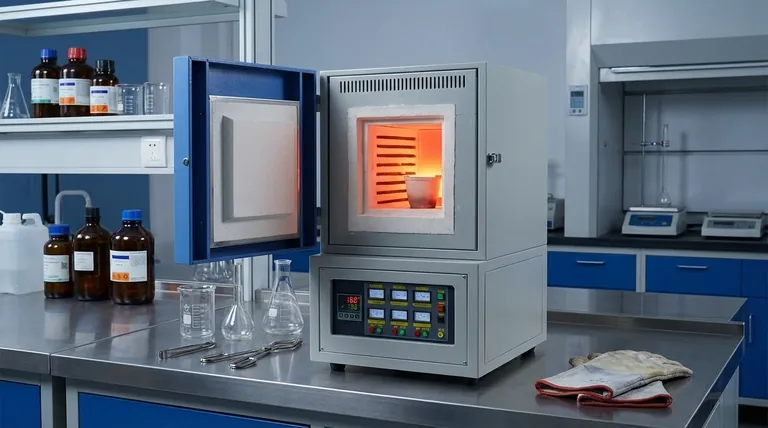
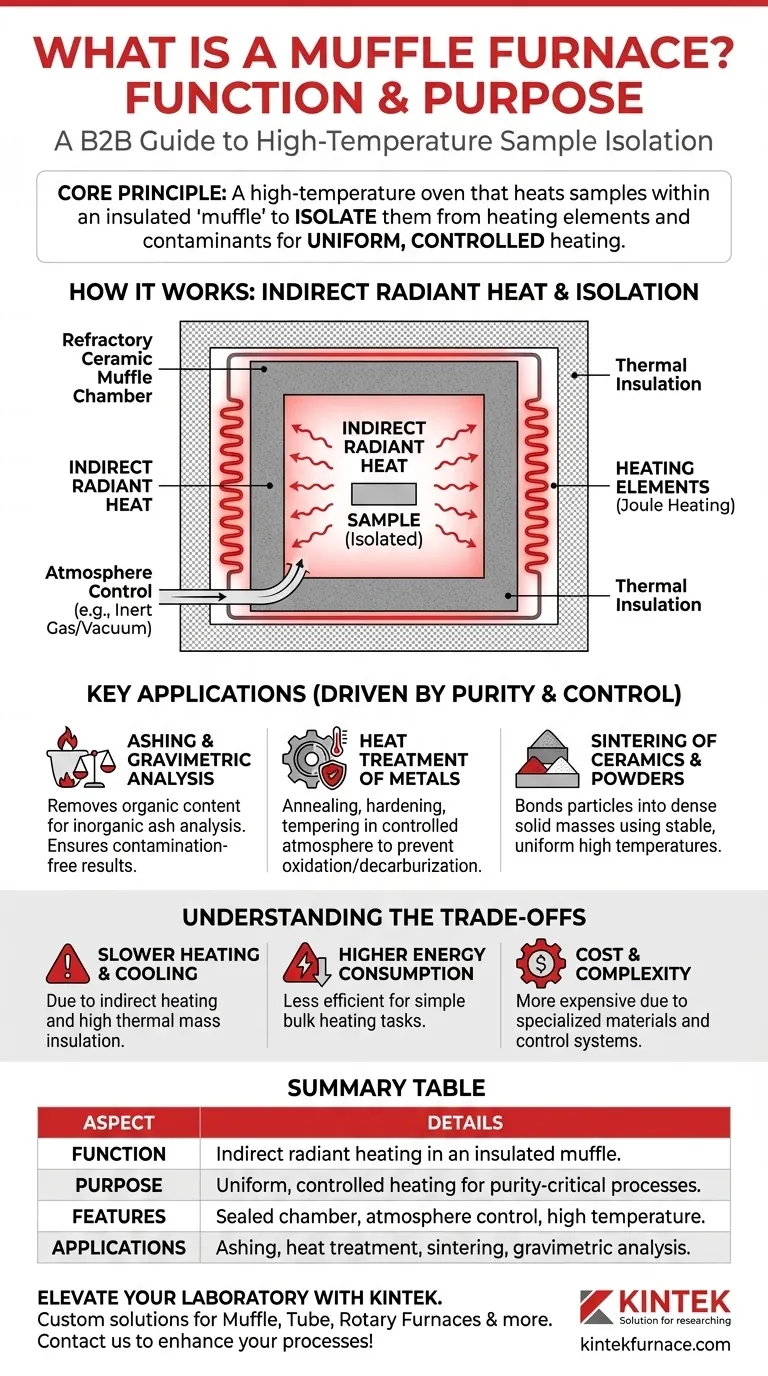
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that functions by heating a sample within an insulated chamber, or "muffle." This design intentionally isolates the material from the heating elements and any external atmospheric contaminants. Its primary purpose is to provide an extremely uniform and controlled heating environment, ensuring that the material is not contaminated by combustion byproducts or direct contact with the heat source itself.
