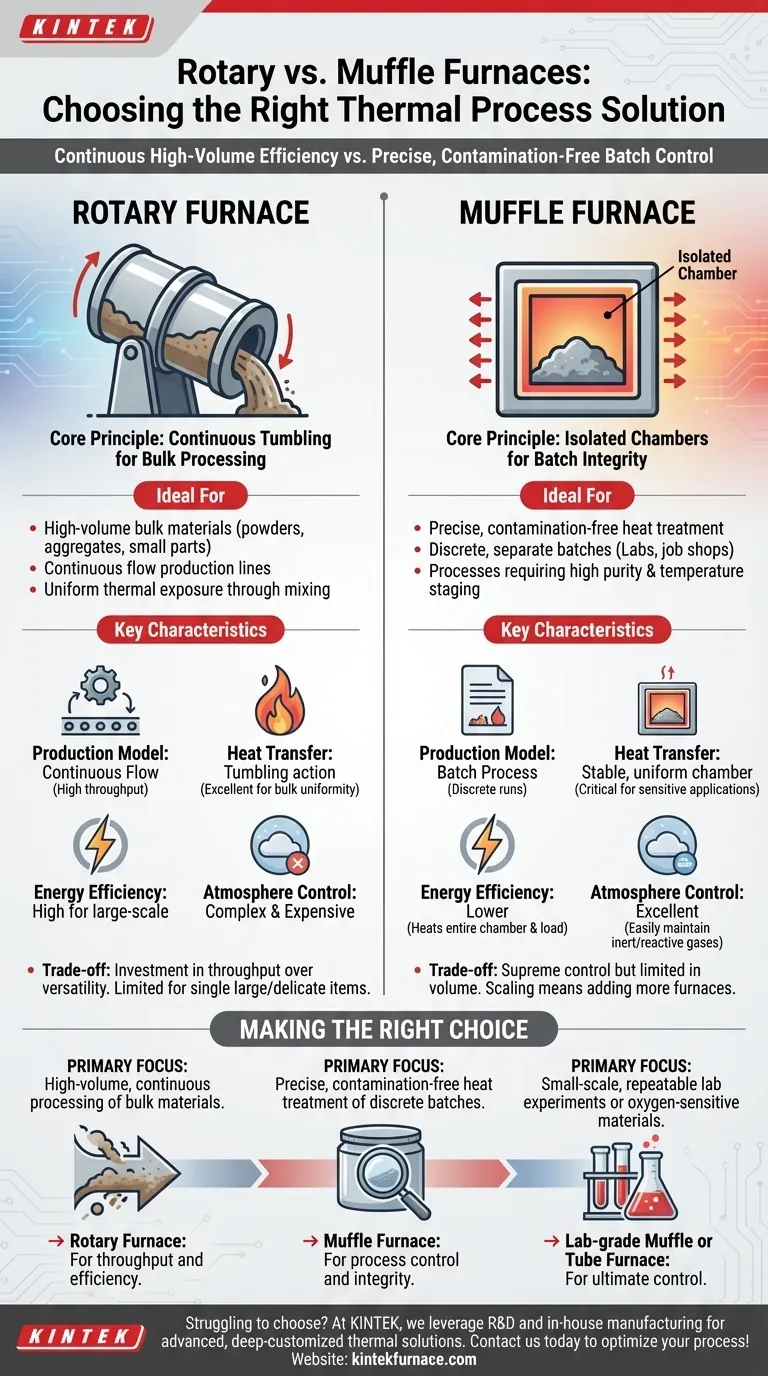
At their core, rotary and muffle furnaces serve fundamentally different operational purposes. A rotary furnace is designed for the continuous, high-volume processing of bulk materials through dynamic tumbling, while a muffle furnace is built for the precise, contamination-free heat treatment of materials in a static, isolated batch environment.
The choice between a rotary and a muffle furnace is not a question of which is "better," but a strategic decision based on your process. You must choose between the high-throughput efficiency of continuous processing and the absolute control and integrity of batch processing.

