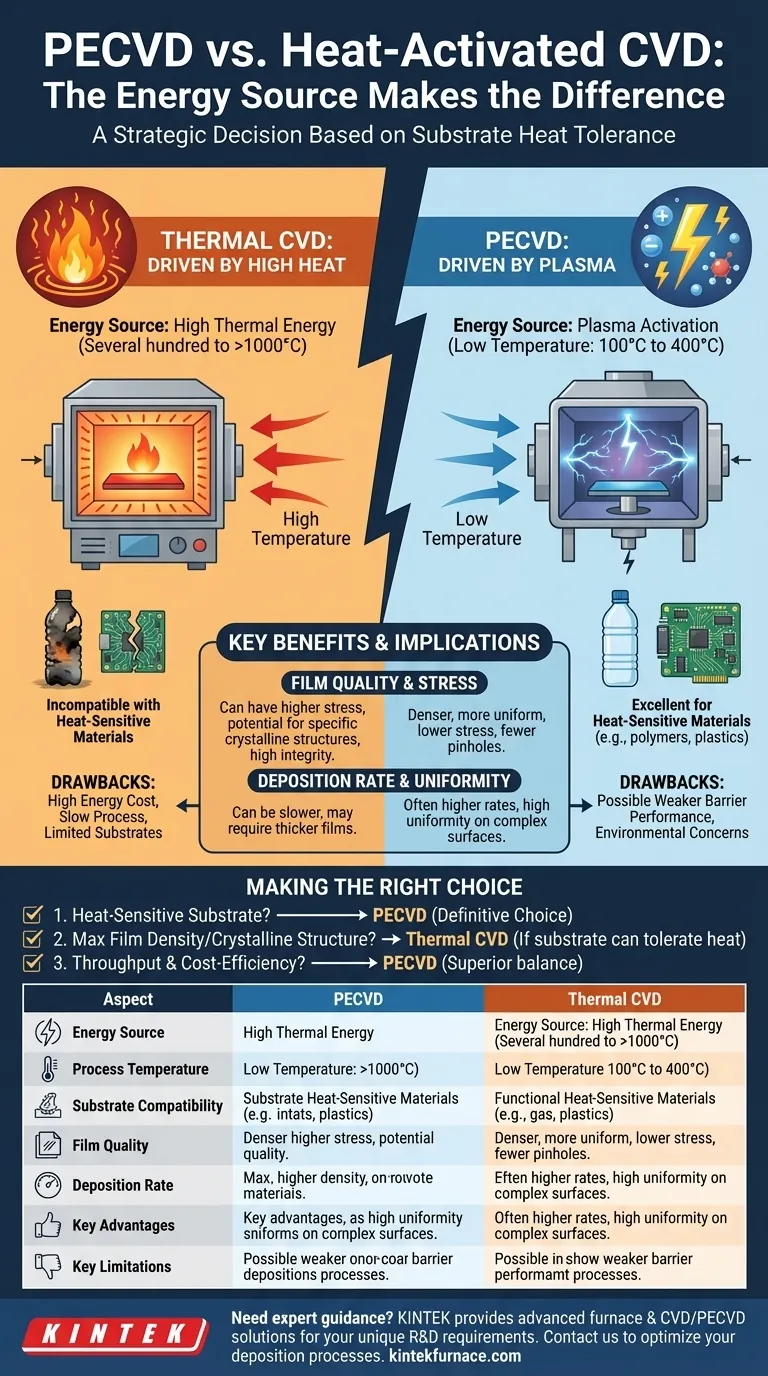
At its core, the difference between Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) and conventional, heat-activated Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the energy source used to drive the reaction. PECVD uses plasma to activate precursor gases at low temperatures, whereas traditional CVD relies exclusively on high thermal energy. This fundamental distinction has profound implications for substrate compatibility, film quality, and operational cost.
The choice between PECVD and thermal CVD is not about which is universally superior. It is a strategic decision based on one critical factor: whether your substrate can withstand the high temperatures required for thermal deposition.

