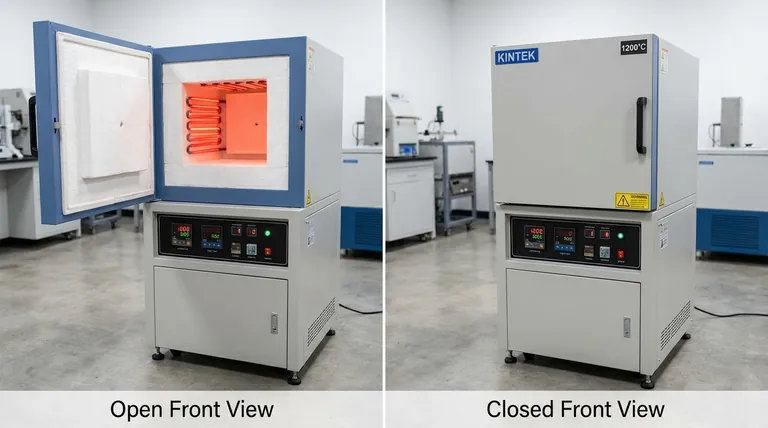
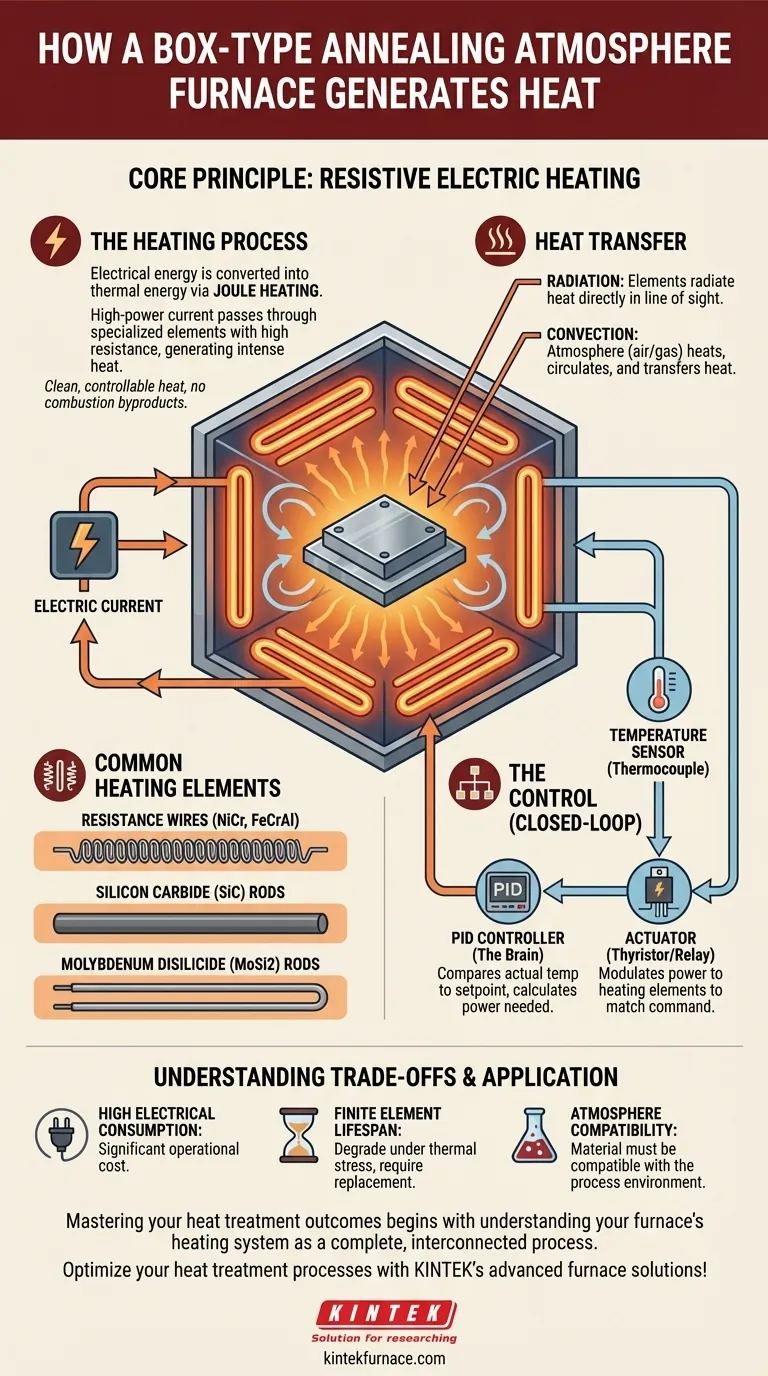
At its core, a box-type annealing atmosphere furnace generates heat through electrical resistance. A powerful electric current is passed through specialized heating elements inside the furnace chamber. As the current encounters resistance from these materials, electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, raising the internal temperature to the precise levels required for annealing or other heat treatments.
