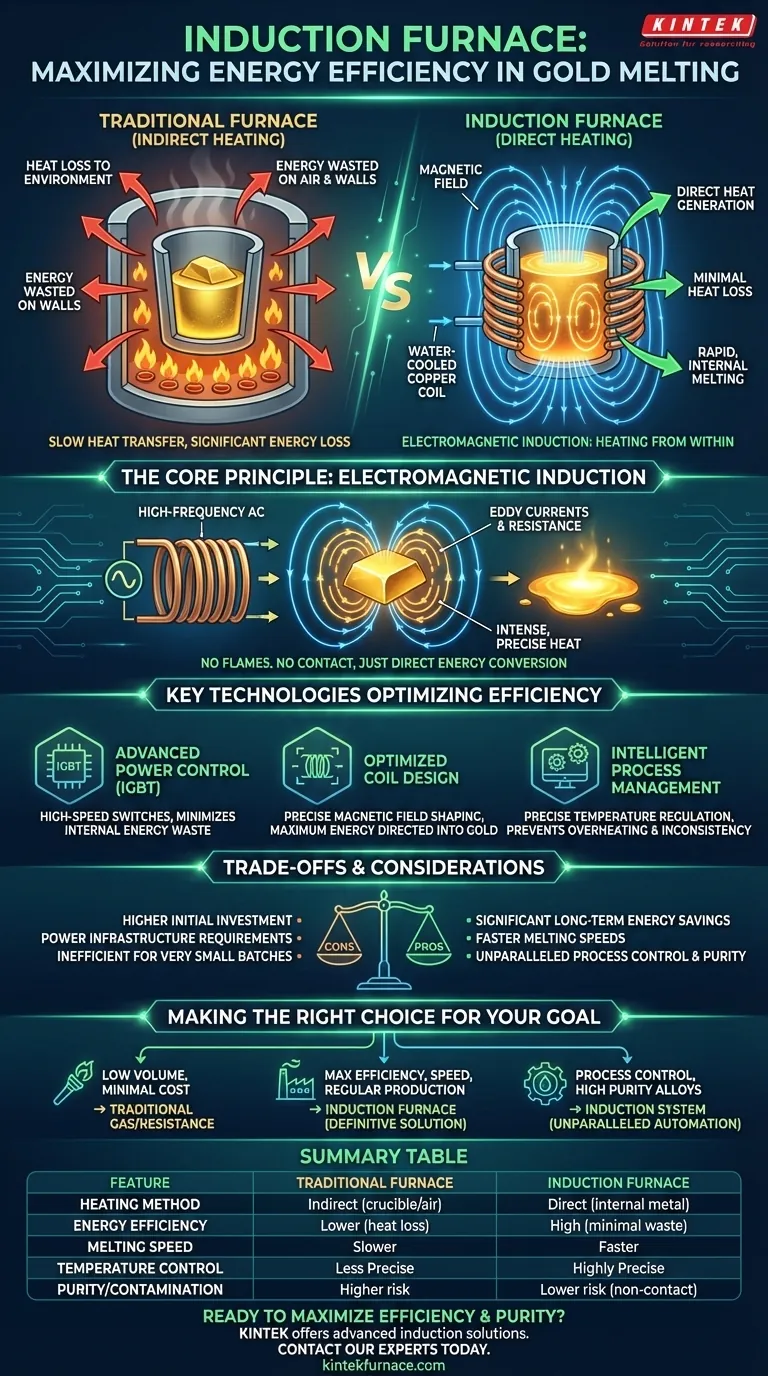
In essence, an induction furnace improves energy efficiency by using a non-contact method to generate heat directly within the gold itself. Unlike traditional furnaces that heat the surrounding air and a crucible to slowly transfer warmth, induction turns the metal into its own heat source, drastically reducing the energy wasted during the process.
Traditional melting wastes significant energy by heating the environment around the metal. Induction technology bypasses this inefficiency by using a magnetic field to make the gold itself the source of the heat, converting nearly all electrical energy directly into the energy needed for melting.

The Core Principle: Heating from Within
The remarkable efficiency of induction melting stems from a fundamental concept in physics: electromagnetic induction. It's a process of heating without flames, external elements, or physical contact.
How Electromagnetic Induction Works
An induction furnace uses a powerful coil made of copper. When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, it creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the crucible holding the gold.
This magnetic field penetrates the gold and induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow directly within the metal. Because gold has natural electrical resistance, the flow of these eddy currents generates intense, precise heat, causing it to melt quickly from the inside out.
Why Direct Heating is More Efficient
In a traditional gas or resistance furnace, energy is spent heating an element or burning fuel. This heat must then travel through the air, into the furnace walls, through the crucible, and finally into the metal. At each step, a significant amount of energy is lost to the surrounding environment.
Induction heating is fundamentally different. It transfers energy with minimal loss because the magnetic field's only job is to create currents in the metal. Almost all the electrical energy is converted directly into heat where it's needed, not in the furnace chamber.
Key Technologies That Maximize Efficiency
Modern induction furnaces integrate several key technologies that build on this core principle to further reduce energy consumption and optimize the melting process.
Advanced Power Control (IGBT)
Modern furnaces use Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) as high-speed power switches. These components are incredibly efficient at converting and controlling the high-frequency electricity needed for induction, minimizing the power that is wasted as heat within the furnace's own electronics.
Optimized Coil Design
The design of the induction coil is critical. It is engineered to shape and focus the magnetic field precisely onto the metal charge. This prevents the magnetic field from "leaking" and inducing wasteful currents in other parts of the furnace, ensuring maximum energy is directed into the gold.
Intelligent Process Management
Advanced control systems provide precise temperature regulation. By constantly monitoring the melt and adjusting power automatically, the furnace uses only the exact amount of energy needed to reach and maintain the target temperature. This prevents wasteful overheating and ensures consistent metallurgical results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly efficient, induction technology is not a universal solution for every context. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Investment Cost
Induction furnaces typically have a higher upfront purchase price compared to simpler gas or resistance-based melting systems. The long-term savings in energy and operational speed must be weighed against this initial capital expenditure.
Power Infrastructure Requirements
These furnaces are powerful electrical devices. Your facility must have an adequate and stable electrical supply to handle the load, which may require an infrastructure upgrade for some smaller workshops.
Batch Size Inefficiency
An induction furnace is designed for a specific range of volumes. Consistently using a large furnace to melt very small quantities of gold can be inefficient, as the system still requires a baseline amount of energy to create the magnetic field.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to adopt induction technology depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is low-volume, infrequent melting with minimal upfront cost: A traditional gas torch or a small resistance furnace may remain a practical choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency, purity, and speed for regular production: An induction furnace is the definitive modern solution that delivers significant long-term cost savings.
- If your primary focus is process control and repeatability for high-value alloys: The automation, precise temperature control, and contamination-free nature of an induction system are unparalleled.
By understanding the principle of direct electromagnetic heating, you can make a strategic investment that pays dividends in efficiency, quality, and operational excellence.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (heats crucible/air) | Direct (heats metal internally) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (significant heat loss) | High (minimal energy waste) |
| Melting Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Temperature Control | Less Precise | Highly Precise |
| Purity/Contamination | Higher risk | Lower risk (non-contact) |
Ready to maximize your gold melting efficiency and purity?
KINTEK's advanced induction furnace solutions leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver unmatched energy efficiency, precise temperature control, and rapid melting speeds for jewelers, refiners, and high-volume producers. Our deep customization capabilities ensure the system is perfectly tailored to your specific batch sizes and operational goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK induction furnace can reduce your energy costs and enhance your production quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