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its method of indirect heating. This separation between the heat source and the sample is what guarantees process purity and temperature uniformity, making it an indispensable tool for sensitive scientific and industrial applications.

The Core Principle: Isolation and Uniformity
A muffle furnace's design is deceptively simple but serves a critical function. Understanding its mechanics reveals why it is chosen over other heating methods.
How It Works: Indirect Radiant Heat
A muffle furnace does not expose the sample to a direct flame or glowing electrical coils. Instead, heating elements (often using Joule heating) heat the walls of the internal chamber.
These superheated chamber walls then radiate thermal energy evenly from all directions toward the sample placed in the center. This indirect, radiant heating is the key to its uniform temperature profile.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The term "muffle" refers to the sealed, high-temperature enclosure that contains the sample. It is typically constructed from refractory ceramic materials that can withstand extreme thermal stress.
This muffle acts as both a heat radiator and a protective barrier, preventing any gases, soot, or particles from the heating elements from reaching and contaminating the sample.
Achieving Controlled Atmospheres
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, it allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere. The chamber can be flooded with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, or a vacuum can be pulled.
This capability is essential for processes that require an oxygen-free or specific reactive environment, which is impossible in a furnace where the sample is exposed to combustion gases or open air.
Key Applications Driven by Purity and Control
The unique design of a muffle furnace makes it essential for applications where the integrity of the sample material is paramount.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
In environmental science and materials testing, ashing involves burning a sample to remove all organic content, leaving only inorganic ash for analysis.
A muffle furnace ensures that the resulting ash is free from contaminants, providing an accurate measurement of the sample's inorganic composition.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering metals often require precise temperature cycles in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation or decarburization on the metal's surface.
The muffle furnace provides the clean, controlled environment needed to achieve specific metallurgical properties without undesirable surface reactions.
Sintering of Ceramics and Powders
Sintering is the process of forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
A muffle furnace provides the stable, uniform high temperatures required to bond ceramic or metal powders into a dense, coherent object with predictable properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is not always the best tool for every heating task. Its design comes with inherent trade-offs.
Slower Heating and Cooling
Because it relies on indirect heating, a muffle furnace generally takes longer to reach its target temperature compared to a direct-fire kiln. The insulated muffle also retains heat, leading to slower cool-down periods.
Higher Energy Consumption
Heating the entire thermal mass of the insulating muffle chamber is less energy-efficient than applying heat directly to a sample. For simple drying or low-temperature tasks, it can be overkill.
Cost and Complexity
The specialized refractory materials and precise control systems make muffle furnaces more expensive and complex than standard laboratory ovens or simpler kilns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on your process requirements for purity, atmosphere, and temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: For applications like ashing, trace metal analysis, or materials science research, the muffle furnace's contamination-free environment is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere control: For heat-treating sensitive metals, sintering advanced materials, or running reactions in an inert environment, the muffle furnace is the only suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is simple bulk heating: For drying samples, curing coatings, or other tasks where contamination is not a concern, a more energy-efficient and faster standard lab oven is the better tool.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive choice whenever the integrity and purity of your material cannot be compromised by the heating process itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Function | Indirect radiant heating in an insulated chamber (muffle) to isolate samples from contaminants |
| Primary Purpose | Provide uniform, controlled heating for purity-critical applications like ashing and sintering |
| Key Features | Sealed chamber, atmosphere control (inert gas/vacuum), high-temperature capability |
| Applications | Ashing, heat treatment of metals, sintering ceramics, gravimetric analysis |
| Trade-offs | Slower heating/cooling, higher energy use, higher cost compared to standard ovens |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for contamination-free heating and controlled atmospheres. Don't let impurities compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















