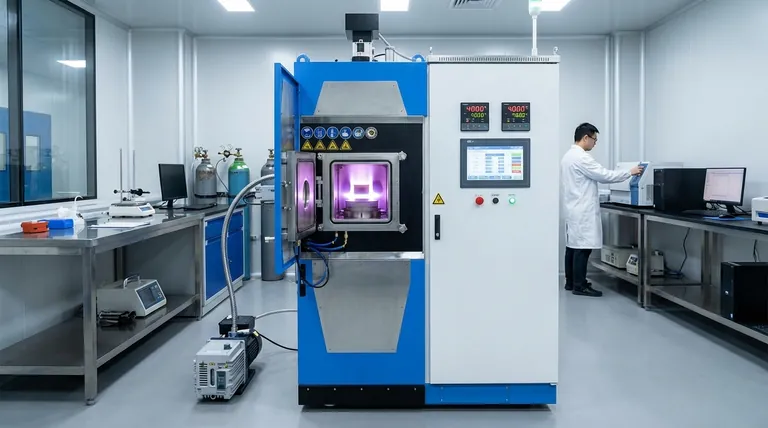
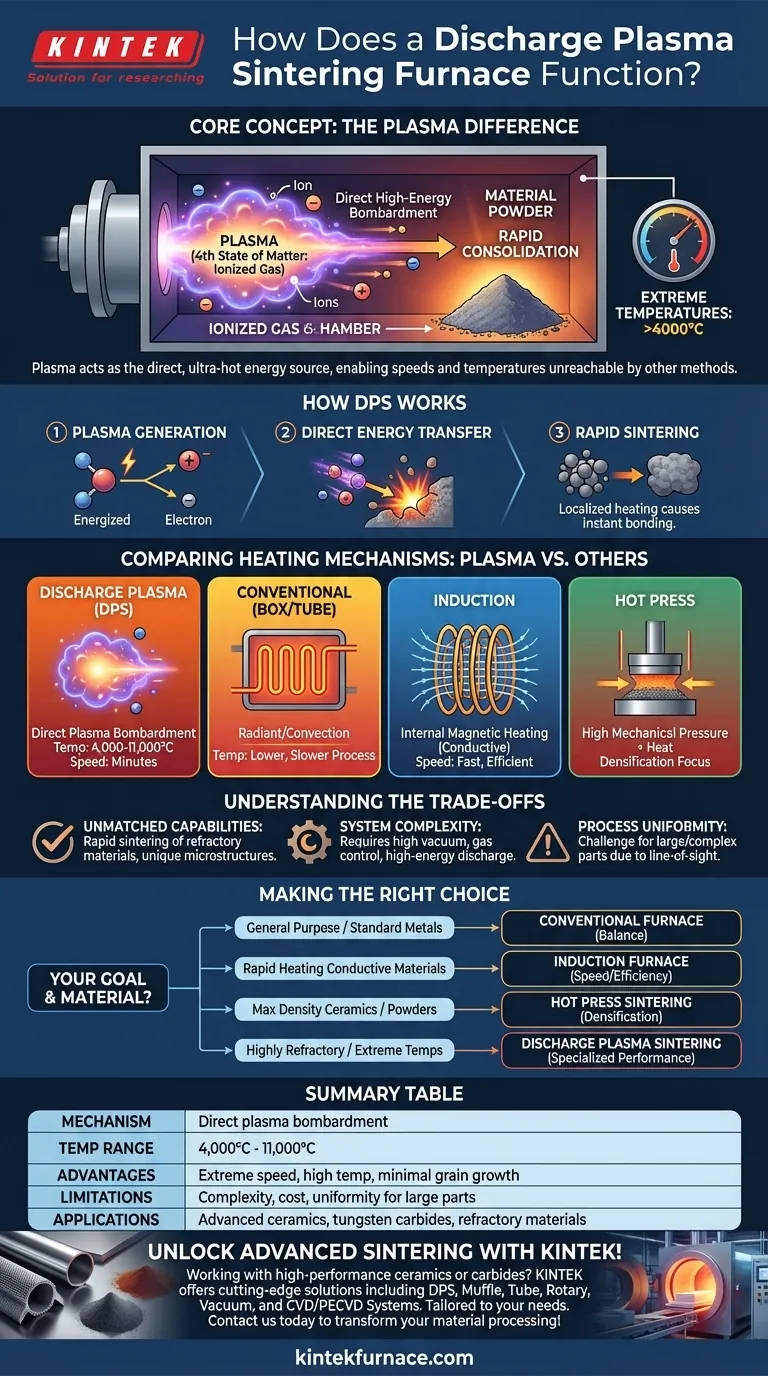
At its core, a discharge plasma sintering furnace uses a superheated, ionized gas—known as plasma—to rapidly heat and consolidate materials. Unlike conventional furnaces that rely on radiant heating elements, this method directly bombards the material with high-energy plasma, achieving exceptionally high temperatures (often exceeding 4000°C) and dramatically shortening the sintering process.
