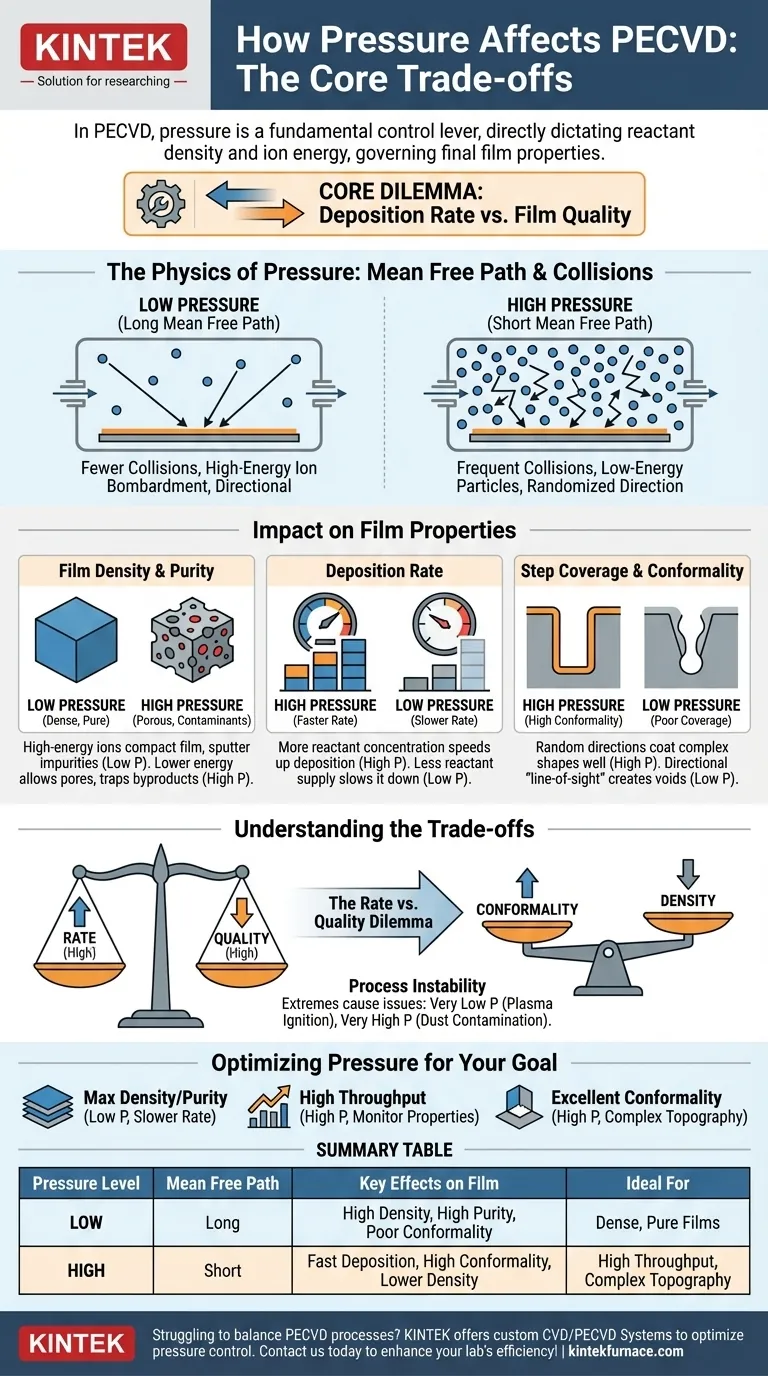
In any PECVD process, chamber pressure is a fundamental control lever. It directly dictates the density of reactant molecules and the energy of ions within the plasma, which in turn governs the final properties of the deposited film. Lowering the pressure increases the distance particles travel before colliding, leading to more energetic ion bombardment that can improve film density, while higher pressure increases the deposition rate but often results in more porous films.
The core dilemma of PECVD pressure control is a trade-off between deposition rate and film quality. High pressure favors faster deposition, while low pressure promotes slower deposition that can yield films with higher density and purity.

