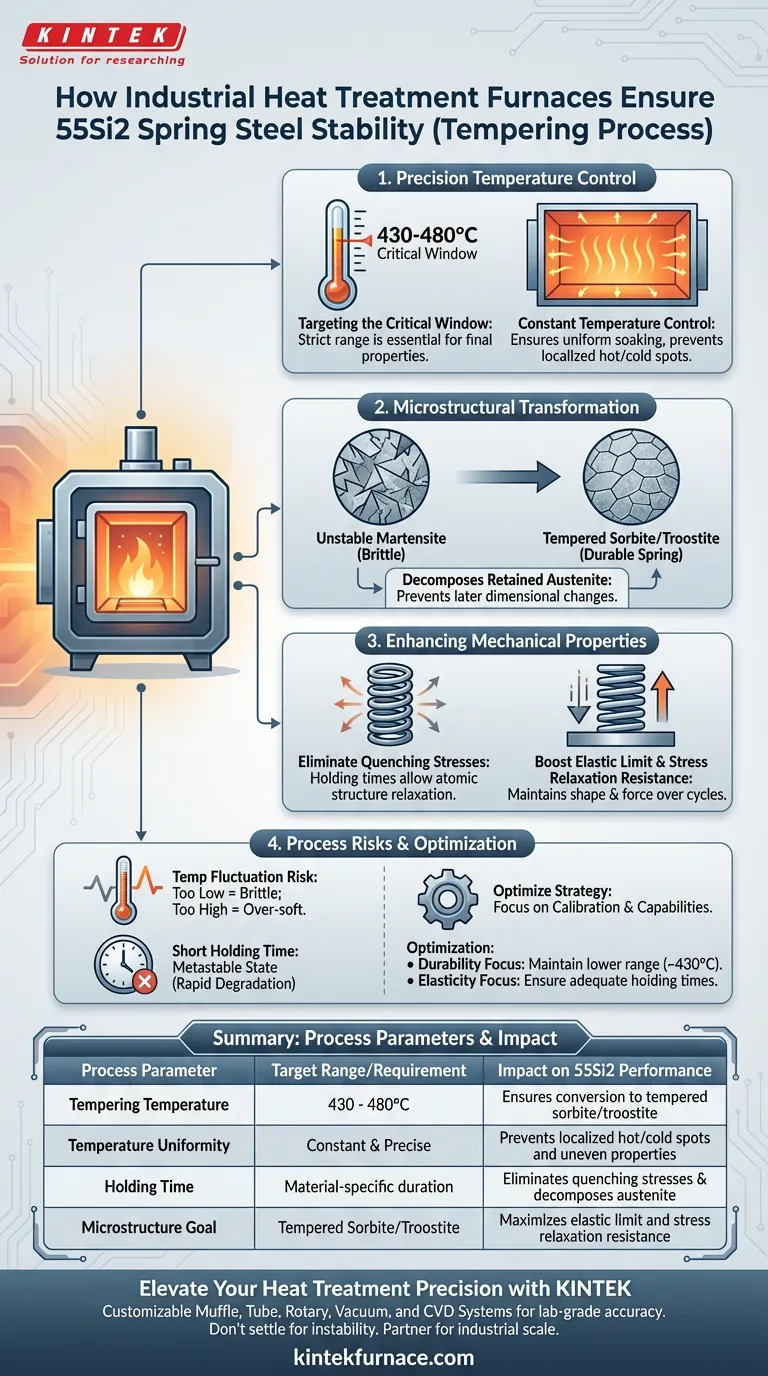
Precision thermal regulation is the key driver of material stability. Industrial heat treatment furnaces ensure the performance of 55Si2 spring steel by maintaining a strict constant temperature range of 430-480°C combined with specific holding times. This controlled environment is essential for converting unstable microstructures into stable forms, thereby eliminating internal stresses and setting the mechanical properties required for high-performance springs.
By facilitating the precise transformation of brittle martensite into tempered sorbite or troostite, the furnace acts as a stabilization chamber that directly determines the spring's elastic limit and resistance to stress relaxation.

The Role of Precision Temperature Control
Targeting the Critical Window
For 55Si2 spring steel, the furnace must maintain a temperature specifically between 430-480°C.
