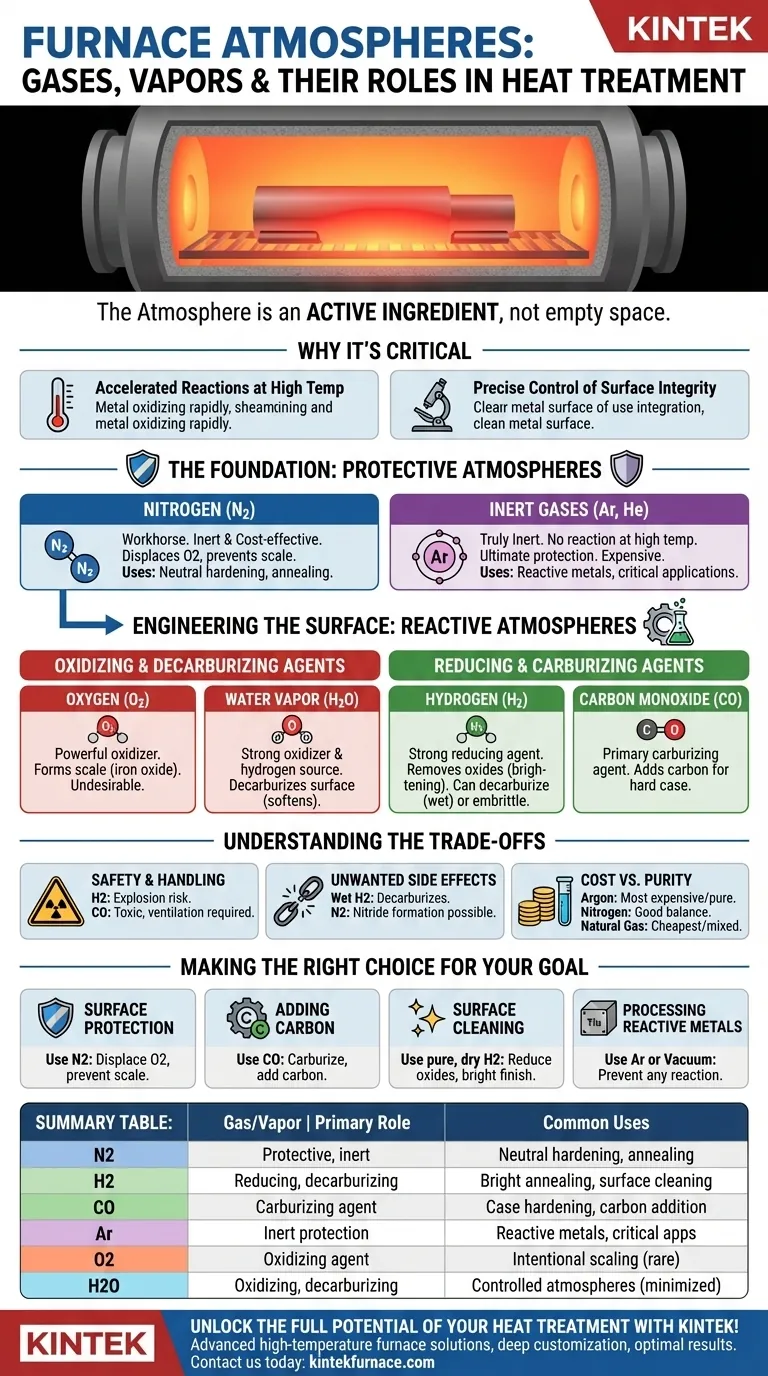
At its core, a furnace atmosphere is a carefully controlled chemical environment designed to interact with a metal's surface during heat treatment. The most common gases used are Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide, Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, and inert gases like Argon, often in mixtures. Their role is to either protect the material from unwanted changes or to deliberately alter its surface chemistry and properties.
The key is to stop thinking of the furnace atmosphere as empty space. Instead, view it as an active ingredient in your metallurgical process, capable of protecting, cleaning, adding, or removing elements from your workpiece's surface.

Why the Furnace Atmosphere is Critical
During heat treatment, elevated temperatures dramatically accelerate chemical reactions. A material that is stable in room-temperature air will rapidly oxidize, or "scale," when heated in that same air.
Controlling the furnace atmosphere allows you to dictate which chemical reactions are allowed to happen, giving you precise control over the final product's surface integrity, hardness, and appearance.
