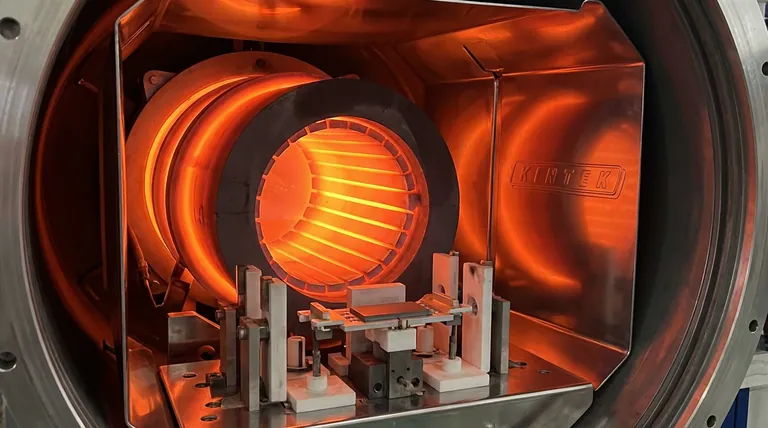
The Crucible and the Void
Imagine an engineer's task: to fuse two exotic metals, creating an alloy stronger than any of its parts. The process demands a temperature so intense it would liquefy most materials.
But the heat is only half the battle.
The true enemy is the air itself. A single stray oxygen atom at that temperature could contaminate the alloy, rendering it useless. The entire process must occur in a near-perfect vacuum—a controlled void where the only thing that matters is the material and the heat.
Inside that void, at the heart of the furnace, is the heating element. And in this extreme environment, one material reigns supreme: graphite.
The Counter-Intuitive Strength of Carbon
In our everyday experience, heat weakens things. Metals soften, plastics melt, and wood turns to ash. We instinctively associate high temperatures with degradation and failure.
Graphite defies this intuition.
As it absorbs energy and its temperature climbs, graphite's crystalline structure becomes stronger. Its tensile strength increases with temperature, peaking around a staggering 2500°C. It doesn't weaken; it hardens for the fight.
This unique property is why it is the default choice for the most demanding metallurgical processes.
A Material That Thrives on Stress
Unlike tungsten or molybdenum, which become ductile and risk deformation near their limits, graphite maintains its structural integrity. It provides the stable, uniform heat needed for processes that require absolute precision.
Beyond Melting: The Sublimation Point
At atmospheric pressure, graphite has no melting point. Instead of turning to liquid, it sublimates—turning directly from a solid into a gas—at approximately 3600°C. This gives it an operational ceiling far beyond almost any other practical heating material.
The Price of Power: A Controlled World
Graphite's incredible strength comes with one crucial, non-negotiable condition: it must be protected from oxygen.
Oxygen: Graphite's Only True Enemy
Expose graphite to air at temperatures above 500°C, and it will rapidly oxidize. It literally burns away. This limitation is not a minor detail; it is the central trade-off that defines its use.
The Vacuum as a Sanctuary
This is why graphite elements are found exclusively inside vacuum furnaces or those filled with an inert gas like argon. The vacuum is not just an environmental requirement for the process—it is a sanctuary for the heating element itself.
By removing the atmosphere, we create the conditions that unlock graphite's unparalleled high-temperature performance. We accept the complexity of a vacuum system to gain access to a level of thermal power and stability that would otherwise be impossible.
Where Theory Meets Practice: Core Applications
This synergy between graphite and a vacuum environment is the engine behind several critical industrial processes.
- Metal Hardening: Creating ultra-hard steels requires rapid, uniform heating in an environment free of contaminants. Graphite provides this with flawless consistency.
- High-Strength Brazing: Joining components with nickel or copper fillers at over 1100°C demands intense, stable heat to ensure the purity and strength of the final bond.
- Sintering Metals: Compacting metallic powders into solid, high-performance parts requires exceptionally high and uniform temperatures, a task for which vacuum furnaces with graphite elements are perfectly suited.
The Engineer's Dilemma: Choosing the Right Tool
While graphite is dominant, it is not a universal solution. The choice of a heating element is a strategic decision dictated by atmosphere, temperature, and cost.
A Tale of Two Atmospheres: Graphite vs. Silicon Carbide
The central question is often: does your process require air?
If high-temperature heating must occur in an open atmosphere, an oxidation-resistant material like Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the necessary choice. SiC elements form a protective glassy layer of silicon dioxide, allowing them to operate in air where graphite cannot.
Decision Framework at a Glance
| Requirement | Optimal Heating Element | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temps (>2000°C) in Vacuum/Inert Gas | Graphite | Unmatched strength and stability in a protected void. |
| High Temps (up to 1600°C) in Air | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Forms a protective layer against oxidation. |
| Moderate Temps (<1300°C) in Air, Cost-Sensitive | Metallic (FeCrAl) | The most practical and economical solution. |
From Components to Systems
Navigating these material and atmospheric trade-offs is fundamental to successful high-temperature processing. It requires not just the right element, but a system—a furnace—designed holistically for the task.
At KINTEK, we specialize in building these precise thermal environments. Our deep expertise in R&D and manufacturing across a range of furnace technologies, from Muffle and Tube to advanced Vacuum and CVD systems, is built around this core principle. Whether your work demands the unparalleled performance of graphite in a perfect vacuum or a robust air-atmosphere system, our focus is on customizing the ideal solution for your specific application.
To build the right environment for your critical process, Contact Our Experts.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
Related Articles
- The Paradox of Strength: Why Graphite Dominates High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
- The Pursuit of Nothing: How Vacuum Furnace Control Defines Material Destiny
- More Than a Void: The Inherent Energy Efficiency of Vacuum Furnace Design
- The Tyranny of Air: How Vacuum Furnaces Forge Perfection by Removing Everything
- Beyond the Heat: The Psychology of Perfect Vacuum Furnace Operation