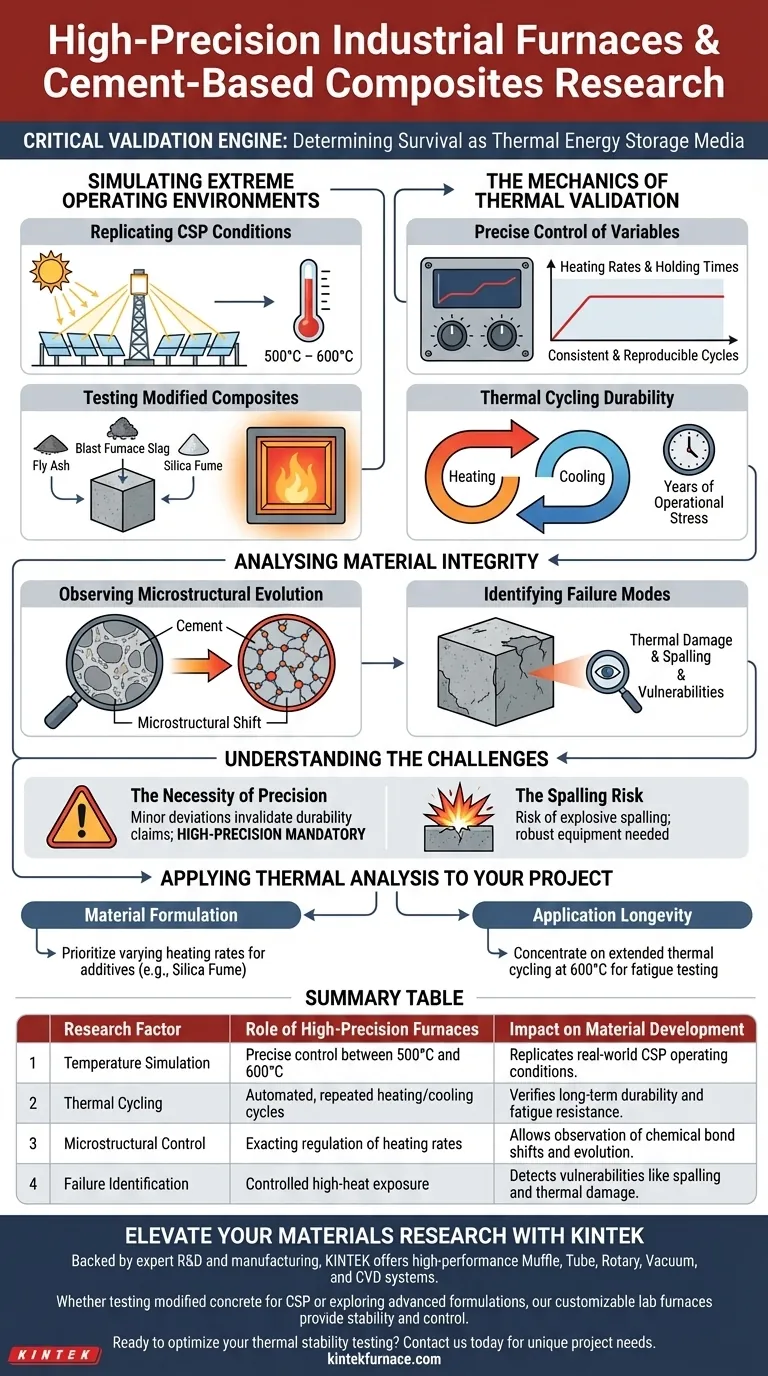
High-precision industrial furnaces act as the critical validation engine for determining if cement-based composites can survive as thermal energy storage media. By simulating the extreme environments of applications like Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)—specifically temperatures between 500°C and 600°C—these systems allow researchers to execute rigorous thermal cycling tests. This controlled exposure is the only way to accurately observe microstructural evolution and verify the material's resistance to thermal damage and spalling over time.
By offering exacting control over heating rates and holding times, these furnaces bridge the gap between theoretical material composition and proven, long-term durability in renewable energy applications.
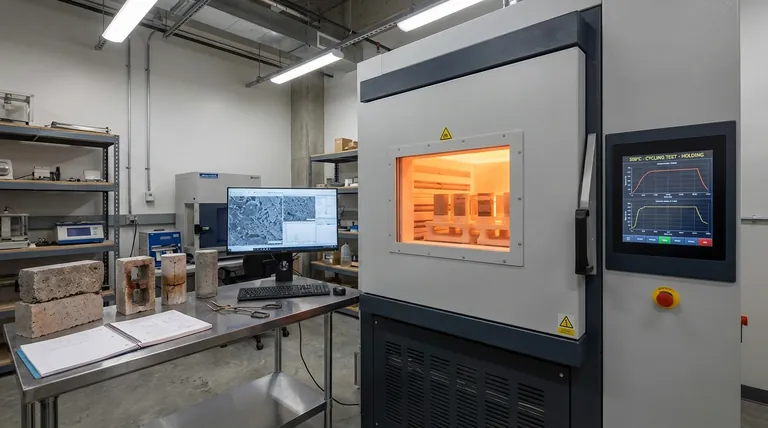

Simulating Extreme Operating Environments
Replicating CSP Conditions
To test viability for energy storage, materials must endure conditions identical to real-world applications.
