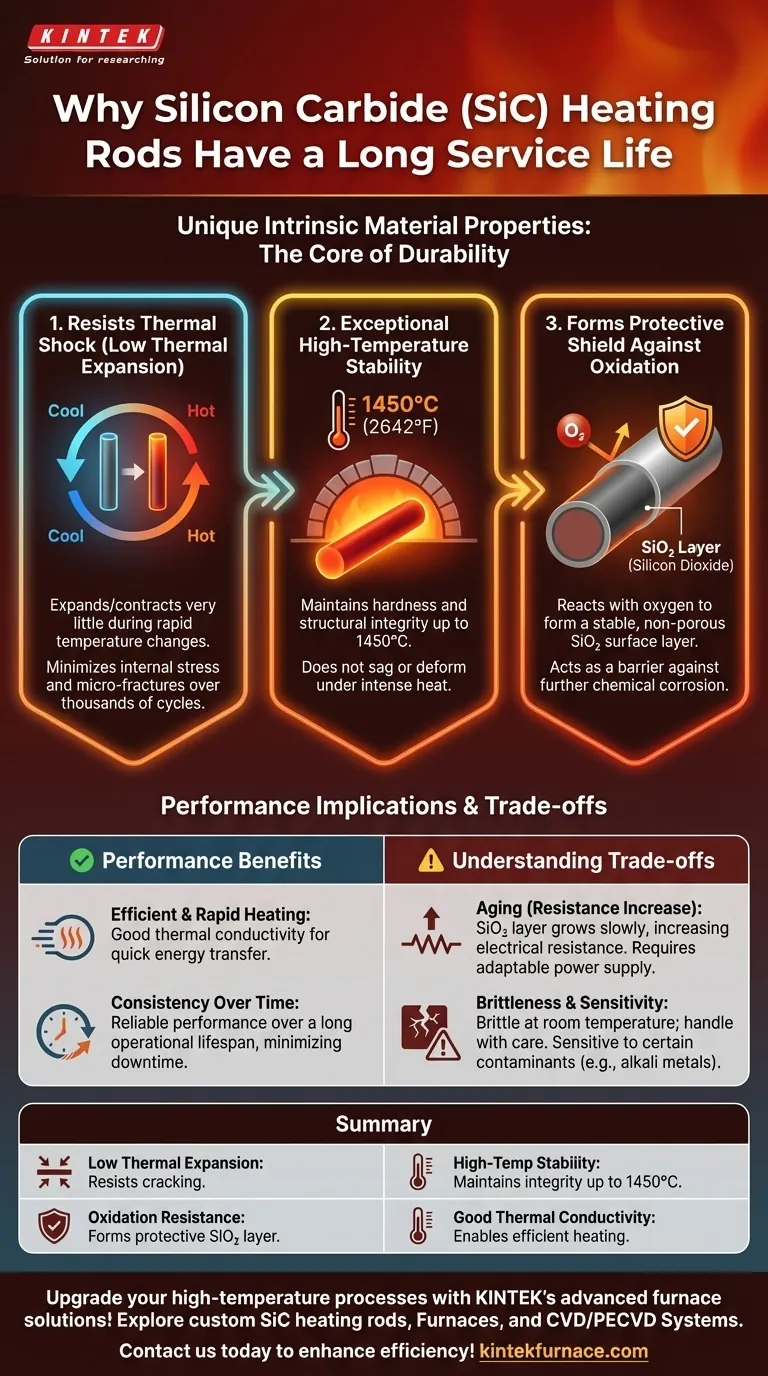
Fundamentally, silicon carbide (SiC) heating rods owe their long service life to a unique combination of intrinsic material properties. This includes exceptional stability at very high temperatures, a low coefficient of thermal expansion that prevents cracking from heat cycles, and a natural resistance to the chemical corrosion that degrades lesser materials.
The longevity of a silicon carbide heating element is not due to a single trait, but its dual resistance to the two primary failure mechanisms in high-temperature environments: physical stress from thermal shock and chemical degradation from oxidation.

The Core Pillars of SiC Durability
To understand why SiC rods endure, we must look at how the material behaves under extreme thermal and chemical stress. Its durability is built on three key characteristics.
Resisting Thermal Shock with Low Thermal Expansion
A material expands when heated and contracts when cooled. A high rate of expansion and contraction creates immense internal stress, leading to micro-fractures and eventual failure. This is known as thermal shock.
Silicon carbide has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little, even during rapid temperature changes. This inherent stability drastically reduces internal stress, minimizing wear and tear over thousands of heating and cooling cycles.
Exceptional High-Temperature Stability
Many materials begin to soften, deform, or creep at high temperatures, compromising their structural integrity.
SiC, however, maintains its hardness and strength at extreme operating temperatures, remaining stable in continuous use up to 1450°C (2642°F). This ensures the heating element does not sag or break down when subjected to the intense heat required in industrial furnaces.
Forming a Protective Shield Against Oxidation
At high temperatures, most materials react with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation (a form of corrosion), which degrades the material over time.
When heated, silicon carbide reacts with oxygen to form a thin, non-porous layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on its surface. This passive layer is extremely stable and acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation and protecting the core material from chemical attack, including from many acids.
Performance Implications of These Properties
These durability characteristics directly translate into reliable and efficient performance in demanding applications.
Efficient and Rapid Heating
Beyond being durable, SiC has good thermal conductivity. This allows it to heat up quickly and transfer energy efficiently to the work environment, whether it's a laboratory furnace or a large-scale metal smelting operation.
Consistency Over Thousands of Hours
The combination of thermal stability and oxidation resistance means that SiC elements provide consistent and predictable performance over a long operational lifespan. This reliability minimizes downtime and the need for frequent replacement, which is critical in industrial production and long-term experiments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the limitations of silicon carbide is key to using it effectively.
The Aging Process is Inevitable
While the silicon dioxide layer is protective, it does continue to grow very slowly over the element's life. This process gradually increases the electrical resistance of the rod.
This "aging" is a predictable trade-off. The heating element does not suddenly fail, but its changing resistance requires a power supply system (often using transformers or SCRs) that can increase the voltage over time to maintain the desired power output.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many ceramic materials, silicon carbide is extremely hard but also brittle at room temperature. This means it must be handled with care during shipping and installation to avoid being cracked by mechanical shock or impact.
Sensitivity to Contaminants
While highly resistant to clean air and many chemicals, the protective SiO₂ layer can be attacked by certain contaminants, particularly alkali metals and some metal vapors. In applications where these are present, the element's lifespan may be reduced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires matching the material's properties to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum operational temperature and reliability: SiC is an exceptional choice, offering stability and longevity in environments up to 1450°C.
- If your application involves rapid heating and cooling cycles: The low thermal expansion of SiC makes it far more resistant to thermal shock than many other ceramic elements.
- If you are designing a new high-temperature system: You must account for the gradual aging (resistance increase) of SiC and specify a power control system capable of compensating for it.
Understanding these material characteristics allows you to leverage the remarkable durability of silicon carbide while planning for its real-world operating behavior.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Resists cracking from rapid temperature changes |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity up to 1450°C |
| Oxidation Resistance | Forms protective SiO₂ layer against corrosion |
| Good Thermal Conductivity | Enables efficient and rapid heating |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with silicon carbide heating rods, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and reliability in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















