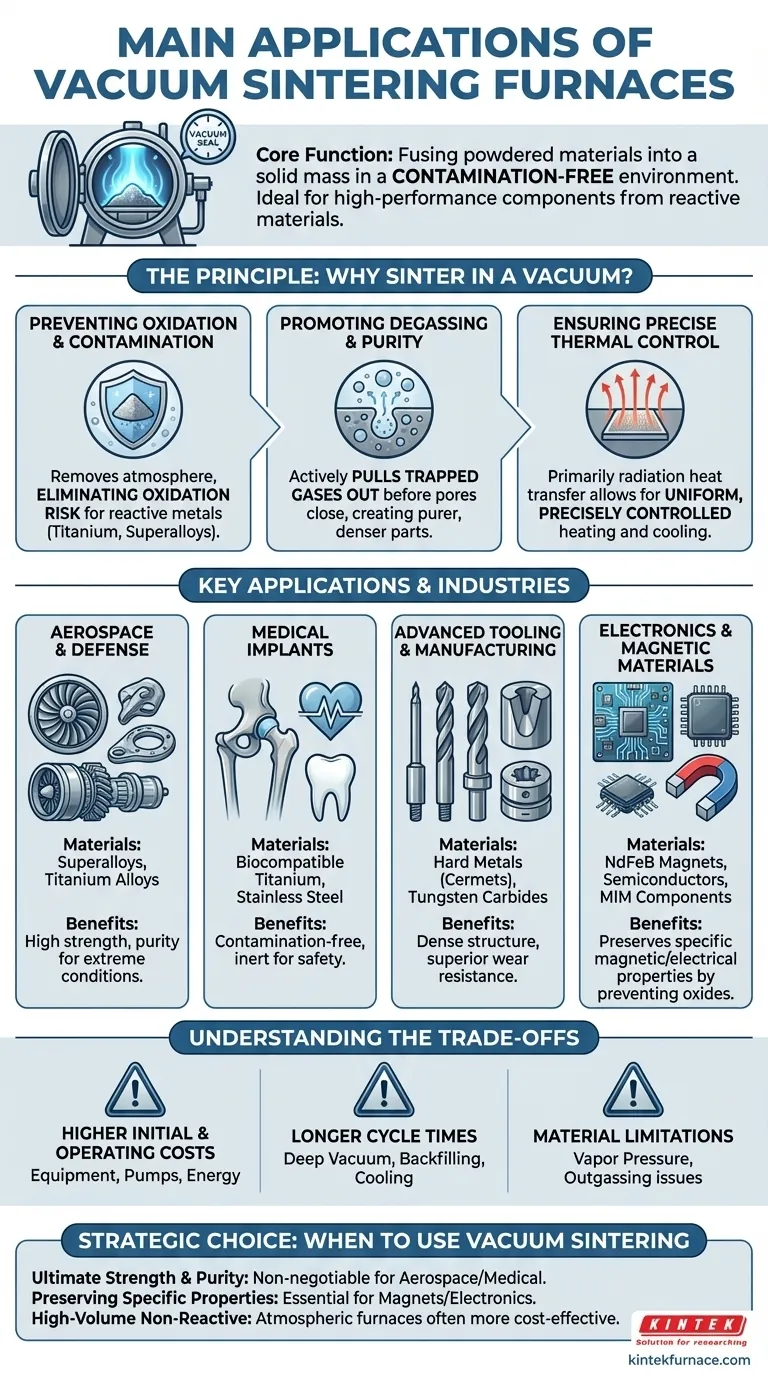
At its core, a vacuum sintering furnace is used to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass in a contamination-free environment. Its primary applications are for producing high-performance components from materials that would be compromised by reacting with air at high temperatures, such as hard alloys, superalloys, reactive metals like titanium, specialized ceramics, and magnetic materials.
The decision to use a vacuum sintering furnace is driven by the material, not just the process. It is the essential tool for creating dense, pure, high-strength parts from materials that are highly reactive or require the removal of trapped gases to achieve their optimal properties.

