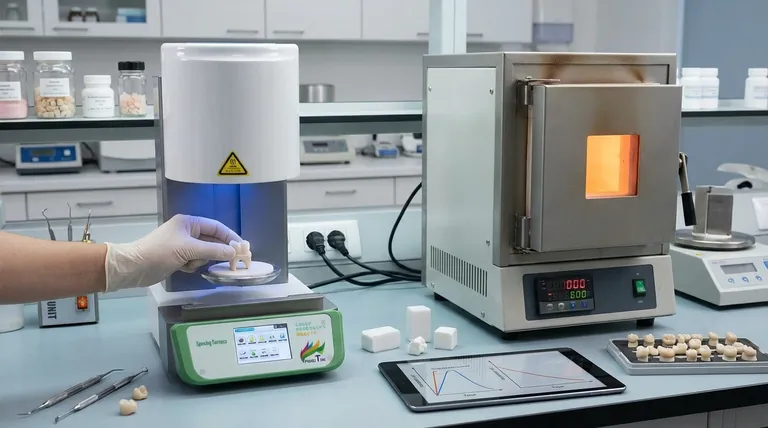
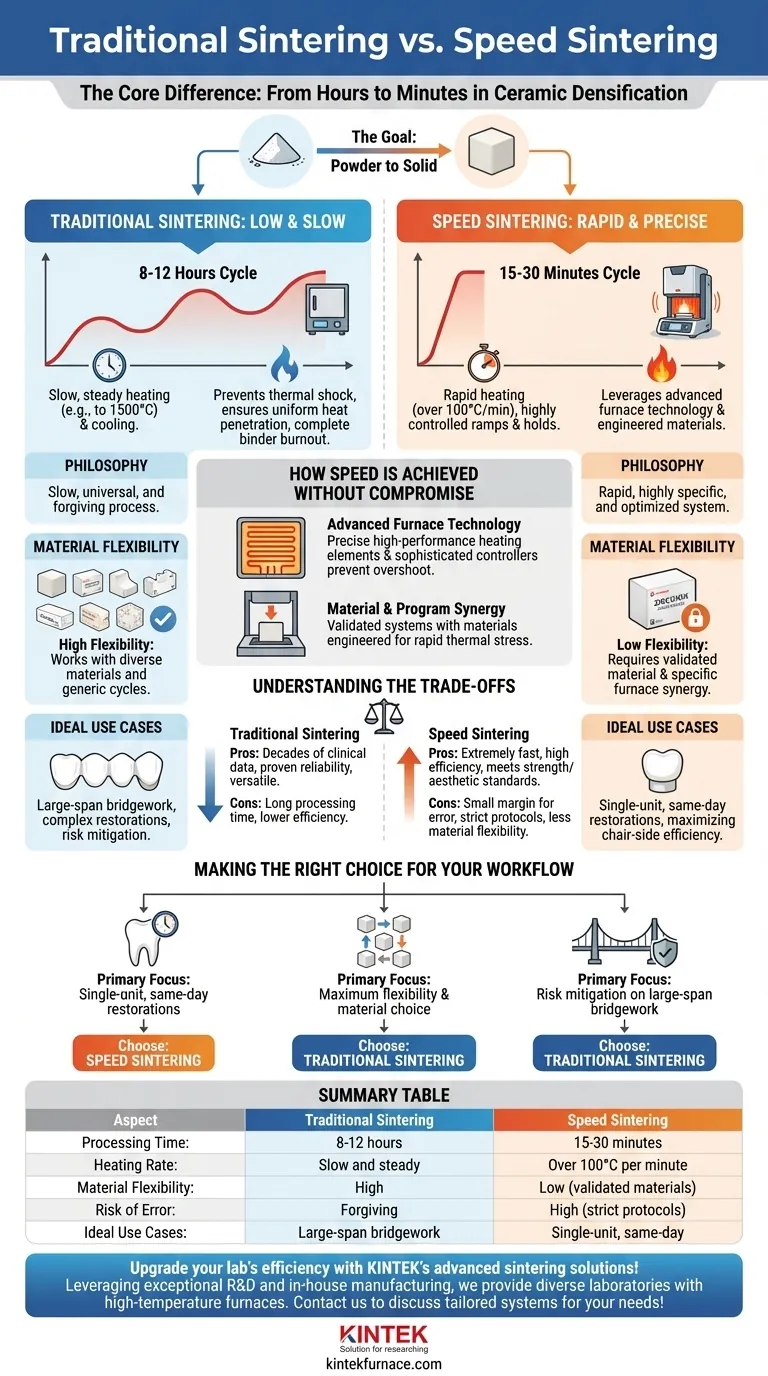
At its core, speed sintering dramatically reduces the processing time required to densify ceramic materials, cutting cycles from many hours down to mere minutes. This is achieved not just by heating faster, but by using highly sophisticated furnaces and precisely engineered heating protocols that are often designed for specific, modern materials like translucent zirconia. While traditional sintering prioritizes a slow, steady process to ensure stability, speed sintering leverages advanced technology to reach the same endpoint without compromising structural integrity.
