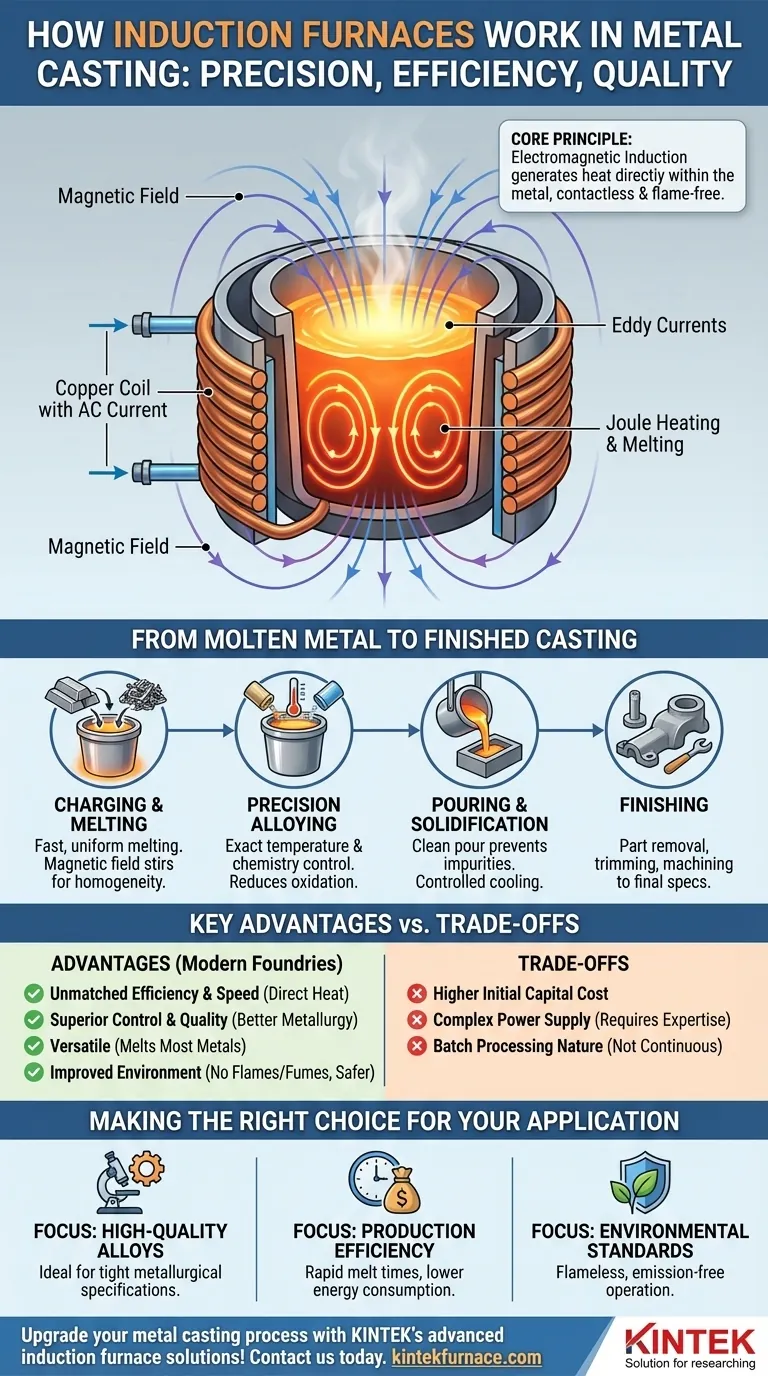
At its core, an induction furnace uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to melt metal without any direct contact or flame. An alternating electrical current is passed through a copper coil, which generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field. This field penetrates the metal placed inside the coil, inducing strong internal electrical currents—known as eddy currents—which generate intense heat through resistance, melting the metal quickly and cleanly.
An induction furnace isn't just a way to melt metal; it's a precision tool for controlling temperature, chemistry, and fluid dynamics. This control directly translates to higher quality castings, reduced waste, and a more efficient, safer foundry operation.
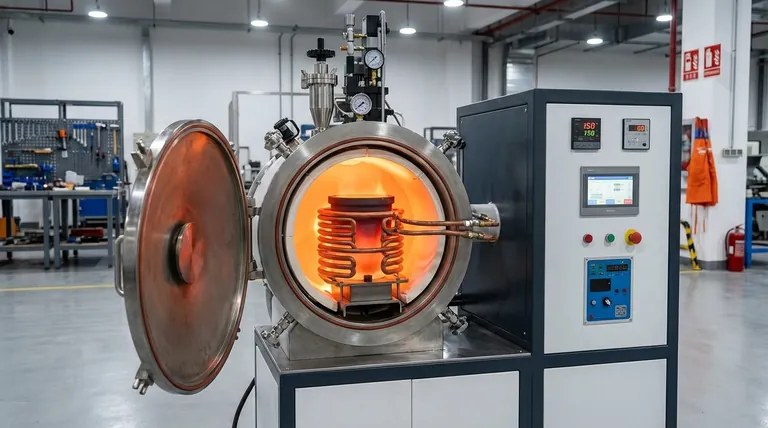

The Core Principle: Heat from Magnetism
The process of induction heating is a non-contact method that turns electrical energy into thermal energy with remarkable efficiency. It relies on fundamental laws of electromagnetism.