The Principle: Why Sinter in a Vacuum?
Sintering involves heating compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles to bond and densify. Performing this process in a vacuum solves critical challenges that cannot be addressed in a standard atmospheric furnace.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At elevated sintering temperatures, most metals readily react with oxygen and other gases in the air. This reaction, called oxidation, forms brittle, unwanted layers on the particle surfaces, preventing them from fusing properly.
A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere, eliminating the risk of oxidation. This is non-negotiable for reactive materials like titanium and superalloys, where even minor contamination can lead to catastrophic component failure.
Promoting Degassing and Purity
Powdered materials inherently contain trapped gases on their surfaces and within their pores. If not removed, these gases create voids in the final product, reducing its density, strength, and overall performance.
The vacuum actively pulls these trapped gases out of the part before the pores close, a process known as degassing. This results in a significantly purer and denser final component with superior mechanical properties.
Ensuring Precise Thermal Control
Without air to create convection currents, heat transfer in a vacuum is primarily through radiation. This allows for extremely uniform and precisely controlled heating and cooling cycles.
This level of control is critical for achieving the exact microstructures required for advanced materials used in high-tech applications.
Key Applications and Industries
The need for purity and strength makes vacuum sintering indispensable across several high-value industries.
Aerospace and Defense
Components like turbine blades, engine components, and structural airframe parts are made from superalloys and titanium alloys. These materials must perform under extreme stress and temperature, and vacuum sintering is the only way to guarantee the required purity and strength.
Medical Implants
The human body is highly sensitive to impurities. For medical devices like hip implants, dental roots, and surgical tools made from biocompatible titanium or stainless steel, vacuum processing is mandatory. It ensures the final product is completely inert and free of contaminants that could cause an adverse biological reaction.
Advanced Tooling and Manufacturing
The exceptional hardness and wear resistance of hard metals (cermets) and tungsten carbides are achieved through vacuum sintering. This process creates the dense, void-free structure needed for high-performance cutting tools, dies, and wear parts.
Electronics and Magnetic Materials
Specialized materials like neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets and certain semiconductors require vacuum sintering. The vacuum environment prevents the formation of oxides that would degrade their specific magnetic or electrical properties. This also applies to Metal Injection Molding (MIM) components used in electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not the default choice for every application due to its specific complexities.
Higher Initial and Operating Costs
Vacuum furnaces, with their requisite pumps, seals, and control systems, are significantly more expensive to purchase and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. The process itself is more energy-intensive.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum (pumping down) and carefully backfilling with inert gas for cooling takes considerable time. This results in longer overall production cycles compared to simpler atmospheric heat treatments.
Material Limitations (Vapor Pressure)
Some elements within an alloy can have a high vapor pressure, meaning they tend to turn into a gas under vacuum at high temperatures. This phenomenon, known as outgassing or vaporization, can alter the final composition of the alloy if not properly managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your material requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength and purity for reactive materials: Vacuum sintering is non-negotiable for applications in aerospace, medical, and defense.
- If your primary focus is producing functional magnetic or electronic components: Vacuum sintering is essential to preserve the specific material properties that would be ruined by oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of non-reactive materials (like basic iron powders): A conventional controlled-atmosphere furnace is often a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum sintering furnace is a strategic decision to control the material's environment, thereby guaranteeing its final integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Materials | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Superalloys, Titanium Alloys | High strength, purity for extreme conditions |
| Medical Implants | Biocompatible Titanium, Stainless Steel | Contamination-free, inert for safety |
| Advanced Tooling | Hard Metals, Tungsten Carbides | Dense structure, wear resistance |
| Electronics & Magnets | NdFeB Magnets, Semiconductors | Preserves magnetic/electrical properties |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and performance in your materials? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is enhanced by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum sintering furnaces can elevate your production and ensure superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures



