The Core Difference: How Energy is Supplied
The method used to break down precursor gases and deposit a thin film dictates the entire process window, including temperature, pressure, and the resulting film properties.
Thermal CVD: Driven by Heat
Traditional CVD is a thermochemical process. It requires very high temperatures, often ranging from several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius, to provide enough energy to break the chemical bonds of the precursor gases and initiate the deposition reaction on the substrate surface.
PECVD: Driven by Plasma
PECVD introduces an additional energy source: plasma. By applying a strong electric field to the precursor gas, a plasma is formed—an ionized state of matter containing high-energy electrons, ions, and free radicals. These energetic particles, not high heat, are what break down the reactant molecules, allowing the deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures, typically between 100°C and 400°C.
Practical Implications of the Temperature Difference
The dramatic reduction in process temperature with PECVD is its single most important advantage, leading to several key benefits over thermal CVD.
Substrate Compatibility
This is the most critical differentiator. The high heat of thermal CVD makes it incompatible with thermally sensitive materials like polymers, plastics, or certain integrated circuits. PECVD's low-temperature nature makes it the go-to method for depositing films on these types of substrates without causing damage or degradation.
Film Quality and Stress
Because PECVD operates at lower temperatures, it minimizes thermal stress in the deposited film and reduces the risk of lattice mismatch with the substrate. This often results in films that are denser, more uniform, and have fewer pinholes. While thermal CVD can also produce very high-quality films, the high temperatures can introduce significant stress.
Deposition Rate and Uniformity
PECVD often achieves higher deposition rates compared to thermal CVD. Furthermore, because it operates at reduced pressures, the precursor gases can diffuse more easily, leading to more uniform and conformal coatings, even on complex, three-dimensional surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Neither method is a perfect solution. Choosing between them involves understanding their respective drawbacks.
Drawbacks of PECVD
The use of plasma, while beneficial for temperature, can introduce its own set of challenges. Films can sometimes have weaker barrier performance or be softer and have less wear resistance than films deposited by other methods. Additionally, the precursors used, particularly halogenated gases, can pose environmental or health concerns if not handled properly.
Drawbacks of Thermal CVD
The primary drawback of thermal CVD is its high energy consumption and associated cost due to the extreme temperatures required. The process can be slow, and the intense heat can limit the operational life of system components. For some applications, the resulting films may need to be relatively thick (over 10µm) to achieve high integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your application's specific requirements for substrate material, desired film properties, and budget will determine the best deposition method.
- If your primary focus is depositing on heat-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the definitive choice due to its fundamentally low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum film density or specific crystalline structures: High-temperature thermal CVD might be necessary, but only if your substrate can tolerate the intense heat.
- If your primary focus is throughput and cost-efficiency on compatible substrates: PECVD often offers a superior balance of higher deposition rates and lower energy costs.
Ultimately, selecting the right deposition technology comes down to matching the energy source of the process to the thermal and chemical constraints of your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PECVD | Thermal CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Plasma (electric field) | High heat (thermal energy) |
| Process Temperature | 100°C to 400°C | Several hundred to over 1000°C |
| Substrate Compatibility | Excellent for heat-sensitive materials (e.g., polymers, plastics) | Limited to high-temperature tolerant substrates |
| Film Quality | Denser, more uniform, lower stress, fewer pinholes | Can achieve high density, but may have higher stress |
| Deposition Rate | Often higher | Can be slower |
| Key Advantages | Low-temperature operation, high uniformity, conformal coatings | Potential for specific crystalline structures, high film integrity |
| Key Limitations | Possible weaker barrier performance, environmental concerns with gases | High energy cost, slow process, limited to compatible substrates |
Need expert guidance on choosing the right CVD system for your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with heat-sensitive substrates or require high-density films, we can help optimize your deposition processes. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















