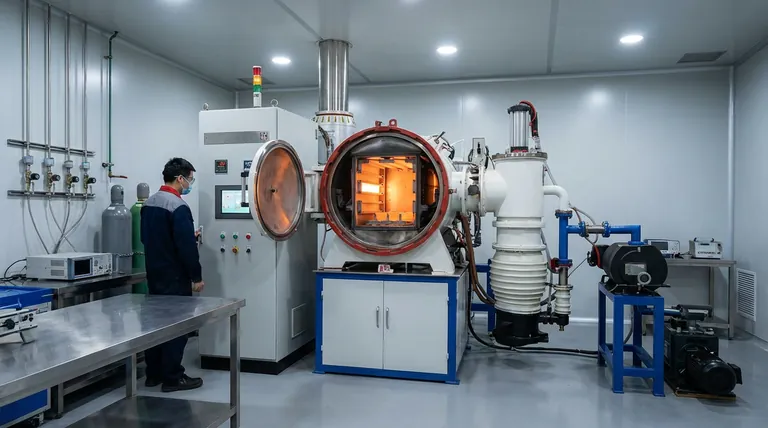
Imagine a laboratory crafting a single-crystal turbine blade for a jet engine. The metallurgy must be perfect. A microscopic impurity, introduced by the furnace itself, could lead to catastrophic failure miles above the earth.
In this world of extreme stakes, the environment is everything. A vacuum furnace is a controlled universe, and its heating element is the sun at its center. The choice of that "sun" isn't just a technical detail; it's a foundational decision that dictates the reliability and purity of the entire process.
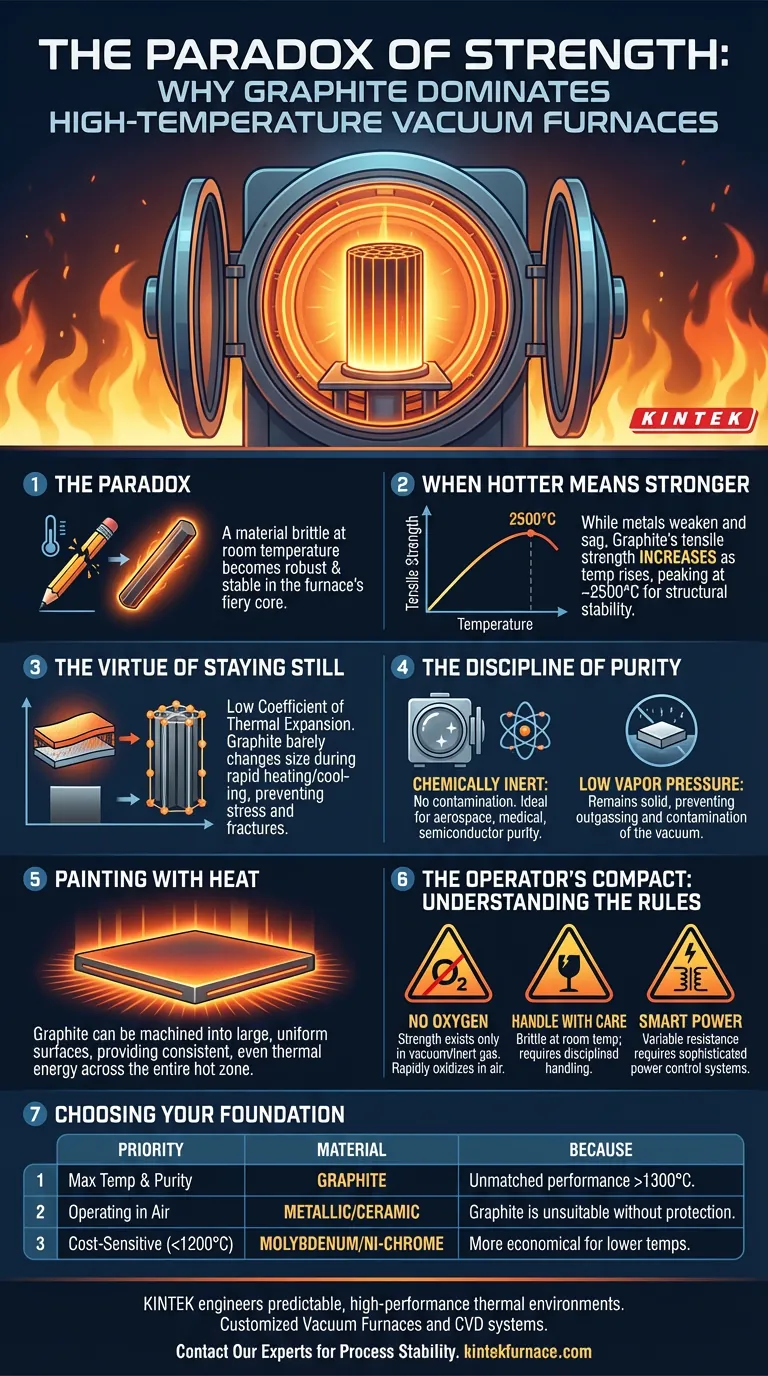
This is where we encounter the paradox of graphite. A material that can be snapped in half with your bare hands at room temperature becomes one of the most robust and stable structures on earth inside the furnace's fiery core.
