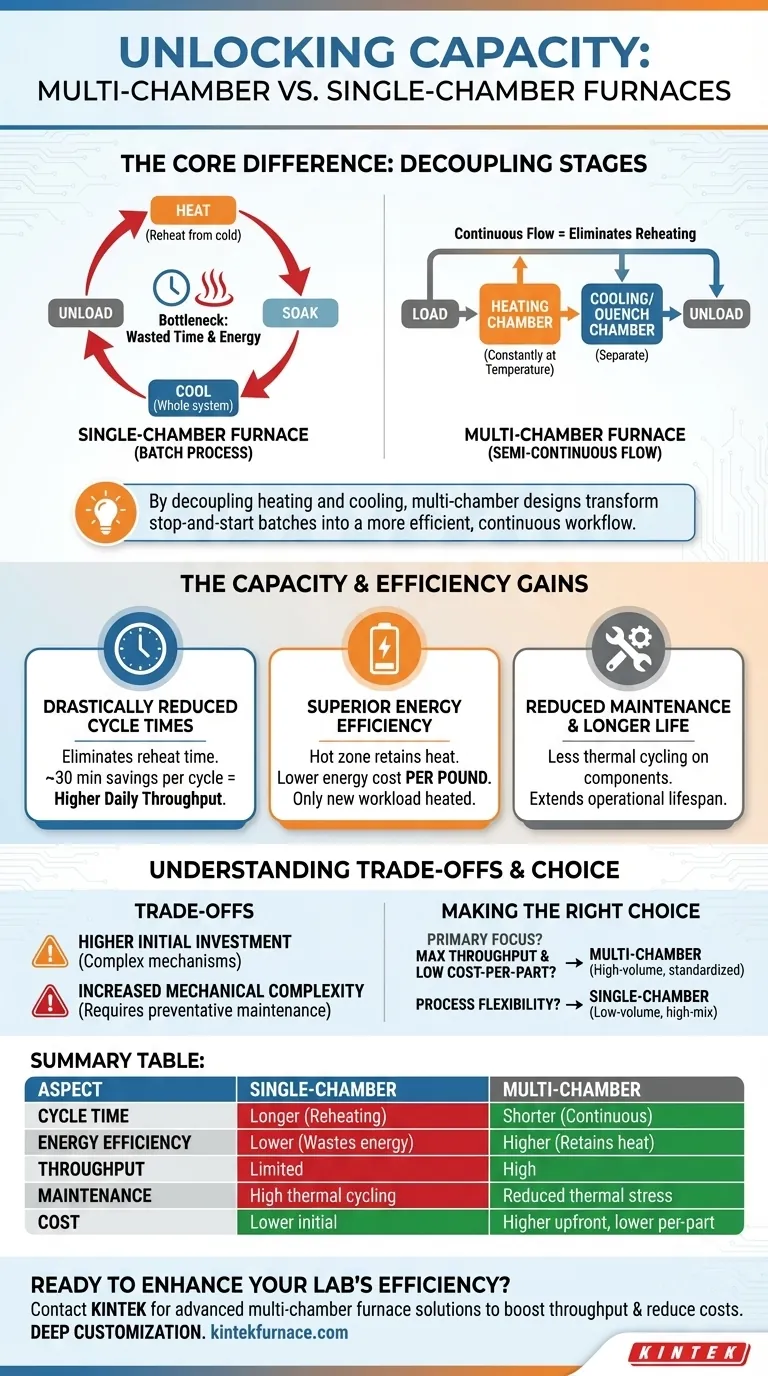
At their core, multi-chamber furnaces achieve significant capacity advantages by physically separating the heating and cooling stages of a thermal process. Unlike a single-chamber furnace that must cool down and reheat between every batch, a multi-chamber design keeps its heating zone constantly at temperature, eliminating a massive bottleneck and allowing for a continuous flow of material. This simple architectural change is the source of its gains in throughput, energy efficiency, and operational lifespan.
By decoupling the heating and cooling processes, a multi-chamber furnace transforms a stop-and-start batch operation into a much more efficient, semi-continuous workflow. This fundamental shift is what unlocks its superior capacity and lower operating costs.

