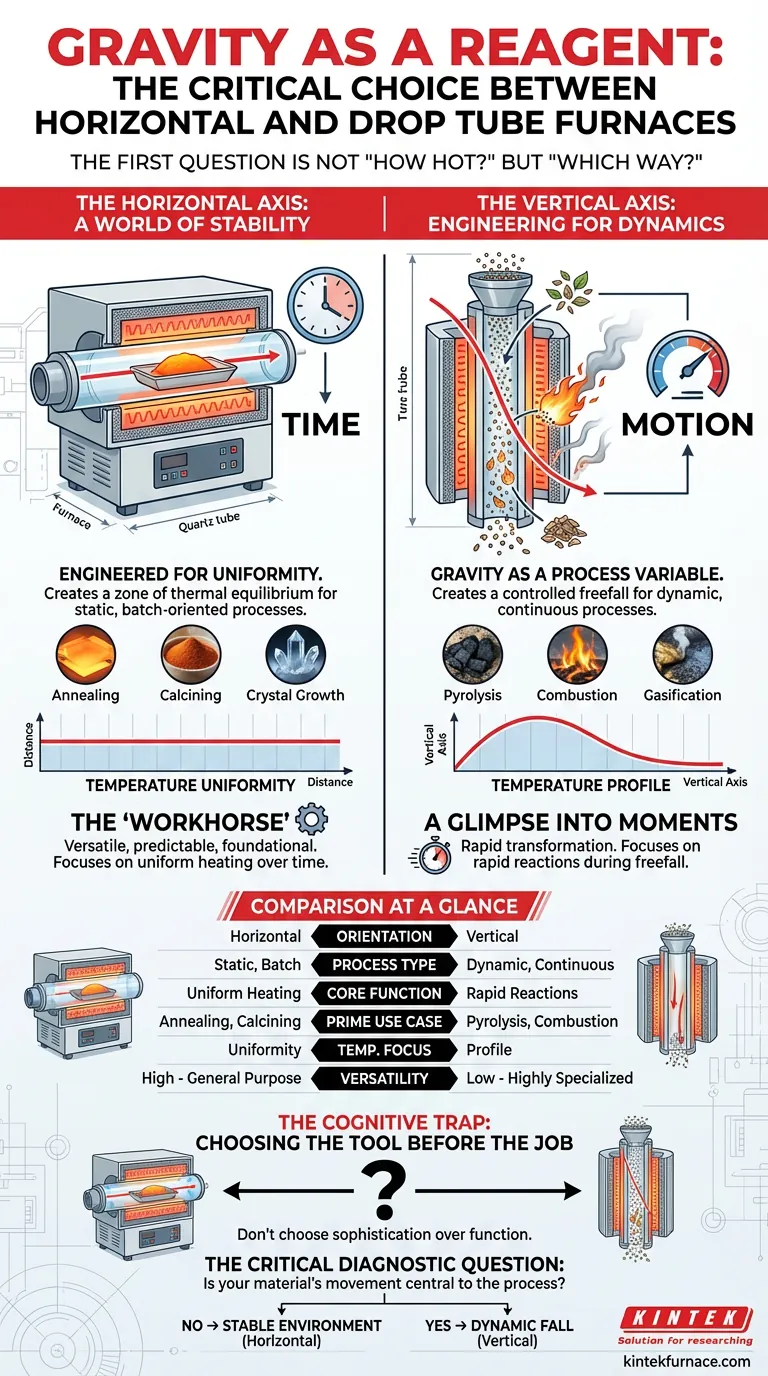
The First Question Is Not "How Hot?" But "Which Way?"
Imagine a materials scientist tasked with a new project. The goal is to understand how a novel material behaves at 1200°C. The first decision they face isn't about temperature ramps or atmospheric composition. It's more fundamental, almost philosophical: should the process respect the pull of gravity, or use it as a tool?
This is the essential question behind the choice between a horizontal tube furnace and a vertical drop tube furnace. It’s a decision that defines the entire experiment before the first gram of material is ever prepared.
Choosing incorrectly isn't just inefficient; it's a category error. It’s like using a telescope to examine a microbe. The tool might be powerful, but it’s designed for an entirely different problem.
The Horizontal Axis: A World of Stability
A horizontal tube furnace is the dependable workhorse of the materials lab. Its design philosophy is built around one single, powerful concept: stability.
Engineered for Uniformity
The goal of a horizontal furnace is to create a zone of thermal equilibrium. A sample, typically held in a quartz or alumina boat, is placed inside and "soaked" in a consistent, uniform temperature field. The laws of physics are allowed to unfold over minutes or hours in a controlled, static environment.