The crucial insight is not just how the furnace generates heat, but how it controls it. The system is a precise partnership between high-power electric heating elements and a sophisticated digital control loop that ensures the exact temperature profile required for treating sensitive materials is achieved and maintained.

The Core Principle: Resistive Electric Heating
The entire heating process is governed by a fundamental principle of physics: converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This method provides clean, controllable heat without the byproducts of combustion.
From Electricity to Heat
The furnace operates on the principle of Joule heating. When electricity flows through a conductor, some energy is lost as heat due to the material's electrical resistance. In this type of furnace, this "loss" is the intended effect.
The heating elements are designed to have a specific, high resistance. This ensures that when a large current is applied, they become intensely hot, serving as the primary heat source for the entire chamber.
Common Heating Elements
The choice of heating element depends on the furnace's maximum temperature and the chemical environment. The most common types include:
- Resistance Wires: Typically made from nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, these are used for lower to medium temperature applications.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: These are robust ceramic elements capable of reaching higher temperatures than wire elements and are common in many industrial applications.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Rods: Used for very high-temperature applications, these elements can operate efficiently in air or specific atmospheres, providing rapid heating.
Ensuring Uniformity: Heat Transfer and Element Placement
Generating heat is only half the battle; distributing it evenly is critical for successful material treatment. The furnace is engineered to ensure the workpiece reaches a uniform temperature.
How Heat Reaches the Workpiece
Heat is transferred from the elements to the material through two primary mechanisms:
- Radiation: The hot elements radiate thermal energy in all directions, directly heating any surfaces in their line of sight, including the furnace walls and the workpiece itself.
- Convection: The atmosphere inside the furnace (whether it's air or a controlled gas like nitrogen or argon) heats up, circulates, and transfers thermal energy to the workpiece through convection currents.
Strategic Element Placement
To prevent hot spots and ensure consistent results, heating elements are strategically placed around the furnace chamber. You will typically find them located on the sides, top, and bottom of the heating zone, enveloping the workpiece in a uniform field of thermal energy.
The Brains of the Operation: The Temperature Control System
A box-type furnace's value lies in its precision. This is achieved through a closed-loop control system that constantly monitors and adjusts the heat output.
Sensing the Temperature
A temperature sensor, most often a thermocouple, is placed inside the furnace chamber to provide a real-time measurement of the internal temperature. This sensor acts as the "eyes" of the control system.
Making Decisions with a PID Controller
The sensor's reading is fed to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This digital controller continuously compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint programmed by the operator.
Based on the difference (the error) and the rate of temperature change, the PID algorithm calculates the precise amount of power the heating elements need.
Executing the Command
The controller's decision is sent to an actuator, such as a thyristor regulator or a solid-state relay. This component acts like a sophisticated valve for electricity, modulating the power flowing to the heating elements to precisely match the controller's command.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this heating method has practical considerations that every operator should understand.
High Electrical Consumption
Converting electricity directly to high-temperature heat is an energy-intensive process. These furnaces represent a significant electrical load, which is a primary operational cost.
Finite Element Lifespan
Heating elements operate under extreme thermal stress. Over time, they degrade, oxidize, or become brittle, eventually requiring replacement. They are a key consumable component of the furnace.
Atmosphere Compatibility
The material of the heating element must be compatible with the controlled atmosphere used during the annealing process. An incorrect choice can lead to element failure or, worse, contamination of the furnace atmosphere and the workpiece.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Process
Understanding the heating system empowers you to achieve better results and manage your equipment effectively.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The consistency of your results depends entirely on the precision of the PID controller and the accuracy of your thermocouple.
- If your primary focus is furnace maintenance: Regularly inspect the heating elements for signs of wear, sagging, or discoloration, as they are the most common point of failure.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Uniform heating is paramount. Ensure proper workpiece placement to avoid blocking radiative heat and impeding convective flow.
Mastering your heat treatment outcomes begins with understanding how your furnace's heating system works as a complete, interconnected process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical resistance | Materials: NiCr, FeCrAl wires, SiC, MoSi2 rods; placed for uniform heating |
| Temperature Control | Maintains precise temperature profiles | Uses PID controller with thermocouple sensor and thyristor/relay actuator |
| Heat Transfer | Distributes heat evenly to workpiece | Mechanisms: Radiation and convection; ensures no hot spots |
| Operational Considerations | Factors affecting performance and cost | High electrical consumption, finite element lifespan, atmosphere compatibility |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