The fundamental difference is not just time, but philosophy. Traditional sintering is a slow, universal, and forgiving process, whereas speed sintering is a rapid, highly specific, and optimized system that relies on a validated synergy between the furnace, the material, and the heating program.

The Goal: From Powder to Solid
To understand the differences, we must first understand the shared goal. Sintering is a thermal process that fuses particles of a material, like zirconia oxide, into a solid, dense, and strong final object without melting it.
The Traditional Approach: Low and Slow
Traditional sintering is a method proven over decades. It involves a long furnace cycle, often lasting 8 to 12 hours.
The heat is increased very slowly, held at a peak temperature (e.g., 1500°C) for an extended period, and then cooled down just as slowly. This deliberate pace is designed to prevent thermal shock, ensure heat penetrates uniformly throughout the entire restoration, and allow any contaminants or binders to burn out completely.
The Speed Sintering Revolution: Rapid and Precise
Speed sintering achieves the same densification in as little as 15 to 30 minutes. This is made possible by a combination of advanced furnace technology and material science.
These systems use extremely rapid heating rates—sometimes over 100°C per minute—to reach the target temperature quickly. This process is anything but crude; it is a highly controlled protocol with specific ramps and holds engineered for the exact material being used.
How Speed is Achieved Without Compromise
The key question is how speed sintering avoids the cracking and internal stress that would occur if you simply heated a traditional furnace too quickly. The answer lies in the controlled application of intense heat and materials designed to handle it.
Advanced Furnace Technology
Speed-sintering furnaces are fundamentally different from their traditional counterparts. They often use high-performance heating elements (like Silicon Carbide or Molybdenum Disilicide) that can generate intense heat very quickly and precisely.
Sophisticated controllers manage the temperature with extreme accuracy, preventing overshoot and ensuring the material follows the exact prescribed thermal profile.
Material and Program Synergy
Speed sintering is not a universal technique. It relies on a validated system where the material (e.g., a specific brand of zirconia block) is explicitly approved for a specific speed cycle on a specific furnace.
Manufacturers engineer these modern zirconia formulations to withstand the thermal stresses of rapid heating. The sintering program is developed and tested by the manufacturer to guarantee predictable shrinkage, color accuracy, and mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While speed sintering offers tremendous efficiency, it's critical to understand its limitations. It is less a replacement for traditional sintering and more a specialized tool for specific applications.
The Risk of Process Deviation
The margin for error in speed sintering is much smaller. Using a non-validated material or the wrong program can easily lead to a failed restoration, exhibiting low strength, poor aesthetics, or even visible cracks. The system's success is entirely dependent on following the manufacturer's exact protocol.
Reduced Material Flexibility
A traditional furnace can sinter almost any dental zirconia with a generic, slow cycle. A speed furnace, however, is often limited to the specific materials for which it has a validated and pre-programmed rapid cycle. This makes the traditional method more versatile for labs that work with a wide variety of materials.
Long-Term Clinical Data
While short-term tests show that speed-sintered zirconia meets all required strength and aesthetic standards, traditional sintering benefits from decades of clinical data and a long-standing reputation for reliability, especially for large-span or complex restorations. Some clinicians prefer the proven track record of the slower, traditional method for high-stakes cases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Workflow
The choice between speed and traditional sintering is not about which is "better," but which is the right process for your specific goal and workflow.
- If your primary focus is single-unit, same-day restorations: Speed sintering is the definitive choice for maximizing chair-side efficiency and patient satisfaction, assuming you adhere to a validated system.
- If your primary focus is maximum flexibility and material choice: Traditional sintering remains the most robust and forgiving option, allowing you to reliably process a diverse range of materials without being locked into a specific system.
- If your primary focus is risk mitigation on large-span bridgework: Many experienced technicians and clinicians still default to traditional sintering for complex, multi-unit cases to ensure absolute thermal stability and lean on its extensive history of clinical success.
By understanding the principles behind each method, you can confidently select the right tool to meet your specific production and clinical demands.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional Sintering | Speed Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | 8-12 hours | 15-30 minutes |
| Heating Rate | Slow and steady | Over 100°C per minute |
| Material Flexibility | High (works with various materials) | Low (requires validated materials) |
| Risk of Error | Forgiving with deviations | High (strict protocols needed) |
| Ideal Use Cases | Large-span bridgework, diverse materials | Single-unit, same-day restorations |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, whether you're processing zirconia or other materials. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace systems can enhance your sintering processes and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns



