This makes it the perfect instrument for processes where time and temperature uniformity are the primary variables, such as annealing metal parts, calcining powders, or growing crystals. The furnace creates a stable stage where the material's internal structure can quietly rearrange itself.
The Psychology of the 'Workhorse'
There’s a reason this design is a staple. It is versatile, predictable, and foundational to materials science. It answers the most common questions: What happens to this solid object if I heat it evenly for an hour? Its reliability makes it the default choice, and for most applications, it is the correct one.
The Vertical Axis: Engineering for Dynamics
A drop tube furnace operates on a completely different principle. It doesn't create a static stage; it creates a controlled freefall. Here, gravity isn't a passive constant; it's an active reagent in the process.
Gravity as a Process Variable
Instead of a stationary boat, the material—a fine powder, a slurry, or biomass—is introduced at the top and falls through the vertical hot zone. The orientation is the entire point. It’s designed to investigate what happens in the fleeting moments a particle spends traversing a precise temperature gradient.
The goal is not equilibrium but rapid transformation.
A Glimpse into Fleeting Moments
This design is for studying dynamic, high-speed phenomena like pyrolysis, combustion, or gasification. The questions it answers are about reactions that occur in milliseconds. How quickly does this biomass particle combust as it falls through a 1000°C zone? What gases are released?
It’s less like an oven and more like a high-speed camera for thermal reactions, capturing a process that is fundamentally defined by motion.
Beyond Orientation: The Trade-offs That Matter
The core design philosophy—static vs. dynamic—creates a cascade of secondary differences that are crucial to understand.
Temperature: Uniformity vs. Profile
A horizontal furnace is obsessed with temperature uniformity along its length. The ideal is a perfectly flat line in the central hot zone.
A drop tube furnace is obsessed with the temperature profile along its vertical axis. The goal is a controlled, predictable temperature curve that the particle experiences during its fall. One seeks to eliminate variation; the other seeks to control it precisely.
The Practical Constraints: Space and Complexity
The physical footprint reflects the function. A horizontal furnace demands bench space. A drop tube furnace demands vertical clearance, sometimes requiring a high-bay lab or even spanning multiple floors. This isn't a flaw; it's a necessary consequence of using gravity as a core experimental parameter. The length of the fall dictates the residence time.
The Cognitive Trap: Choosing the Tool Before the Job
The most common mistake in selecting a furnace is a psychological one: becoming enamored with the perceived sophistication of a specialized tool without having a specialized problem.
A drop tube furnace is not an "upgraded" horizontal furnace. It is a different tool for a different job. Using it for a simple annealing process is not just overkill; it won't work. The temptation is to choose the more complex instrument, but the real engineering elegance lies in perfectly matching the simplest possible tool to the task at hand.
The critical diagnostic question is this: Is your material's movement central to the process you're studying?
- If the answer is no, you need a stable, uniform environment.
- If the answer is yes, you need a dynamic, controlled fall.
Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | Horizontal Tube Furnace | Drop Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Horizontal | Vertical |
| Process Type | Static, Batch-Oriented | Dynamic, Continuous/Semi-Continuous |
| Core Function | Uniform heating over time | Rapid reactions during freefall |
| Prime Use Case | Annealing, Brazing, Calcining | Pyrolysis, Combustion, Gasification |
| Temp. Focus | Uniformity across a stable zone | Profile along the path of travel |
| Versatility | High (General-purpose lab workhorse) | Low (Highly specialized for particle dynamics) |
A Decision Guided by Physics
Ultimately, the choice between these two furnaces is a direct reflection of the physics you aim to study. One provides a world of calm equilibrium, the other a controlled, dynamic cascade.
Navigating this choice requires understanding both your material's behavior and the intricate engineering of modern thermal systems. At KINTEK, our expertise is built on developing and manufacturing a wide range of high-temperature solutions, from versatile Muffle and Tube Furnaces to specialized Vacuum and CVD systems. Our R&D-driven approach means we don't just sell equipment; we provide tailored thermal solutions designed to meet the specific physical demands of your research. Whether you need absolute stability or controlled dynamics, we have the technology and the knowledge to help you make the right choice. To ensure your equipment perfectly matches your experimental goals, Contact Our Experts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
Related Articles
- The Physics of Control: Inside the High-Temperature World of a Tube Furnace
- The Unsung Hero of the Lab: The Deliberate Design of the Single-Zone Split Tube Furnace
- The Art of Isolation: Mastering Material Properties with Tube Furnaces
- The Alchemy of Control: Mastering Material Properties with High-Temperature Tube Furnaces
- Why Your High-Temperature Furnace Fails: The Hidden Culprit Beyond the Cracked Tube




