The Foundation: Protective Atmospheres
The most basic function of a controlled atmosphere is to prevent unwanted reactions, primarily oxidation and decarburization.
Nitrogen (N2) Nitrogen is the workhorse of protective atmospheres because it is relatively inert and cost-effective. It displaces oxygen, preventing the formation of oxide scale on the part's surface.
It is widely used for processes like neutral hardening and annealing where the goal is to heat and cool the part without altering its surface chemistry.
Inert Gases (Argon, Helium) Gases like Argon (Ar) are truly inert, meaning they will not react with the metal even at very high temperatures.
While providing the ultimate protection, they are significantly more expensive than nitrogen. Their use is typically reserved for highly reactive metals like titanium or for critical applications where even the slight reactivity of nitrogen is unacceptable.
Engineering the Surface: Reactive Atmospheres
Beyond simple protection, reactive gases are used to intentionally change the surface of the steel. This is where you can add or remove specific elements.
Oxidizing and Decarburizing Agents
These gases are often considered contaminants that must be minimized, but they can be used intentionally in some processes.
Oxygen (O2) Oxygen is a powerful oxidizing agent. Even in small amounts, it reacts with iron to form iron oxide, or scale. Its presence is almost always undesirable in high-quality heat treatment.
Water Vapor (H2O) Often overlooked, water vapor is also a strong oxidizing agent at heat-treating temperatures. It is also a source of hydrogen, which can lead to decarburization—the removal of carbon from the steel's surface, resulting in a soft outer layer.
Reducing and Carburizing Agents
These gases are used to clean the surface or add carbon to it.
Hydrogen (H2) Hydrogen is a strong reducing agent, meaning it actively reverses oxidation. It will react with and remove iron oxides on the surface, a process known as "brightening."
However, hydrogen is also a powerful decarburizing agent in the presence of any moisture, and it can cause hydrogen embrittlement in some high-strength steels.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Carbon Monoxide is the primary gas used for carburizing. It decomposes at the steel's surface, introducing carbon atoms that diffuse into the material to create a hard, wear-resistant case.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace atmosphere involves balancing chemical effectiveness, safety, and cost.
Safety and Handling
Hydrogen (H2) is extremely flammable and presents an explosion risk if not handled with rigorous safety protocols. Carbon Monoxide (CO) is highly toxic and requires atmosphere monitoring and robust ventilation.
Unwanted Side Effects
"Wet" hydrogen (containing water vapor) will aggressively decarburize steel, which is often the opposite of the desired outcome. "Dry" hydrogen is needed to act solely as a reducing agent.
While nitrogen is mostly inert, it can form nitrides on the surface of certain alloy steels, which can be undesirable.
Cost vs. Purity
The cheapest protective atmosphere is generated from combusted natural gas, but it contains a mix of N2, CO, CO2, and H2O that must be carefully balanced. The most expensive and purest is Argon. Nitrogen offers an excellent balance of cost and protective quality for most applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal atmosphere is dictated entirely by the desired outcome of your heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is surface protection (neutral hardening, annealing): Use a nitrogen-based atmosphere to displace oxygen and prevent scale formation.
- If your primary focus is adding carbon (case hardening): Use an endothermic atmosphere rich in Carbon Monoxide (CO) to facilitate carbon transfer into the steel.
- If your primary focus is surface cleaning (bright annealing of stainless steel): Use a pure, dry Hydrogen atmosphere to reduce any existing surface oxides for a bright finish.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals (titanium, exotic alloys): Use a pure inert gas like Argon or perform the process in a high vacuum to prevent any gas-metal reaction.
Mastering heat treatment begins with understanding and controlling the invisible chemical reactions happening inside your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Gas/Vapor | Primary Role | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N2) | Protective, inert | Neutral hardening, annealing |
| Hydrogen (H2) | Reducing agent, decarburizing | Bright annealing, surface cleaning |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Carburizing agent | Case hardening, carbon addition |
| Argon (Ar) | Inert protection | Reactive metals, critical applications |
| Oxygen (O2) | Oxidizing agent | Intentional scaling (rare) |
| Water Vapor (H2O) | Oxidizing, decarburizing | Controlled atmospheres (minimized) |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Heat Treatment with KINTEK!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on surface protection, carburizing, or processing reactive metals, our tailored furnace atmospheres and reliable equipment ensure optimal results, enhanced efficiency, and superior material properties. Don't let uncontrolled reactions compromise your outcomes—contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs and drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















