At their core, tube furnaces are enhanced with multiple heating zones by incorporating several independent heating elements and controllers along the length of the processing tube. This design transforms the furnace from a simple uniform heat source into a highly sophisticated instrument capable of creating precise and dynamic temperature gradients, which is the fundamental benefit.
The crucial shift from a single-zone to a multi-zone furnace is the ability to move beyond simple, uniform heat. It allows you to engineer a specific thermal landscape along the tube, granting precise control over complex processes like materials synthesis, crystal growth, and advanced thermal analysis.
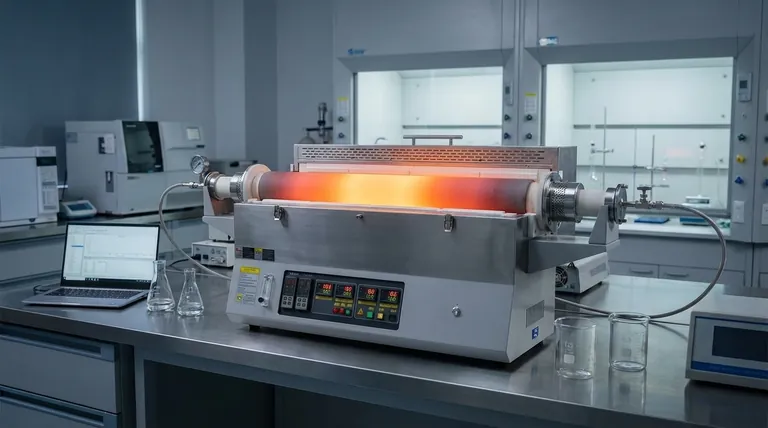

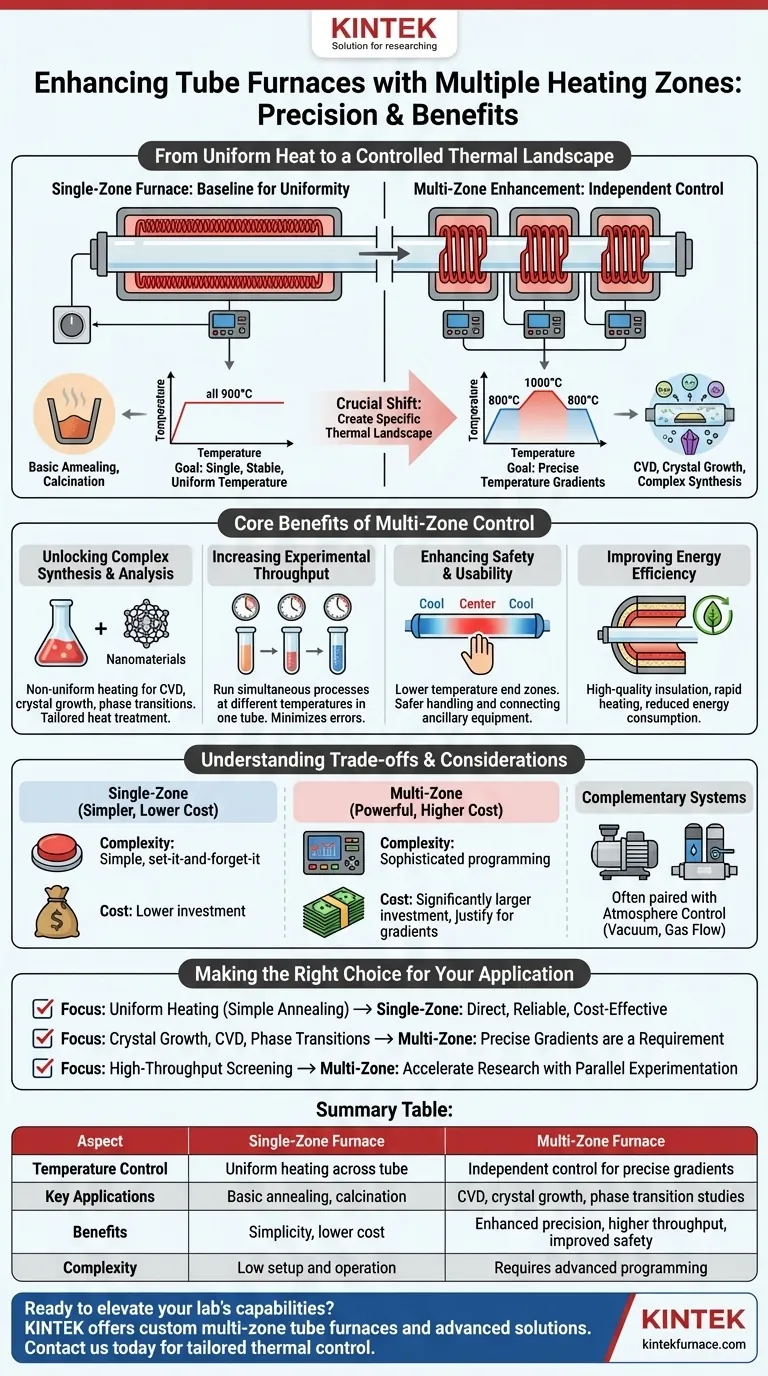
From Uniform Heat to a Controlled Thermal Landscape
To understand the value of multiple zones, we must first establish the baseline: the single-zone furnace.
