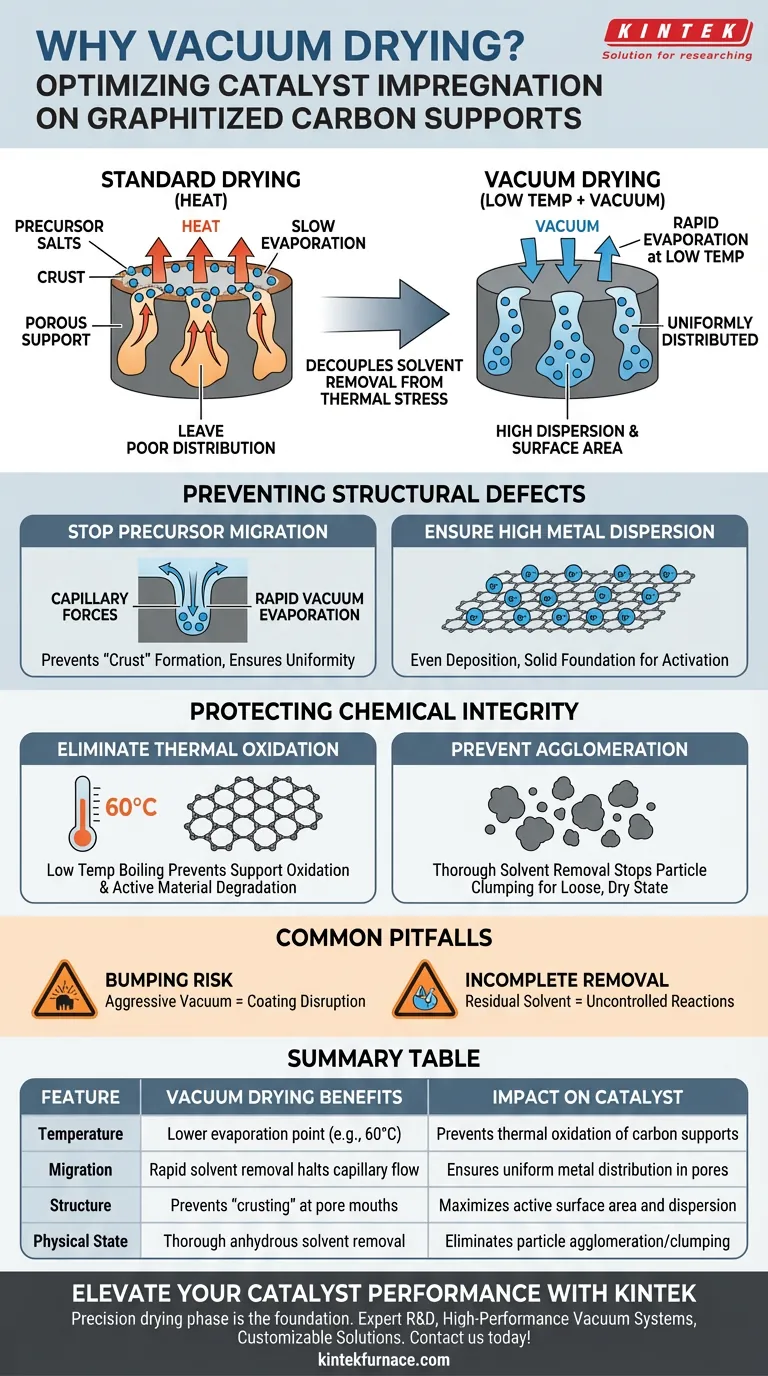
The primary utility of a vacuum drying system is to decouple solvent removal from high thermal stress, allowing for the preservation of a uniform catalyst structure. It is used to evaporate solvents at low temperatures, which prevents the dissolved precursor salts (such as nickel and copper) from migrating unevenly to the exterior surface of the porous support during the drying phase.
The Core Insight Standard drying relies on heat, which often drags active metals to the surface of the material as the solvent evaporates, leading to poor distribution. Vacuum drying bypasses this by lowering the pressure to remove moisture and solvents rapidly at low temperatures, locking the active ingredients deep within the pores and ensuring high dispersion.

Preventing Structural Defects via "Dynamic" Drying
The vacuum drying process is not merely about removing liquid; it is a structural control mechanism. By utilizing dynamic vacuum treatment, you exert precise control over how the active components settle onto the support.