The fundamental difference lies in the heating mechanism. While traditional furnaces heat the chamber environment, and induction furnaces heat the material internally, a discharge plasma furnace uses the plasma itself as the direct, ultra-hot source of energy transfer, enabling speeds and temperatures unattainable by other methods.

How Discharge Plasma Sintering Fundamentally Works
To understand this technology, we must first distinguish its heating source from all other furnace types. Its uniqueness stems from creating and applying the fourth state of matter.
The Role of Plasma
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter, created when a gas is energized to the point where its electrons are stripped from their atoms. The result is a highly activated and ionized gas.
This cloud of ions and electrons is incredibly energetic and serves as the primary tool for heating within the furnace.
The Sintering Mechanism
In a discharge plasma furnace, this plasma is generated within a vacuum chamber and directed at the powdered material being sintered.
The high-energy particles of the plasma collide with the surfaces of the material powder, transferring immense kinetic and thermal energy almost instantaneously. This intense, localized heating causes the particle surfaces to bond and fuse, densifying the material into a solid mass.
The Key Advantage: Extreme Speed and Temperature
The direct energy transfer from plasma allows for heating rates and ultimate temperatures that are far beyond the capabilities of most other furnaces.
Reaching temperatures between 4,000°C and 11,000°C allows for the sintering of highly refractory materials, such as advanced ceramics and tungsten carbides, in minutes rather than hours.
Comparing Heating Mechanisms: Plasma vs. Other Furnaces
The choice of a furnace depends entirely on the material, the desired outcome, and the required process conditions. Understanding how plasma sintering differs from other common methods is key to making an informed decision.
Conventional Furnaces (Box/Tube)
These furnaces operate like a conventional oven. They use electrical resistance heating elements to heat the inside of an insulated chamber.
Heat is transferred to the material indirectly through radiation and convection. This process is slower, less direct, and generally limited to lower temperatures compared to plasma or induction methods.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use a powerful alternating magnetic field to generate heat. This field induces electrical eddy currents directly within a conductive material or a conductive crucible.
The material's own electrical resistance to these currents generates the heat. This is very efficient for conductive materials but is a fundamentally different physical principle than the surface bombardment of plasma.
Hot Press & Pressure Sintering Furnaces
These methods are defined by their use of high mechanical pressure in combination with heat, typically within a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Their primary goal is to physically press powder particles together to aid densification, which is especially effective for materials like ceramics. While plasma sintering can be combined with pressure, its defining feature is its unique heating source, not the application of force.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is universally superior. Discharge plasma sintering offers incredible performance but comes with specific considerations.
The Benefit: Unmatched Capabilities
For processing advanced or refractory materials that will not sinter effectively at lower temperatures, plasma offers a clear advantage. Its speed also enables the creation of novel materials with unique microstructures by minimizing grain growth.
The Challenge: System Complexity
These are not simple machines. A discharge plasma furnace requires sophisticated systems to manage high vacuum, control the process gas, and generate the high-energy electrical discharge needed to create plasma. This complexity translates to higher initial cost and operational expertise.
The Limitation: Process Uniformity
Because the heating is dominated by a direct line-of-sight plasma bombardment, ensuring perfectly uniform temperature across large or complex-shaped parts can be a challenge. It is best suited for applications where intense surface heating is the primary requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sintering Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology requires aligning the tool with the task at hand. Your material and desired outcome are the most important factors.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or sintering standard metals: A conventional box or tube furnace offers the best balance of cost and capability.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating conductive materials: An induction furnace provides excellent speed and efficiency through direct internal heating.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in ceramics or powders: A hot press sintering furnace is specifically designed to use mechanical pressure to eliminate porosity.
- If your primary focus is processing highly refractory materials at extreme temperatures: A discharge plasma sintering furnace is the specialized tool required for the most demanding applications.
Ultimately, choosing the right sintering technology is about matching the heating mechanism to your specific material challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Direct bombardment with high-energy plasma for rapid energy transfer |
| Temperature Range | 4,000°C to 11,000°C, enabling sintering of refractory materials |
| Key Advantages | Extreme speed (minutes vs. hours), high temperatures, minimal grain growth |
| Limitations | System complexity, higher cost, potential non-uniform heating for large parts |
| Ideal Applications | Advanced ceramics, tungsten carbides, and other highly refractory materials |
Unlock the Power of Advanced Sintering with KINTEK!
Are you working with high-performance materials like ceramics or carbides that demand extreme temperatures and rapid processing? KINTEK specializes in cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer advanced options including Discharge Plasma Sintering Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, boosting efficiency and innovation in your lab.
Don't let sintering challenges hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your material processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for diffusion bonding? Precision in Atomic Diffusion
- What are the advantages of industrial SPS vs traditional sintering for SiC? Superior Density and Fine-Grain Structure
- What are the process advantages of using SPS for protonic ceramic electrolytes? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What are the technical advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for maraging steel? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for TiC alloys? Preserve Precision and Microstructure



