High-precision furnaces are calibrated to reach and maintain the 500°C to 600°C range found in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems.
Testing Modified Composites
Standard concrete cannot withstand these extremes without degradation.
Therefore, researchers use these furnaces to test modified concrete mixes enhanced with additives like fly ash, blast furnace slag, or silica fume.
The Mechanics of Thermal Validation
Precise Control of Variables
The reliability of the data depends entirely on the stability of the testing environment.
These furnaces allow for the precise regulation of heating rates and holding times, ensuring that every test cycle is consistent and reproducible.
Thermal Cycling Durability
A single heating event is insufficient to prove longevity.
Through repeated thermal cycling (heating and cooling), the equipment simulates years of operational stress to verify the material's long-term durability as a storage medium.
Analyzing Material Integrity
Observing Microstructural Evolution
Heat drastically alters the internal architecture of cement composites.
Researchers utilize these controlled environments to track microstructural evolution, observing how the chemical bonds and physical structure shift under sustained heat.
Identifying Failure Modes
The ultimate goal is to predict catastrophic failure before it happens in the field.
The testing process highlights specific vulnerabilities, such as thermal damage and spalling (surface peeling), allowing engineers to adjust mixtures to prevent these issues.
Understanding the Challenges of Thermal Testing
The Necessity of Precision
In thermal storage research, a minor deviation in temperature control can invalidate durability claims.
Standard industrial ovens often lack the fine-grained control over heating rates required to mimic the specific stress of CSP cycles, making high-precision equipment mandatory rather than optional.
The Spalling Risk
While the furnace controls the environment, the material behavior remains the primary variable.
Concrete, even when modified, is susceptible to explosive spalling at these temperatures; the testing equipment must be robust enough to handle material failure while maintaining accurate data logging.
Applying Thermal Analysis to Your Project
To leverage high-precision furnaces effectively, you must align your testing protocols with your specific performance criteria.
- If your primary focus is Material Formulation: Prioritize tests that vary heating rates to see how additives like silica fume inhibit microstructural degradation.
- If your primary focus is Application Longevity: Concentrate on extended thermal cycling at the upper limits (600°C) to stress-test against spalling and long-term fatigue.
Ultimately, the precision of your thermal simulation dictates the reliability of your energy storage solution.
Summary Table:
| Research Factor | Role of High-Precision Furnaces | Impact on Material Development |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Simulation | Precise control between 500°C and 600°C | Replicates real-world CSP operating conditions. |
| Thermal Cycling | Automated, repeated heating/cooling cycles | Verifies long-term durability and fatigue resistance. |
| Microstructural Control | Exacting regulation of heating rates | Allows observation of chemical bond shifts and evolution. |
| Failure Identification | Controlled high-heat exposure | Detects vulnerabilities like spalling and thermal damage. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precise thermal validation is the cornerstone of developing durable cement-based composites for renewable energy. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of thermal cycling and microstructural analysis.
Whether you are testing modified concrete for CSP applications or exploring advanced material formulations, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and control your research requires.
Ready to optimize your thermal stability testing? Contact us today to discuss your unique project needs with our technical experts.
Visual Guide
References
- Mohammad Rahjoo, Jorge S. Dolado. Reviewing numerical studies on sensible thermal energy storage in cementitious composites: report of the RILEM TC 299-TES. DOI: 10.1617/s11527-024-02548-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What functions does glucose perform in lithium-ion sieve synthesis? Enhance Carbothermal Reduction for LiMnO2 Purity
- Why is vacuum sealing technology essential for K2In2As3 synthesis? Master High-Purity Solid-State Reactions
- What is the basic principle of a sintering furnace? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory electric thermostatic blast drying oven in the pretreatment of sludge? Efficiency & Accuracy
- How do atomizers and furnaces function in Spray Pyrolysis? Master Nanoparticle Synthesis
- How does low-temperature volatilization equipment function? Efficient Electrolyte Removal for Battery Recycling
- How does a circulating mineral oil jacket heating system function? Ensure Precision in Wood Thermal Modification
- How do high-power IR furnaces compare to traditional equipment for nanocomposites? Unlock Superior Material Control



