Stopping Precursor Migration
When a catalyst support impregnated with a precursor solution dries, capillary forces tend to pull the liquid—and the dissolved salts—toward the mouth of the pores.
If unchecked, this results in a "crust" of active metal on the outside and very little inside. Vacuum drying accelerates evaporation so quickly that this migration is halted, ensuring salts remain uniformly distributed throughout the pore structure.
Ensuring High Metal Dispersion
For catalysts containing metals like nickel or copper, performance is dictated by surface area and dispersion.
Vacuum treatment ensures that these ions deposit evenly across the graphitized carbon surface. This establishes a solid structural foundation, which is critical for the success of subsequent high-temperature decomposition and reduction steps.
Protecting the Chemical Integrity of the Support
Graphitized carbon supports and complex precursors are often sensitive to the harsh conditions found in standard convection ovens. Vacuum drying mitigates these environmental risks.
Eliminating Thermal Oxidation
Standard drying requires higher temperatures to drive off solvents effectively, which introduces the risk of oxidizing the carbon support or the active functional groups.
By reducing the ambient pressure, vacuum systems allow solvents (like ethanol or isopropyl alcohol) to boil off at much lower temperatures, often around 60 °C. This preserves the chemical nature of the support and prevents the active materials from degrading before they are even activated.
Preventing Agglomeration
Residual solvents can act as bridges that pull particles together, leading to agglomeration (clumping).
Vacuum ovens remove anhydrous ethanol and other solvents thoroughly. This ensures the raw materials remain in a loose, dry physical state, preventing the precursors from fusing together and ensuring they are ready for high-temperature pyrolysis or cyclization.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While vacuum drying is superior for impregnation consistency, it requires careful parameter control to be effective.
The Risk of "Bumping"
If the vacuum is applied too aggressively without temperature regulation, the solvent may flash-boil violently. This can physically disrupt the coating or structure you are trying to preserve, rather than settling it gently.
Incomplete Solvent Removal
Relying solely on vacuum without mild heat (e.g., 60 °C) can leave residual solvent trapped in deep micropores. This residue can cause uncontrolled reactions or oxidation during the subsequent high-temperature furnace stages, compromising the final catalyst.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum drying over standard drying should be driven by the specific sensitivity of your precursor and support materials.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Active Surface Area: Use vacuum drying to freeze precursor salts in place, preventing them from migrating to the surface and agglomerating.
- If your primary focus is Protecting Carbon Supports: Use vacuum drying to lower the evaporation temperature, ensuring that the graphitized carbon or functional groups do not undergo thermal oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Pre-Pyrolysis Preparation: Use vacuum drying to ensure the material is physically loose and completely devoid of solvents that could interfere with high-temperature decomposition.
Vacuum drying transforms the drying step from a passive wait time into an active process of structural engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Drying Benefits | Impact on Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Lower evaporation point (e.g., 60°C) | Prevents thermal oxidation of carbon supports |
| Migration | Rapid solvent removal halts capillary flow | Ensures uniform metal distribution in pores |
| Structure | Prevents "crusting" at pore mouths | Maximizes active surface area and dispersion |
| Physical State | Thorough anhydrous solvent removal | Eliminates particle agglomeration/clumping |
Elevate Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precision in the drying phase is the foundation of high-performance catalysts. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance vacuum drying systems and a full range of lab equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are working with sensitive graphitized carbon or complex precursor salts, our customizable solutions ensure your materials maintain their chemical integrity and structural uniformity.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact us today to speak with our specialists about your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Suzan E. Schoemaker, Petra E. de Jongh. Balancing act: influence of Cu content in NiCu/C catalysts for methane decomposition. DOI: 10.1039/d4ma00138a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a vacuum environment in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- How do the drying conditions in a vacuum drying oven affect NiS2 electrode quality? Optimize Your Battery Performance
- What is 'hydrogen disease' in copper heat treatment and how does vacuum annealing prevent it? Learn to Avoid Catastrophic Failure
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Optimize Fe-Mn-Si Alloy Solution Treatment
- What combination of pumps is typically used for vacuum sintering furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Rotary Vane & Roots Pumps
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary during the SPS of CoCrFeMnNi alloy powders? Ensure Purity and Density
- What is the necessity of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven for catalyst powders? Protect Active Micro-Nano Structures
- 1200°C Annealing for LPBF Silicon Steel (Fe-Si): Enhancing Soft Magnetic Performance



















