At its core, a rotary kiln handles feedstock variations through its fundamental design, which combines continuous mixing with precise, adjustable control over processing time and temperature. The slow, constant rotation tumbles the material, averaging out inconsistencies in size, moisture, and composition, while operators fine-tune process parameters to ensure a consistent final product.
The key to a rotary kiln's flexibility is not just its ability to tolerate varied inputs, but its active mechanism for homogenizing that material through physical tumbling while allowing operators to dynamically adjust thermal and retention parameters.
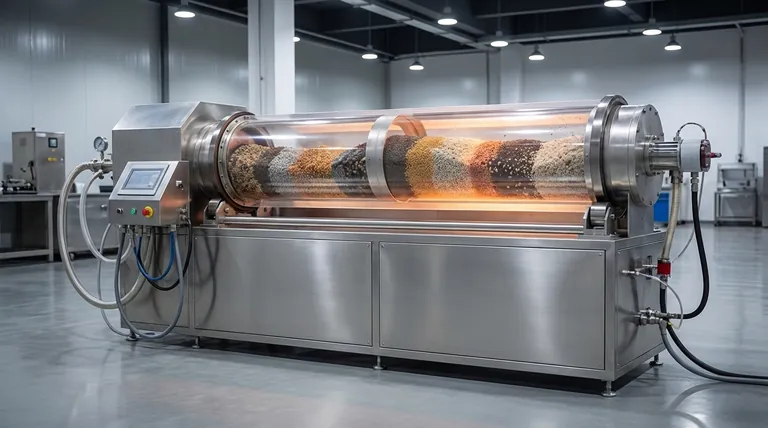

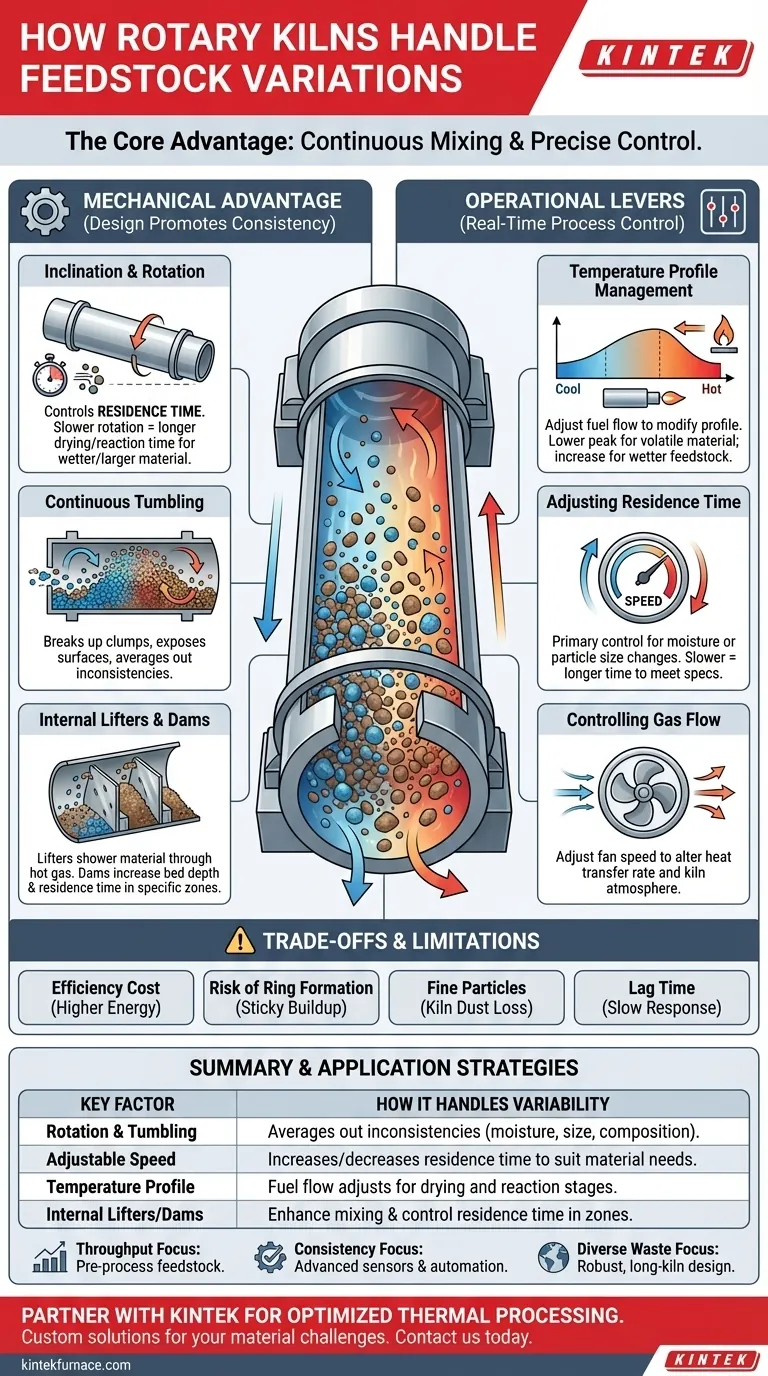
The Mechanical Advantage: How a Kiln's Design Promotes Consistency
A rotary kiln's inherent physical properties are its first line of defense against feedstock variability. These design elements work together to normalize inconsistent material before it ever reaches the hottest zones.