When Hotter Means Stronger
Our intuition, shaped by experiences with metals, tells us that materials weaken as they heat up. Metals soften, sag, and eventually melt. Graphite defies this logic completely.
The Physics of Defiance
As temperature rises, graphite's tensile strength actually increases, peaking around 2500°C.
This isn't just a curious fact; it's a profound engineering advantage. While metallic elements warp and deform under their own weight over countless cycles, graphite elements remain structurally sound. They provide a predictable, stable heating core, cycle after cycle.
The Virtue of Staying Still
High-temperature processes involve violent thermal swings. Materials expand and contract, creating internal stress that can lead to fatigue and fracture.
Graphite possesses an exceptionally low coefficient of thermal expansion. It barely changes its size during rapid heating and cooling. This thermal stability prevents the buildup of stress, making it uniquely resilient to the rigors of vacuum furnace operations.
The Discipline of Purity
In the pristine environment of a vacuum, the greatest threat of contamination often comes from the equipment itself. The heating element, bathing the product in energy, can also poison it with unwanted atoms.
An Oath of Silence
Graphite is almost completely chemically inert. It does not react with or contaminate the vast majority of materials being processed. For applications in aerospace, medical implants, or semiconductor manufacturing, where purity is paramount, graphite’s refusal to participate in chemical reactions is its greatest asset.
Remaining Solid Under Pressure
At high temperatures and low pressures, even solids can begin to "boil," releasing atoms in a process called outgassing. This vapor can contaminate the vacuum and deposit onto the product.
Graphite has an extremely low vapor pressure. It remains solid and stable, ensuring that the only thing it adds to the chamber is pure, radiant heat. This is the foundation of process repeatability.
Painting with Heat
The goal of any furnace is to deliver uniform temperature. Hot spots and cold spots in the heating zone lead to inconsistent results and scrapped parts.
Because graphite can be precisely machined into large, monolithic cylinders or plates, it provides a vast, even surface area for heat radiation. This architecture allows it to "paint" the entire hot zone with uniform thermal energy, ensuring every part of the product receives the exact same treatment.
The Operator's Compact: Understanding the Rules
No material is a magic bullet. Graphite's incredible performance is bound by a strict set of rules. Violating them leads to failure.
-
The Oxygen Taboo: Graphite’s strength exists only in a vacuum or inert gas. A small air leak at high temperatures will cause it to rapidly oxidize—effectively, to burn. This demands a robust and perfectly sealed furnace vessel.
-
Handle with Care: While a titan when hot, graphite is a brittle ceramic at room temperature. It requires careful, disciplined handling during installation and maintenance to prevent chipping or cracking.
-
The Demand for a Smart Grid: Graphite's electrical resistance changes significantly with temperature. This necessitates a sophisticated power control system (like a multi-tap transformer or SCR) to manage the energy input precisely.
Choosing Your Foundation
The decision to use graphite is a decision about your process priorities. It’s a trade-off between ultimate performance and operational constraints.
| If Your Priority Is... | Your Best Material Choice Is Likely... | Because... |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature & Purity | Graphite | It offers unmatched performance above 1300°C where metals fail or contaminate. |
| Operating in Air/Oxidizing Gas | Metallic or Ceramic Elements | Graphite is unsuitable and will be destroyed without complex protection. |
| Cost-Sensitive, Lower-Temp Vacuum | Molybdenum or Ni-Chrome Alloys | For processes below 1200°C, they can offer a more economical solution. |
Understanding these principles is the first step. The second is implementing them within a system engineered for reliability from the ground up. At KINTEK, our expertise in R&D and manufacturing allows us to build customized Vacuum Furnaces and CVD systems where every component is matched to the specific demands of your process. We don't just select a heating element; we engineer a predictable, high-performance thermal environment.
Whether your work demands the uncompromising performance of graphite or another specialized material, achieving process stability starts with the right system design. Contact Our Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
Related Articles
- Beyond the Void: The Hidden Costs of a Perfect Vacuum Furnace
- The Unseen Engine: Why Graphite Dominates High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
- Designing for the Void: The Counter-Intuitive Physics of Graphite in Vacuum Furnaces
- Purity Under Pressure: The Unseen Elegance of Graphite in Vacuum Furnaces
- Strength in the Fire: The Counterintuitive Genius of Graphite in Vacuum Furnaces




















