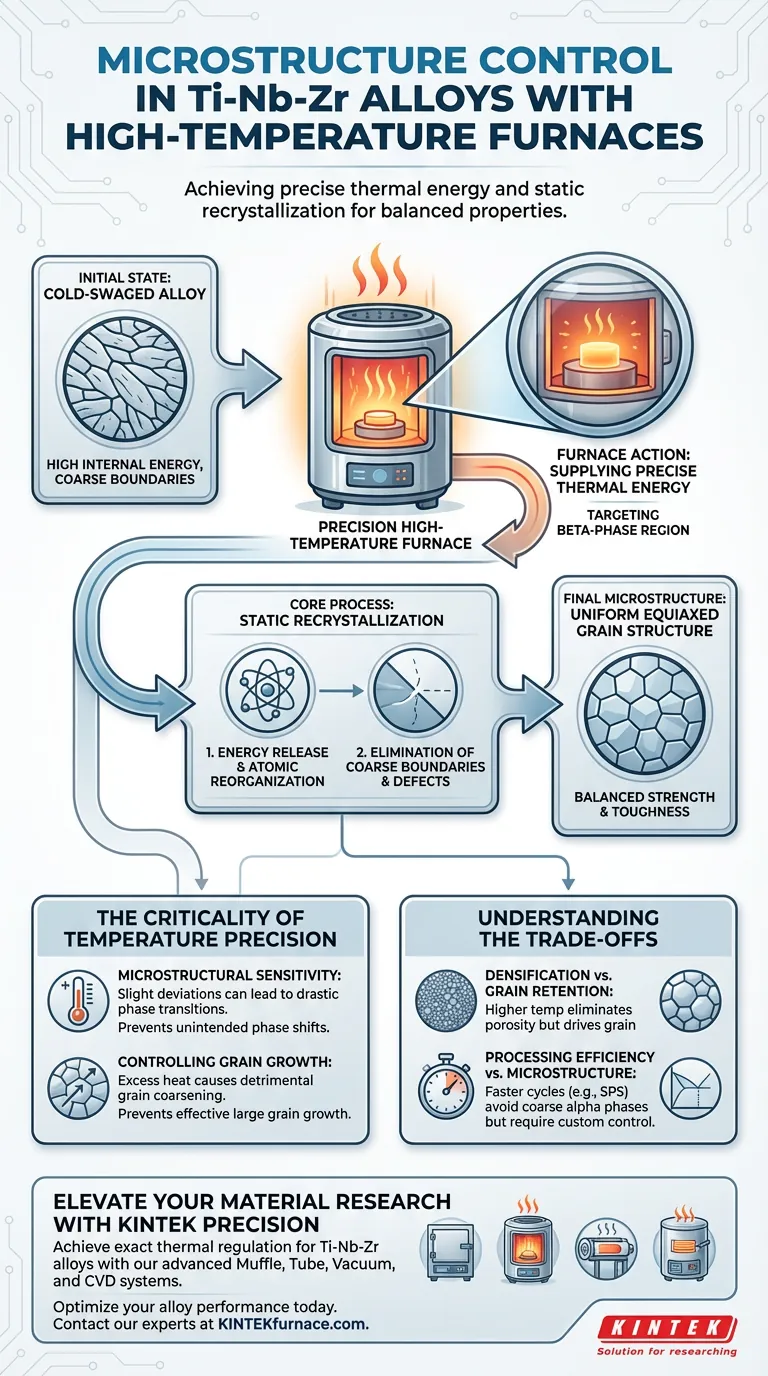
Laboratory high-temperature furnaces achieve microstructure control by supplying the precise thermal energy required to trigger static recrystallization within the alloy. By heating the material specifically within the beta-phase region, these furnaces release the high internal energy stored in cold-swaged structures. This process transforms the material, eliminating coarse parent grain boundaries and resulting in a uniform, equiaxed grain structure that balances strength and toughness.
Core Takeaway The furnace acts as a precision tool for energy release and structural reorganization, not just heating. Its primary role is to induce static recrystallization to replace inconsistent, high-energy cold-worked structures with a homogenized, equiaxed microstructure.
Mechanisms of Structural Transformation
Targeting the Beta-Phase Region
To alter the microstructure of Ti-Nb-Zr alloys effectively, the furnace must reach specific solution treatment temperatures. The objective is to heat the alloy within the beta-phase region. This specific thermal window provides the necessary activation energy to initiate changes at the atomic level.
