At its core, graphite is used in furnaces because of its unique and unparalleled ability to withstand extreme temperatures while remaining chemically stable and structurally sound. This combination of properties allows it to perform critical functions in high-temperature environments, such as vacuum furnaces, where most other materials, especially metals, would melt, deform, or react.
Graphite's value isn't just its heat resistance; it's the material's versatility. It can simultaneously serve as a heating element, a structural support, and a thermal insulator within the same furnace, a feat that makes it indispensable for modern high-temperature industrial processes.

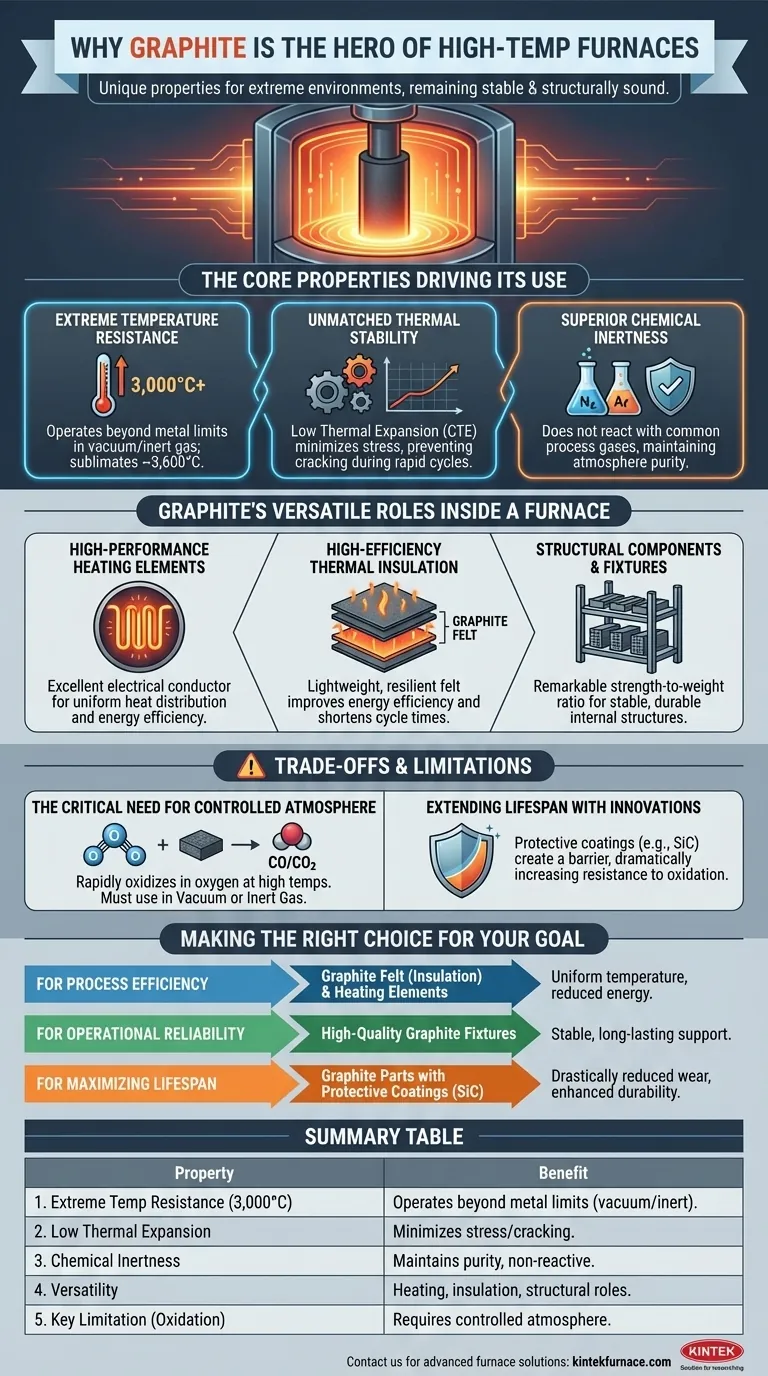
The Core Properties Driving Graphite's Use
To understand why graphite is so dominant in furnace design, you must first appreciate its fundamental material characteristics. These properties work in concert to deliver reliability and performance under conditions that would destroy lesser materials.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Graphite does not have a traditional melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature, around 3,600°C.