The Physics of Pressure: Mean Free Path and Collisions
To control a PECVD process, you must first understand how pressure changes the behavior of particles within the reaction chamber. The central concept is the mean free path.
Defining Mean Free Path
The mean free path is the average distance a particle—be it an ion, an electron, or a neutral gas molecule—travels before it collides with another particle.
Pressure is inversely proportional to the mean free path. As you lower the pressure, you remove particles from the chamber, increasing the average distance between them and thus lengthening the mean free path.
The Impact of Low Pressure (Long Mean Free Path)
At low pressure, reactant molecules and ions experience fewer collisions on their way to the substrate.
This allows ions to accelerate to higher kinetic energies in the plasma sheath before striking the surface. The result is a highly directional, energetic bombardment of the growing film.
The Impact of High Pressure (Short Mean Free Path)
At high pressure, the chamber is crowded with particles, resulting in a very short mean free path.
Ions and reactant precursors collide frequently, losing energy and randomizing their direction of travel. This reduces the energy of particles hitting the substrate and makes their arrival angles much more varied.
How Pressure Directly Impacts Film Properties
Understanding the mean free path allows us to predict how pressure will affect the critical characteristics of your deposited material.
Film Density and Purity
Low-pressure processes produce denser, purer films. The high-energy ion bombardment acts like a microscopic hammer, physically compacting the deposited atoms and sputtering away weakly bonded atoms or impurities.
Conversely, high-pressure processes often result in lower-density films with more contaminants. The lower-energy deposition allows for more porous microstructures and can trap byproducts (like hydrogen in silicon nitride films) within the material.
Deposition Rate
Deposition rate is strongly influenced by the concentration of reactant gases.
Higher pressure means more precursor molecules are available for reaction, which almost always leads to a faster deposition rate. Lowering the pressure reduces the supply of reactants, slowing the process down.
Step Coverage and Conformality
Conformality describes how uniformly a film coats a surface with complex topography, like trenches or steps.
High-pressure processes, with their frequent collisions and randomized particle directions, are superior for achieving high conformality. The reactants arrive from many angles, allowing them to coat sidewalls effectively.
Low-pressure processes are highly directional ("line-of-sight") and typically produce poor step coverage, leading to voids or "keyholes" in deep features.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pressure is not about finding a single "best" setting; it is about managing a series of critical trade-offs.
The Rate vs. Quality Dilemma
This is the most common trade-off. Pushing for a higher deposition rate with increased pressure often comes at the direct expense of film quality, specifically its density and purity.
The Conformality vs. Density Problem
Achieving excellent step coverage requires the random, low-energy deposition characteristic of high pressure. However, achieving high film density requires the energetic bombardment characteristic of low pressure. You must prioritize one over the other.
Process Instability
Extremes in pressure introduce their own problems. Very low pressures can make the plasma difficult to ignite or sustain. Very high pressures can cause precursors to react in the gas phase before reaching the substrate, creating dust particles that contaminate the chamber and the wafer.
Optimizing Pressure for Your Specific Goal
There is no universal pressure setting for PECVD. The optimal parameter depends entirely on the desired outcome for your film.
- If your primary focus is maximum film density and purity: Opt for a lower pressure regime to increase ion bombardment energy, but be prepared for a significantly lower deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and deposition rate: Use higher pressures to increase reactant concentration, but you must monitor film properties like density and stress to ensure they remain within acceptable limits.
- If your primary focus is excellent conformality over complex topography: A higher pressure process is necessary to promote surface-reaction-limited growth and reduce shadowing effects.
Ultimately, mastering pressure control is about consciously balancing these competing factors to achieve your specific film requirements.
Summary Table:
| Pressure Level | Mean Free Path | Key Effects on Film | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Long | High density, high purity, poor conformality | Dense, pure films |
| High | Short | Fast deposition, high conformality, lower density | High throughput, complex topography |
Struggling to balance deposition rate and film quality in your PECVD processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you optimize pressure control for superior film properties. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications



