The Role of Inclination and Rotation
The kiln is a long, rotating cylinder set at a slight angle. This inclination, combined with the speed of rotation, directly controls how long the material stays inside—a metric known as residence time.
If a batch of feedstock is wetter or contains larger particles, an operator can simply slow the kiln's rotation. This increases the residence time, giving the material the necessary duration to dry and react completely.
Continuous Tumbling and Mixing
As the kiln rotates, the feedstock is continuously lifted up the side of the shell and then tumbles back down. This constant mixing is the most critical factor in handling variability.
This action breaks up clumps, exposes all particle surfaces to the hot gases flowing through the kiln, and averages out differences in the material bed. It ensures that pockets of wetter material are blended with drier parts, creating a more uniform state.
Internal Lifters and Dams
Many kilns are equipped with internal structures to enhance this mixing. Lifters, or flights, are metal plates that lift material higher before it tumbles, showering it through the hot gas stream and improving heat transfer.
Dams or retaining rings can be installed to increase the depth of the material bed in certain zones. This intentionally increases residence time for a specific process step, like driving off moisture, before the material moves on.
The Operational Levers: Real-Time Process Control
Beyond the kiln's physical design, operators have several powerful tools to compensate for feedstock changes on the fly.
Precise Temperature Profile Management
A kiln doesn't have one single temperature. It maintains a temperature gradient along its length, from cooler at the feed end to hottest at the discharge end near the burner.
Operators can adjust the fuel flow to the burner to modify this profile. If a more volatile material is introduced, they can lower the peak temperature. If a wetter feedstock enters, they can increase fuel to add the energy needed for drying.
Adjusting Residence Time
As mentioned, rotation speed is a primary control. This is the most common adjustment made to compensate for changes in moisture content or particle size, giving the material the time it needs to meet product specifications.
Controlling Gas Flow
The velocity of the hot gas moving through the kiln (typically counter-current to the material flow) is another key variable. Adjusting fan speeds can alter the rate of heat transfer and control the kiln's internal atmosphere, which is critical for specific chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly flexible, a rotary kiln is not a perfect solution for all variability, and pushing its limits comes with consequences.
The Efficiency Cost
The most efficient and cost-effective way to run a kiln is with a stable, predictable feedstock. Constantly adjusting for variations requires more energy and often results in lower overall throughput compared to steady-state operation.
Risk of Ring Formation
Significant variations in feedstock chemistry, particularly with alkali, sulfur, or chloride content, can cause material to become sticky at certain temperatures. This material can adhere to the kiln's refractory lining, creating thick buildups known as "rings" that disrupt material flow and require costly shutdowns for removal.
The Challenge of Fine Particles
Excessive fine particles in the feedstock can become entrained in the fast-moving exhaust gas. This results in material loss, known as "kiln dust," and places a heavier load on the facility's air pollution control systems.
Lag Time in Response
Rotary kilns are massive systems with enormous thermal inertia. A change made by an operator—such as an increase in fuel—can take a long time to stabilize and fully impact the product. This makes compensating for rapid, high-frequency variations extremely difficult.
Applying This to Your Process
Your strategy for managing feedstock should align directly with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Invest in pre-processing your feedstock through blending, crushing, or drying to create a more homogenous input before it ever enters the kiln.
- If your primary focus is absolute product consistency: Implement advanced process controls with sensors (e.g., shell scanners, exit gas analyzers) to automate real-time adjustments to rotation speed and temperature.
- If your primary focus is processing highly diverse waste streams: Prioritize a robust and conservative kiln design with a longer length-to-diameter ratio to guarantee sufficient residence time for even the most difficult materials.
By understanding these mechanical and operational principles, you can leverage the rotary kiln's inherent flexibility to turn material variability from a liability into a manageable part of your process.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | How It Handles Variability |
|---|---|
| Rotation & Tumbling | Averages out inconsistencies in moisture, size, and composition. |
| Adjustable Speed | Increases/decreases residence time to suit material needs. |
| Temperature Profile | Fuel flow can be adjusted to manage drying and reaction stages. |
| Internal Lifters/Dams | Enhance mixing and control residence time in specific zones. |
Struggling with inconsistent feedstock in your thermal processing? Our experts can help you select or customize a rotary kiln solution that turns variability into a manageable asset. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers robust, high-temperature furnaces and systems, all customizable for your unique material challenges. Contact our team today to discuss how we can optimize your process for consistency and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















