fracturing, setting the stage for the mechanical work to follow.
The Function of the Rolling Mill
Once the furnace establishes the correct plasticity, the rolling mill performs the heavy lifting. The mill is designed to execute high reduction rate processing.
Because the alloy is thermally prepped, the mill can apply immense pressure to drastically reduce the material's thickness. This aggressive mechanical deformation is the physical driver that forces the internal structure of the alloy to evolve.
Microstructural Evolution
The physical cooperation between the furnace and the mill drives specific metallurgical phenomena that enhance the alloy's quality.
Dynamic Recovery and Recrystallization
The combination of heat (from the furnace) and deformation energy (from the mill) activates dynamic recovery and recrystallization processes.
These internal mechanisms reorganize the crystal lattice of the alloy while it is being worked. This dynamic restructuring is essential for relieving internal stresses and preventing premature failure during processing.
Eliminating Casting Defects
Raw high-entropy alloys often contain imperfections inherent to the casting process. The coordinated processing effectively eliminates these casting defects.
The high reduction rates crush voids and homogenize the structure, resulting in a denser, more reliable material.
Grain Refinement and Property Enhancement
The ultimate goal of this coordination is grain refinement. The process breaks down coarse grains into finer structures.
This structural refinement leads to a dual improvement in mechanical properties: it significantly enhances both the strength and plasticity of the final product.
Understanding the Operational Constraints
While this coordination is powerful, it relies heavily on maintaining a delicate balance between thermal and mechanical inputs.
The Temperature-Plasticity Dependency
The process is strictly bound by the specific temperature range mentioned earlier. If the coordination fails and the temperature drops below this window, plasticity is lost.
Without adequate plasticity, the rolling mill cannot perform high reduction processing effectively. This could lead to incomplete recrystallization or the inability to eliminate casting defects, compromising the final mechanical properties.
Optimizing the Processing Strategy
To maximize the benefits of processing high-entropy alloys, you must view the furnace and mill not as separate tools, but as a single, integrated system.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure the rolling mill applies sufficient reduction rates to fully trigger dynamic recrystallization and close casting porosities.
- If your primary focus is Formability: Prioritize the furnace's ability to maintain the alloy strictly within the temperature range that maximizes plasticity during deformation.
Success depends on the precise synchronization of heat to soften the structure and force to refine it.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Primary Function | Impact on High-Entropy Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Furnace | Thermal Maintenance | Maintains plasticity within a precise temperature window |
| Rolling Mill | Mechanical Deformation | Executes high reduction rates to eliminate casting defects |
| Synergy | Dynamic Recrystallization | Refines grain structure for superior strength and plasticity |
Elevate Your Alloy Processing with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when managing the delicate thermal-mechanical balance required for high-entropy alloys. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique processing needs.
Ready to achieve superior grain refinement and structural integrity? Contact our technical experts today to find the ideal thermal solution for your lab or production line.
Visual Guide
References
- Yukun Lv, Jian Chen. Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying. DOI: 10.3390/ma17020529
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are inert gases like nitrogen and argon used in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- Why is a controlled oxygen environment necessary for high-entropy alloy powders? Master HEA Oxidation & Phase Purity
- What are the common gases and vapors used in furnace atmospheres and their roles? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are the cost considerations when using argon in heat treatment? Maximize Savings and Quality
- What is the function of a controlled atmosphere in Violet Phosphorus research? Achieve High-Purity Material Restoration
- What are the typical applications of an atmosphere furnace? Unlock Precision in Metal and Material Processing
- What types of gases are commonly used in atmosphere furnaces and what are their purposes? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Processes
- What is the function of an air annealing furnace? Enhance Ho:Y2O3 Ceramics Transparency and Performance



