Triggering Static Recrystallization
Ti-Nb-Zr alloys that have undergone cold swaging possess high internal energy due to deformation. The furnace uses heat to trigger static recrystallization. This mechanism consumes the stored internal energy to nucleate and grow new, defect-free grains.
Eliminating Coarse Boundaries
A critical function of this thermal processing is the removal of structural defects. The recrystallization process effectively eliminates the coarse original parent grain boundaries. Removing these boundaries is essential for preventing premature failure and ensuring consistent mechanical performance.
Optimizing Grain Morphology
Achieving Equiaxed Grains
The ultimate goal of microstructure control in this context is uniformity. Proper furnace control produces a uniform equiaxed grain structure. Unlike elongated or irregular grains, equiaxed grains provide isotropic properties, meaning the material performs consistently regardless of the direction of load.
Balancing Mechanical Properties
Microstructure directly dictates performance. By standardizing the grain structure, the furnace optimizes the balance between strength and toughness. This ensures the alloy is robust enough to resist deformation while remaining ductile enough to absorb energy without fracturing.
The Criticality of Temperature Precision
Managing Microstructural Sensitivity
Titanium-based alloys are extremely sensitive to thermal variations. Even slight deviations in holding temperature can lead to drastic transitions in microstructure types. Precision furnaces prevent unintended phase shifts that could compromise the material's integrity.
Controlling Grain Growth
While heat is necessary for recrystallization, excess heat is detrimental. If the temperature exceeds the optimal window, the material risks grain coarsening. precise regulation ensures the grains recrystallize without growing effectively large, which would reduce the material's yield strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Densification vs. Grain Retention
In thermal processing, there is often a conflict between eliminating defects and maintaining fine grains. Higher temperatures are excellent for eliminating porosity and ensuring full density. However, these same temperatures drive rapid grain growth, which degrades mechanical properties.
Processing Efficiency vs. Microstructure
Techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offer shorter cycles than traditional methods. While faster processing helps avoid the formation of coarse alpha phases, it requires distinct control strategies. The trade-off is often between the speed of the cycle and the ability to customize the microstructure strictly within the beta transus limits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the desired results with Ti-Nb-Zr alloys, align your furnace parameters with your specific mechanical objectives:
- If your primary focus is Strength-Toughness Balance: Target the beta-phase region to induce static recrystallization, ensuring the formation of uniform equiaxed grains.
- If your primary focus is Defect Elimination: select a temperature high enough to remove porosity but strictly capped to prevent grain coarsening.
Success lies in utilizing the furnace not merely as a heater, but as a precise regulator of the alloy's internal energy and phase stability.
Summary Table:
| Transformation Phase | Mechanism Involved | Structural Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Beta-Phase Region | Precise Thermal Activation | Initiation of atomic-level reorganization |
| Recrystallization | Internal Energy Release | Elimination of coarse parent grain boundaries |
| Grain Refinement | Isotropic Morphing | Uniform equiaxed grain structure |
| Property Balancing | Thermal Regulation | Optimized strength and toughness ratio |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect balance of strength and toughness in Ti-Nb-Zr alloys requires more than just heat—it requires exact thermal regulation. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides the advanced Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems necessary for precise microstructure control.
Whether you need to manage grain growth or trigger static recrystallization, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces are engineered to meet your unique research demands. Optimize your alloy performance today—Contact our experts at KINTEK!
Visual Guide
References
- Chan-Byeol Han, Dong‐Geun Lee. Effect of Oxygen on Static Recrystallization Behaviors of Biomedical Ti-Nb-Zr Alloys. DOI: 10.3390/met14030333
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of vacuum sintering furnaces? Essential for High-Purity, High-Strength Components
- How does a Vacuum Oven improve the catalyst drying process? Maximize ECSA and Prevent Thermal Degradation
- How does a vacuum oven improve LaMO3 electrode sheets? Optimize Drying for Peak Electrochemical Performance
- What is the Bell Jar Furnace designed for? Achieve Ultra-Clean Processing for Sensitive Components
- What is the core function of a vertical vacuum furnace in recycling waste magnesium alloys? Purify Magnesium via Vacuum Sublimation
- What is the purpose of a high vacuum welding furnace in cemented carbide and tool manufacturing? Ensure Strong, Contamination-Free Bonds
- Why is a vacuum drying oven utilized for Al2O3/PTFE powder? Prevent Defects and Ensure Composite Density
- What role do the vacuum arc furnace and titanium getter play in refractory medium-entropy alloy production? Mastering Purity & Power



