The Single-Zone Furnace: A Baseline for Uniformity
A standard single-zone furnace has one heating element and one controller. Its goal is to create a single, stable, and uniform temperature across its central heated length.
This design is perfectly suitable for many common applications, such as basic annealing, calcination, or experiments where the entire sample must be held at one constant temperature.
The Multi-Zone Enhancement: Independent Control
A multi-zone furnace divides the heated length into two, three, or even more sections. Each zone has its own independent heating element and temperature controller.
This allows an operator to program a different temperature for each distinct zone. For example, the center zone could be set to 1000°C while the two end zones are held at 800°C.
Creating Precise Temperature Gradients
The true power of this independent control is the ability to create a smooth and precisely defined temperature gradient—a gradual change in temperature over distance.
This is critical for processes that must be initiated, propagated, and terminated under very specific thermal conditions, something a single-zone furnace cannot achieve.
The Core Benefits of Multi-Zone Control
This level of thermal precision unlocks capabilities that are essential in advanced research and manufacturing.
Unlocking Complex Synthesis and Analysis
Many advanced processes depend on non-uniform heating. Multi-zone control is critical for applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where different precursor gases must react at specific temperatures along the tube.
It is also essential for growing crystals, studying phase transitions, and synthesizing complex nanomaterials where the formation process requires tailored heat treatment at different stages.
Increasing Experimental Throughput
A multi-zone furnace can function as several furnaces in one. It allows for simultaneous processes to be run at different temperature points within the same tube.
This significantly increases experimental throughput and minimizes the potential for contamination or errors that can occur when transferring samples between different furnaces.
Enhancing Safety and Usability
By programming the end zones to a lower temperature, the central section of the furnace can operate at peak heat while the ends remain cooler.
This not only helps define the effective "hot zone" with greater precision but also makes handling the tube and connecting ancillary equipment like gas lines safer.
Improving Energy Efficiency
Modern multi-zone furnaces incorporate high-quality insulation, such as polycrystalline mullite fiber, and double-layer furnace shells.
This design enables rapid heating rates where needed while minimizing heat loss to the environment, leading to reduced energy consumption and more efficient operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a multi-zone furnace is not always the necessary choice. Understanding the trade-offs is key to making a sound investment.
Complexity vs. Simplicity
A multi-zone furnace requires more sophisticated programming and setup to properly define the desired temperature profile. A single-zone furnace offers simpler, "set-it-and-forget-it" operation for straightforward tasks.
Cost vs. Capability
The additional controllers, thermocouples, and more complex construction make multi-zone furnaces a significantly larger investment than their single-zone counterparts. Their benefits only justify the cost when the application explicitly demands gradient control.
Complementary Systems: Atmosphere Control
The precision of a multi-zone furnace is often paired with atmosphere control. To protect sensitive materials, these furnaces are frequently equipped with vacuum systems and gas flow controllers to operate in a protected, oxygen-free environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is a matter of matching the tool to the scientific or industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating for simple annealing or debinding: A single-zone furnace is the most direct, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or studying material phase transitions: The precise temperature gradients of a multi-zone furnace are almost certainly a requirement.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening or process optimization: A multi-zone furnace can dramatically accelerate your research by enabling parallel experimentation within a single run.
Ultimately, choosing a multi-zone furnace is a decision to invest in a level of thermal control that opens the door to more complex and demanding material processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Single-Zone Furnace | Multi-Zone Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Uniform heating across the tube | Independent control for precise gradients |
| Key Applications | Basic annealing, calcination | CVD, crystal growth, phase transition studies |
| Benefits | Simplicity, lower cost | Enhanced precision, higher throughput, improved safety |
| Complexity | Low setup and operation | Requires advanced programming |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom multi-zone tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in materials synthesis, crystal growth, or thermal analysis, we can help you achieve precise temperature gradients and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