The Core Operational Difference
To select the right tool, you must first understand how each furnace applies heat. Their designs dictate their ideal applications.
Rotary Furnaces: Continuous Tumbling for Bulk Processing
A rotary furnace operates on a principle of constant motion. Material is fed into one end of a slightly inclined, rotating tube that passes through a heated chamber.
This tumbling action continuously mixes the material, exposing new surfaces to the heat source. Think of it as an industrial-scale clothes dryer, ensuring every granule or part receives uniform thermal exposure. This design is inherently built for continuous flow.
Muffle Furnaces: Isolated Chambers for Batch Integrity
A muffle furnace works on a principle of isolation. The material is placed inside a sealed chamber (the "muffle"), which is then heated from the outside.
The key is that the material never comes into direct contact with the heating elements or combustion byproducts. This "box-within-a-box" design creates a highly stable and clean environment, making it ideal for processes where purity and precise temperature staging are critical. It is inherently a batch process.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The operational differences lead to distinct advantages and disadvantages across several key areas.
Production Model: Continuous vs. Batch
Rotary furnaces are integrated into continuous production lines. Raw material goes in one end, and the processed product comes out the other, enabling high throughput without interruption.
Muffle furnaces handle discrete, separate batches. This is perfect for job shops, laboratories, or production runs where each batch may have unique requirements or requires careful quality control before the next begins.
Heat Transfer and Uniformity
The tumbling action in a rotary furnace provides excellent heat uniformity for bulk materials like powders, aggregates, and small parts.
Muffle furnaces provide extremely stable and uniform temperatures within their enclosed chamber, which is critical for sensitive scientific applications. However, achieving uniformity for a large, static load can be challenging without proper furnace design and air circulation.
Energy Efficiency and Speed
Due to their continuous nature and direct heating of the rotating tube, rotary furnaces are generally more energy-efficient for large-scale production.
Muffle furnaces can be slower to heat up, as you must heat the entire muffle chamber in addition to the workload. This makes them less efficient for rapid, high-volume work but is a necessary trade-off for process control.
Process Atmosphere Control
Muffle furnaces excel at atmosphere control. Because the chamber is sealed and static, it is relatively simple to create and maintain an inert or reactive gas atmosphere, which is crucial for preventing oxidation or enabling specific chemical reactions.
While possible, achieving a perfect seal and controlled atmosphere in a rotary furnace is more mechanically complex and expensive due to the rotating seals at either end of the tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is a universally superior solution. Your choice involves accepting a set of compromises.
The Commitment of a Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace is a commitment to a specific type of high-volume process. It is exceptionally efficient for its intended use—processing bulk solids—but lacks the flexibility to handle a single, large component or a delicate one-off heat treatment. It is an investment in throughput over versatility.
The Limitation of a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace offers supreme control but is inherently limited in volume. Scaling up production means adding more furnaces, not simply increasing the flow rate of one. Its strength in precision becomes a bottleneck for any process demanding continuous, high-volume output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous processing of bulk materials (like minerals, powders, or small parts): A rotary furnace is the clear choice for its throughput and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is precise, contamination-free heat treatment of discrete batches: A muffle furnace provides the process control and integrity you need.
- If your primary focus is small-scale, highly repeatable lab experiments or processing oxygen-sensitive materials: A laboratory-grade muffle furnace or a specialized tube furnace offers the ultimate control.
Understanding the fundamental difference between continuous tumbling and isolated batch heating empowers you to select the furnace that serves as a true asset to your operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Production Model | Continuous flow | Batch process |
| Heat Transfer | Tumbling action for bulk uniformity | Stable, isolated chamber for precision |
| Energy Efficiency | High for large-scale | Lower, suited for controlled environments |
| Atmosphere Control | Complex, expensive seals | Excellent for inert/reactive gases |
| Ideal Use | High-volume bulk materials | Contamination-free, sensitive applications |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab or production needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need high-throughput efficiency or absolute batch control, we can help optimize your thermal processes. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your operations and deliver precise results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