This allows it to function effectively in inert gas or vacuum atmospheres at temperatures up to 3,000°C, far beyond the operational limits of most metals and ceramics.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
A material's reaction to heat is just as important as its resistance to it. Graphite excels here, with a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE).
This means that when heated, it expands very little. This stability minimizes internal stress and prevents cracking or deformation during rapid temperature cycles, ensuring component longevity.
Superior Chemical Inertness
In the controlled environments of vacuum furnaces, process gasses like nitrogen and argon are common. Graphite is valued for being chemically inert, meaning it does not react with these gasses.
This chemical stability is crucial for maintaining the purity of the process atmosphere and the integrity of the furnace components themselves.
Graphite's Versatile Roles Inside a Furnace
Graphite's properties allow it to be engineered into several distinct components, each playing a critical role in the furnace's operation and efficiency.
As High-Performance Heating Elements
Graphite is an excellent electrical conductor, which allows it to function as a resistive heating element. Its high thermal conductivity ensures that heat is distributed uniformly throughout the furnace chamber.
This results in consistent processing, high energy efficiency, and reliable, repeatable performance for applications like heat treating and sintering.
As High-Efficiency Thermal Insulation
In the form of graphite felt, the material becomes an exceptional insulator. This lightweight, resilient material traps heat effectively within the hot zone of the furnace.
By preventing heat loss, graphite felt dramatically improves the furnace's energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and shortening cycle times.
As Structural Components and Fixtures
Graphite possesses remarkable strength-to-weight ratio at high temperatures. This makes it the ideal material for internal furnace structures.
It is used to create fixtures, racks, and holders that support workpieces during processing. Its light weight makes these components easier and safer for operators to handle, reducing labor costs and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While graphite is a superior material, its application is not without critical considerations. Understanding its primary limitation is key to using it successfully.
The Critical Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite's single greatest vulnerability is oxidation. In the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, graphite will rapidly burn and degrade, turning into CO and CO2 gas.
For this reason, graphite components are almost exclusively used in vacuum furnaces or furnaces filled with an inert gas. They are not suitable for high-temperature applications in an open-air or oxygen-rich environment.
Extending Lifespan with Modern Innovations
To mitigate wear, even in trace-oxygen environments, modern graphite components are often treated with protective coatings.
A silicon carbide (SiC) coating, for example, can be applied to the graphite surface. This creates a barrier that dramatically increases resistance to oxidation, extending the component's operational life and improving furnace reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific form and application of graphite you prioritize will depend on your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Leverage graphite felt for superior thermal insulation and graphite heating elements for uniform temperature control and reduced energy use.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Invest in high-quality graphite fixtures and structural components, which provide stable, long-lasting support for workpieces.
- If your primary focus is maximizing component lifespan: Specify graphite parts with protective coatings, such as silicon carbide, to drastically reduce wear from oxidation and enhance durability.
Ultimately, graphite is the enabling material that makes modern, high-performance, high-temperature manufacturing possible.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Furnace Applications |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Resistance (up to 3,000°C) | Operates beyond metal limits; ideal for vacuum/inert gas atmospheres. |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Minimizes stress and cracking during rapid temperature cycles. |
| Chemical Inertness | Maintains purity; does not react with process gases like nitrogen or argon. |
| Versatility | Serves as heating element, thermal insulator (graphite felt), and structural fixture. |
| Key Limitation | Requires controlled atmosphere (vacuum/inert gas) to prevent oxidation. |
Ready to leverage graphite's unparalleled properties in your high-temperature processes?
At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, or CVD/PECVD Systems, our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace operates with maximum efficiency, reliability, and longevity.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite-based components and high-temperature expertise can enhance your lab's performance and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity



