The Induction Coil and AC Power
The heart of the furnace is a water-cooled coil made of highly conductive copper. A specialized power supply sends a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through this coil.
Generating the Magnetic Field
As the alternating current flows, it generates a strong, rapidly reversing magnetic field in the space within and around the coil, where the metal charge (or crucible) is located.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This magnetic field passes directly through the metal. According to Faraday's law of induction, the changing magnetic field induces circular electrical currents within the metal itself. These are called eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat (Joule Heating)
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As the strong eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate immense friction and heat—a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This heat rapidly raises the metal's temperature to its melting point.
From Molten Metal to Finished Casting
The melting process is just the first step. The control offered by induction technology impacts the entire casting workflow.
Charging and Melting
The furnace is charged with solid metal, which can be in the form of ingots, scrap, or recycled returns. Once energized, the melting process is fast and uniform, and the magnetic field naturally stirs the molten bath, promoting a homogenous temperature and alloy mix.
Precision Alloying and Temperature Control
Induction systems allow for exceptionally precise temperature control. This prevents overheating, which reduces metal loss due to oxidation and preserves the integrity of alloying elements. New alloys can be added with confidence, knowing they will mix thoroughly.
Pouring and Solidification
Once the metal reaches the target temperature and composition, it is poured into a mold. The clean nature of induction melting, free from combustion byproducts, helps prevent gas porosity and other impurities from entering the casting.
Finishing the Casting
After the metal solidifies and cools, the casting is removed from the mold. It may then undergo secondary processes like trimming, machining, or surface treatments to meet final specifications.
Key Advantages in Modern Foundries
The adoption of induction furnaces is driven by clear and measurable operational benefits that address the core challenges of modern metal casting.
Unmatched Efficiency and Speed
Induction is significantly more energy-efficient than traditional fuel-fired furnaces because the heat is generated directly within the metal. This results in faster melting cycles, higher throughput, and lower energy consumption per ton of metal melted.
Superior Control and Quality
The ability to precisely manage temperature and the inherent stirring action lead to castings with enhanced metallurgical properties. This reduces defects, improves dimensional accuracy, and provides a better surface finish, minimizing costly rework.
Versatility Across Metals and Techniques
Induction furnaces can melt nearly any metal, including iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious alloys. Their precise nature makes them especially well-suited for demanding techniques like investment casting, where tight control is paramount.
Improved Workplace Environment
Unlike combustion-based furnaces, induction systems produce no flames or harmful exhaust gases. They operate with significantly lower noise levels, creating a safer, cleaner, and healthier environment for foundry workers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, induction technology is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for proper evaluation.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Induction furnace systems, including their sophisticated power supplies, typically require a higher initial investment compared to traditional cupola or resistance furnaces.
Power Supply Complexity
The high-frequency power units are complex electronic devices that require specialized knowledge for maintenance and repair. They also rely on a stable and robust electrical grid infrastructure.
Batch Processing Nature
Most induction furnaces operate in batches. For foundries requiring a continuous, uninterrupted flow of molten metal, a channel-type induction furnace or alternative technology might be more suitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your operational priorities and the specific demands of your products.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, complex alloys: The precise temperature and chemistry control of induction melting is essential for meeting tight metallurgical specifications.
- If your primary focus is production efficiency and energy savings: The rapid melt times and low energy consumption of induction furnaces offer a clear advantage in reducing operational costs.
- If your primary focus is environmental standards and worker safety: The flameless, emission-free operation of an induction furnace provides an immediate and significant improvement over fossil fuel-fired alternatives.
Ultimately, adopting induction furnace technology is a strategic decision that empowers foundries to produce higher-quality castings more efficiently and safely.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses electromagnetic induction to generate heat via eddy currents in metal, enabling non-contact melting. |
| Key Advantages | High energy efficiency, precise temperature control, versatility across metals, improved safety with no emissions. |
| Applications | Ideal for investment casting, alloy production, and foundries prioritizing quality and efficiency. |
| Limitations | Higher initial cost, complex power supply, typically batch processing. |
Upgrade your metal casting process with KINTEK's advanced induction furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on high-quality alloys, production efficiency, or environmental standards, our solutions deliver reliable performance and enhanced results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your foundry operations and drive success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















