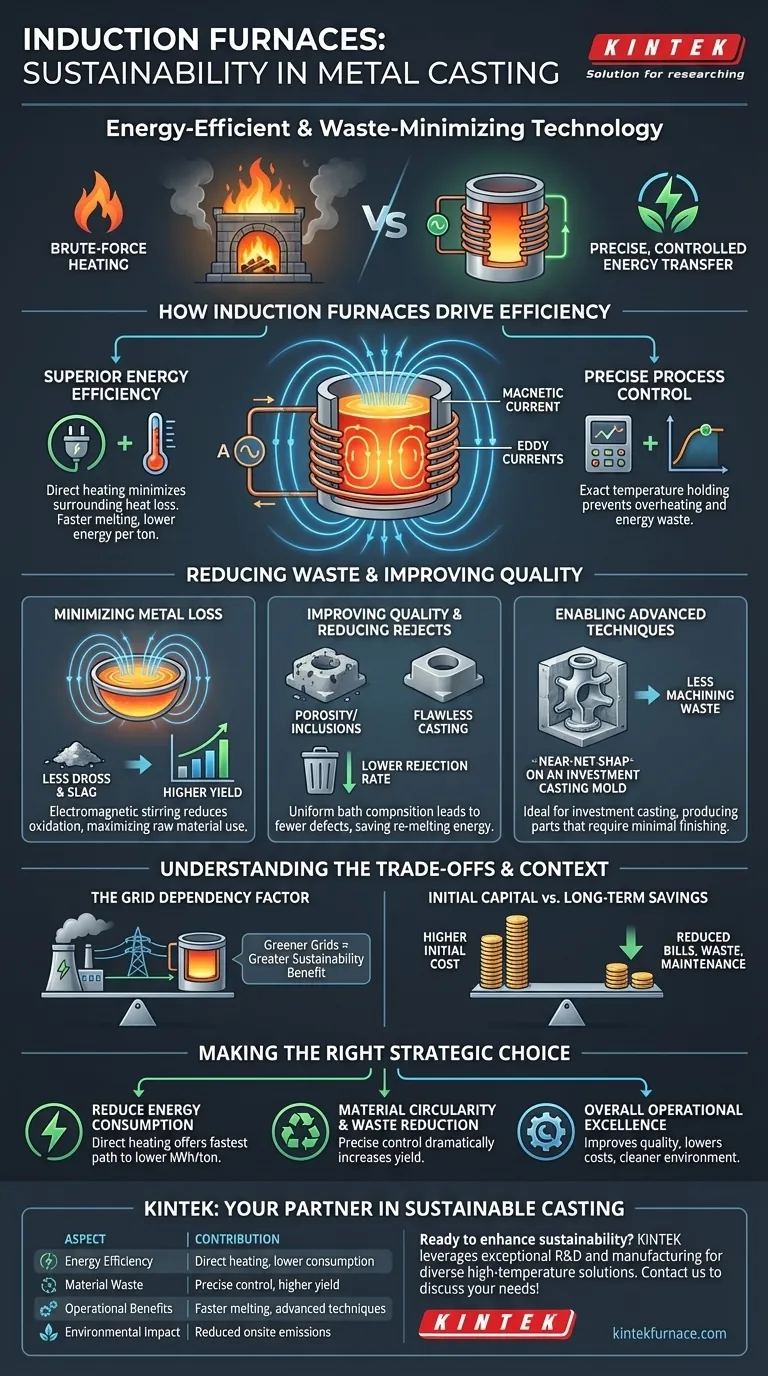
In short, induction furnaces contribute to sustainability by being exceptionally energy-efficient and by minimizing material waste. Their method of heating metal directly using electromagnetic fields reduces the energy required for melting, while precise temperature control ensures less metal is lost to oxidation and fewer parts are rejected due to defects.
The core principle is simple: induction technology shifts metal casting from a process of brute-force heating to one of precise, controlled energy transfer. This fundamental change not only cuts operational costs but directly aligns foundry operations with key sustainability goals of resource conservation and waste reduction.
How Induction Furnaces Drive Efficiency
At the heart of an induction furnace's sustainability is its unique heating method. Unlike traditional furnaces that burn fuel to heat a chamber (and then the metal), induction furnaces work more directly.
The Principle: Direct Electromagnetic Heating
An alternating electrical current passes through a copper coil, which generates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. When conductive metal is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents—known as eddy currents—within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
Benefit 1: Superior Energy Efficiency
Because the heat is generated within the metal, very little energy is wasted heating the furnace walls or the surrounding air. This results in significantly faster melting times and lower overall energy consumption per ton of metal produced compared to fossil-fuel-fired furnaces.
Benefit 2: Precise Process Control
The power supplied to the induction coil can be controlled with extreme precision. This allows operators to achieve and hold exact temperatures required for specific alloys. This eliminates overheating, which wastes energy and can damage metal properties.
Reducing Waste and Improving Quality
Sustainability isn't just about energy; it's also about using materials effectively. Induction furnaces excel at maximizing the yield from raw materials.
Minimizing Metal Loss
The electromagnetic field gently stirs the molten metal. This stirring action promotes a more uniform temperature and alloy composition, but more importantly, it minimizes the metal's exposure to oxygen at the surface. This leads to significantly less formation of dross and slag (oxidized metal waste), meaning more of your raw material ends up in the final casting.
Improving Casting Quality and Reducing Rejects
Precise temperature and alloy control lead to a higher-quality molten metal bath. This translates directly to castings with fewer defects like porosity or inclusions. The result is a lower rejection rate, which saves the immense amount of energy and material that would be wasted on re-melting faulty parts.
Enabling Advanced Casting Techniques
Induction melting is highly effective for processes like investment casting, which produces complex, near-net-shape parts. By creating high-quality castings that require minimal subsequent machining, the furnace helps reduce material waste and energy consumption during downstream finishing steps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, it is critical to view the technology within its complete operational context.
The Grid Dependency Factor
An induction furnace's environmental footprint is directly tied to the source of its electricity. If the power grid is predominantly supplied by fossil fuels, the carbon emissions are merely shifted from the foundry to the power plant. However, as grids become greener with more renewables, the sustainability benefit of induction technology grows exponentially.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Induction furnace systems typically have a higher upfront investment cost compared to some traditional furnace types. This cost is, however, often offset over the long term by reduced energy bills, lower material waste, and decreased maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting induction technology is a strategic decision that aligns operational improvements with sustainability targets.
- If your primary focus is reducing energy consumption: The direct heating mechanism of induction furnaces offers the most significant and immediate path to lowering your kilowatt-hour usage per ton of metal.
- If your primary focus is material circularity and waste reduction: The precise temperature control and minimized oxidation inherent to induction melting will dramatically increase your material yield and reduce scrap.
- If your primary focus is overall operational excellence: Induction furnaces provide a unified solution that improves casting quality, reduces costs, and creates a cleaner, safer work environment by eliminating onsite combustion emissions.
Ultimately, choosing an induction furnace is an investment in a more controlled, efficient, and responsible manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution to Sustainability |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Direct electromagnetic heating reduces energy waste, lowering consumption per ton of metal. |
| Material Waste Reduction | Precise temperature control minimizes oxidation and defects, increasing material yield. |
| Operational Benefits | Faster melting, lower rejection rates, and support for advanced casting techniques like investment casting. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces onsite emissions; sustainability depends on grid electricity sources. |
Ready to enhance your metal casting sustainability with advanced induction furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior efficiency and waste reduction!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















