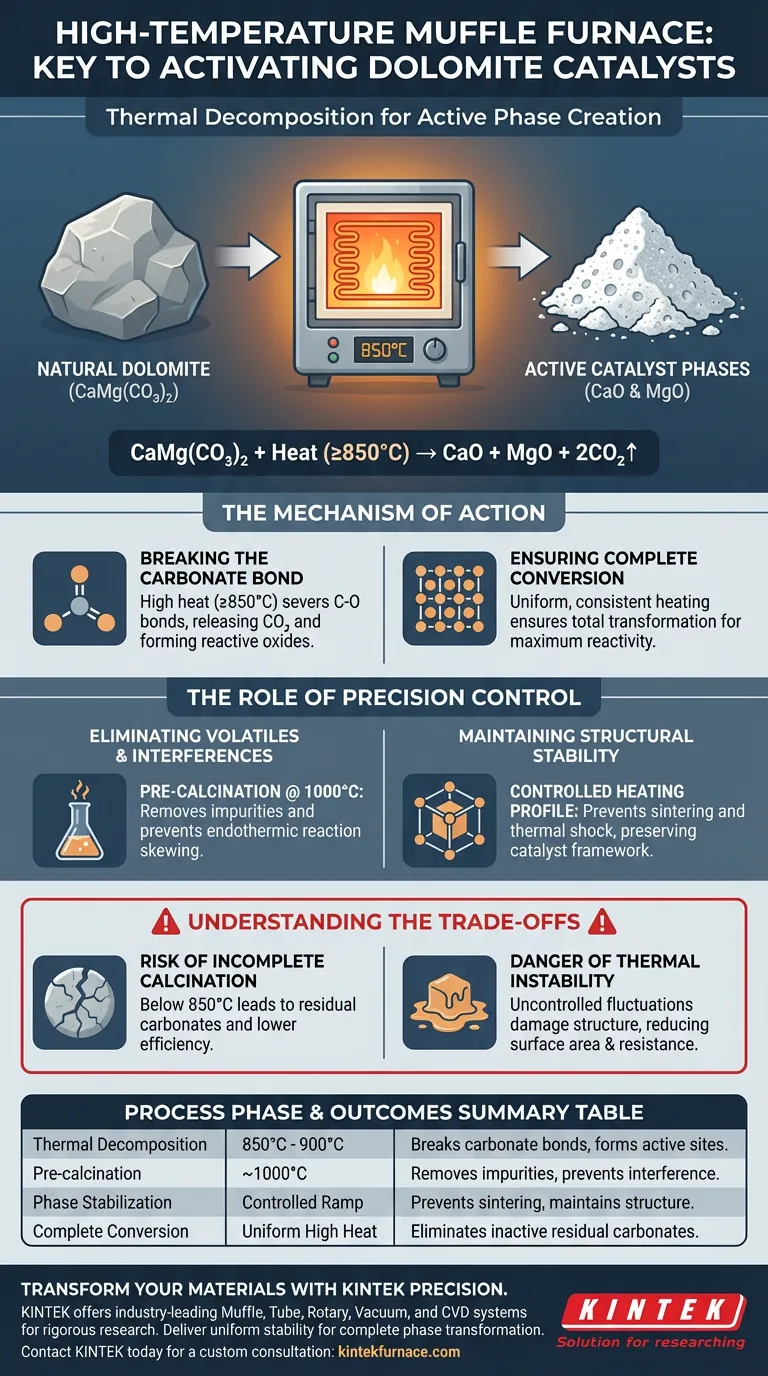
The requirement for a high-temperature muffle furnace is dictated by the thermal decomposition threshold of natural dolomite. Inert dolomite ($CaMg(CO_3)_2$) must be subjected to an ultra-high temperature environment, specifically around 850°C, to break its chemical bonds. This intense thermal treatment is the only mechanism that effectively converts the raw carbonate material into the active catalyst phases of calcium oxide ($CaO$) and magnesium oxide ($MgO$).
The muffle furnace acts as a reactor, not just a heater, driving the specific thermochemical transformation of inert rock into reactive metal oxides. Its value lies in providing the precise thermal stability required to ensure complete carbonate conversion without compromising the catalyst's structural integrity.