Operating outside this narrow band compromises the material's final properties. The equipment’s ability to hold this window without fluctuation is the first line of defense against material instability.
Ensuring Uniform Soaking
Beyond simply reaching temperature, the furnace provides constant temperature control.
This consistency ensures that every part of the batch receives the same thermal energy. It prevents localized hot or cold spots that could lead to uneven mechanical properties across the spring.
Driving Microstructural Transformation
Converting Unstable Phases
The primary function of the tempering process is to transform unstable martensite.
Through controlled heating, the furnace converts this brittle structure into tempered sorbite or troostite. This transformation is the fundamental mechanism that creates a usable, durable spring.
Managing Retained Austenite
The furnace environment promotes the decomposition of retained austenite.
This is a critical step for stability. If retained austenite is not properly decomposed, it can transform later during service, leading to dimensional changes or unexpected failure.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
Eliminating Quenching Stresses
Prior to tempering, the steel contains significant internal stresses from the hardening process.
The "necessary holding times" provided by the furnace allow the atomic structure to relax. This effectively eliminates internal quenching stresses that would otherwise cause cracks or premature fatigue.
Boosting Elasticity and Resistance
The ultimate goal of this thermal cycle is to enhance the elastic limit.
Simultaneously, the process improves stress relaxation resistance. This ensures the spring maintains its shape and force output even after repeated loading cycles over long periods.
Understanding Process Variables and Risks
The Consequence of Temperature Fluctuation
If the furnace fails to maintain the 430-480°C range, the trade-off is immediate.
Temperatures that are too low will fail to relieve internal stress or fully convert the martensite, resulting in a brittle part. Temperatures that drift too high will over-soften the material, destroying the elastic limit required for spring applications.
The Importance of Holding Time
Time is just as critical as temperature.
Rushing the process by shortening the holding time prevents the complete decomposition of retained austenite. This creates a "metastable" state where the material looks correct initially but degrades rapidly under physical load.
Optimizing Your Heat Treatment Strategy
To ensure maximum stability and performance in 55Si2 components, focus on the calibration and capabilities of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is Durability: Ensure your furnace can maintain the lower end of the temperature range (near 430°C) without dropping below it to maximize hardness while relieving stress.
- If your primary focus is Elasticity: Verify that the furnace provides adequate holding times to fully convert unstable martensite into tempered sorbite.
True material stability is achieved when the furnace operates not merely as an oven, but as a precision instrument for microstructural control.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Target Range/Requirement | Impact on 55Si2 Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Tempering Temperature | 430 - 480°C | Ensures conversion to tempered sorbite/troostite |
| Temperature Uniformity | Constant & Precise | Prevents localized hot/cold spots and uneven properties |
| Holding Time | Material-specific duration | Eliminates quenching stresses & decomposes austenite |
| Microstructure Goal | Tempered Sorbite/Troostite | Maximizes elastic limit and stress relaxation resistance |
Elevate Your Heat Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect microstructural transformation for 55Si2 spring steel requires more than just heat—it requires uncompromising precision. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces.
Our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique thermal profiles, ensuring your materials achieve the exact elastic limits and stress resistance your customers demand. Don't settle for instability. Partner with KINTEK for lab-grade accuracy at an industrial scale.
Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution
Visual Guide
References
- Enhancing the mechanical and functional characteristics of structural spring steel through the advancement of heat treatment technologies. DOI: 10.21595/vp.2025.24992
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in eggshell powder pretreatment? Optimize AA6061 Composites
- Why is a temperature-controlled heating system required for firing silver electrodes? Ensure Precision Ohmic Contacts
- Why is a constant temperature drying oven necessary for CN/BOC-X composites? Ensure High Photocatalytic Activity
- How does the secondary heat treatment process improve battery performance? Optimize SHPC/N-CNT Composites Today
- How does a gas evolution analysis system monitor gas release? Optimize Your Casting Integrity
- Why Use the Modified Two-Temperature Synthesis for ZnGeP2? Ensure Safety and Material Quality
- What role does phosphoric acid (H3PO4) play during the chemical activation stage of sawdust? Boost Porosity & Efficiency
- How is a laboratory oven utilized during the impregnation stage of APC preparation? Optimize Biochar Activation



