The Core Principle: Decoupling Process Stages
To understand the advantage, you must first compare the workflow of a single-chamber furnace to that of a multi-chamber system.
The Single-Chamber Bottleneck
In a traditional single-chamber (or "batch") furnace, the entire process happens in one place. The workload is loaded, the chamber is heated to the target temperature, the material is soaked, and then the entire system—furnace and workload—is cooled before the next batch can begin.
This cycle creates two major inefficiencies: wasted time and wasted energy. The furnace must be completely reheated for every new load, a process that consumes a significant portion of the total cycle time.
The Multi-Chamber Advantage: A Continuous Flow
A multi-chamber furnace operates more like an assembly line. It typically consists of a loading chamber, a dedicated heating chamber, and a separate cooling or quenching chamber.
The heating chamber is brought to temperature and remains there. A workload moves from the loading area into the hot zone, is processed, and then moves into the separate cooling chamber. While that load cools, the next one can immediately enter the already-hot heating chamber.
Unpacking the Capacity and Efficiency Gains
This continuous-flow model creates a cascade of operational benefits that directly contribute to higher capacity and lower costs.
Drastically Reduced Cycle Times
The most direct advantage is a major reduction in total cycle time per batch. The time spent reheating the furnace structure from a low temperature is completely eliminated.
For example, heating a 1,000-pound load might take 90 minutes in a furnace starting from cold, but only 60 minutes in a pre-heated chamber. This 30-minute savings on every cycle directly translates to higher daily or weekly throughput.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Energy is no longer wasted reheating thousands of pounds of insulation, heating elements, and the steel furnace shell for every batch. The vast majority of thermal energy is retained in the hot zone.
The only significant energy input is that required to heat the new workload (the "charge"). This results in a dramatically lower energy cost per pound of processed material, a critical metric for any high-volume operation.
Reduced Maintenance and Longer Component Life
Thermal cycling—the repeated expansion and contraction from heating and cooling—is a primary cause of wear and failure for furnace components like heating elements, insulation, and structural welds.
Because the heating chamber in a multi-chamber system remains at a stable high temperature, it experiences almost no thermal cycling. This significantly reduces maintenance costs and extends the operational life of the most critical and expensive furnace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the multi-chamber design is not universally superior. Its advantages come with clear trade-offs that must be considered.
Higher Initial Investment
Multi-chamber furnaces are mechanically more complex systems. They involve internal doors, seals, and transfer mechanisms between chambers, leading to a higher upfront capital cost compared to a simpler single-chamber furnace of similar size.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
While thermal-stress maintenance is reduced, mechanical maintenance may increase. The seals, doors, and transport systems that enable the continuous workflow are additional points of potential failure that require a consistent preventative maintenance program.
Best Suited for Standardized Production
The primary benefit of a multi-chamber furnace is realized in high-volume production of similar parts with consistent time and temperature profiles. For a job shop or R&D lab that processes a wide variety of parts with different heat-treat cycles, the flexibility and lower cost of a single-chamber furnace may be more appropriate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing between a single-chamber and multi-chamber furnace depends entirely on your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and low cost-per-part: The multi-chamber furnace is the definitive choice for high-volume, standardized production.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied workloads: A single-chamber furnace provides greater adaptability for low-volume, high-mix environments like job shops or R&D.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational reliability: The multi-chamber design reduces thermal stress on core components but requires diligent maintenance of its mechanical systems.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental design difference empowers you to select the right tool for your specific manufacturing strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Single-Chamber Furnace | Multi-Chamber Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | Longer due to reheating | Shorter with continuous flow |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, wastes energy reheating | Higher, retains heat in hot zone |
| Throughput | Limited by batch processing | High, ideal for standardized production |
| Maintenance | High thermal cycling wear | Reduced thermal stress, longer lifespan |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront, lower per-part cost |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with advanced furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our multi-chamber furnaces can boost your throughput and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control



