The Mechanism of Active Phase Creation
Breaking the Carbonate Bond
Natural dolomite is composed of calcium and magnesium carbonates, which are chemically stable and catalytically inactive in their raw state. To unlock their potential, you must induce thermal decomposition.
A high-temperature muffle furnace provides the energy required—typically 850°C or higher—to sever the bonds holding carbon dioxide within the crystal lattice. This process releases $CO_2$ and leaves behind the reactive oxides ($CaO$ and $MgO$) that function as the active catalyst sites.
Ensuring Complete Conversion
Partial heating is insufficient for catalytic applications. If the temperature is inconsistent or too low, residual carbonates will remain, diluting the activity of the final product.
The muffle furnace ensures the environment remains uniform, driving the reaction to completion. This total conversion is critical for maximizing the chemical reactivity of the raw materials.
The Role of Precision Control
Eliminating Volatiles and Interferences
Beyond the primary decomposition, the furnace plays a critical role in purification. Operating at temperatures up to 1000°C allows for the pre-calcination of the dolomite.
This step effectively removes volatile components and eliminates potential endothermic reactions that could occur during later processing stages. By stabilizing the material beforehand, you ensure the accuracy of subsequent experimental data and reaction predictability.
Maintaining Structural Stability
The physical structure of a catalyst is just as important as its chemical composition. The muffle furnace allows for a controlled heating profile, which is essential for maintaining the structural stability of the resulting catalyst.
By avoiding rapid thermal shocks or uneven heating, the furnace preserves the integrity of the newly formed oxide phases. This controlled environment prevents the degradation of the catalyst's framework during the critical transition from carbonate to oxide.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incomplete Calcination
If the furnace fails to maintain the target temperature (e.g., dropping below 850°C), the decomposition of dolomite will be incomplete. This results in a hybrid material containing inactive carbonates, significantly lowering catalytic efficiency.
The Danger of Thermal Instability
While high heat is necessary, uncontrolled fluctuations can damage the catalyst's physical properties.
Without the precise regulation provided by a high-quality muffle furnace, you risk altering the crystalline structure or sintering the material. This can lead to a loss of surface area or reduced resistance to peeling and deactivation in future applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your dolomite catalyst preparation, align your furnace settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Reactivity: Ensure your furnace can sustain a minimum of 850°C to guarantee the total conversion of carbonates into active $CaO$ and $MgO$ phases.
- If your primary focus is Data Accuracy: Utilize a pre-calcination step around 1000°C to fully eliminate volatiles and prevent endothermic reactions from skewing subsequent experimental results.
Precision thermal treatment is the fundamental bridge between raw mineral potential and high-performance catalytic activity.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Requirement | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | 850°C - 900°C | Breaks carbonate bonds; releases CO2; forms active CaO/MgO sites |
| Pre-calcination | ~1000°C | Removes volatile impurities and prevents endothermic interference |
| Phase Stabilization | Controlled Ramp | Prevents sintering and maintains structural integrity of the catalyst |
| Complete Conversion | Uniform High Heat | Eliminates inactive residual carbonates for maximum reactivity |
Transform Your Raw Materials with KINTEK Precision
Don't let inconsistent heating compromise your catalytic yields. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed for rigorous research and production. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific temperature and atmospheric needs.
Whether you are performing dolomite calcination or advanced material synthesis, our furnaces deliver the uniform stability required for complete phase transformation.
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency? Contact KINTEK today for a custom consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Rasa Šlinkšienė, Eglė Sendžikienė. The Regeneration of Dolomite as a Heterogeneous Catalyst for Biodiesel Production. DOI: 10.3390/catal14020139
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace ensure uniform heating and prevent contamination? Discover the Key Design Secrets
- What is the primary advantage of a muffle furnace compared to other types of furnaces? Superior Purity and Element Protection
- Why might a muffle furnace consume high energy? Tips to Cut Costs and Boost Efficiency
- Why is it important to check the power supply of a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Accurate Results
- How does a high-precision resistance furnace ensure T6 solution treatment? Achieve Peak Alloy Strength with KINTEK
- Why is the separation of chambers important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Purity and Uniform Heating
- What are the typical temperature ranges for muffle furnaces and their applications? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processes
- Why is the size of the furnace important when selecting a muffle furnace? Ensure Precise Heating and Efficiency



















