To put it directly, a retort furnace is the essential tool for any thermal process that requires absolute control over the atmospheric environment. It is purpose-built to carry out processes like carburizing, nitriding, annealing, and sintering, where the material must be heated in a sealed chamber, either to protect it from air or to expose it to specific reactive gases.
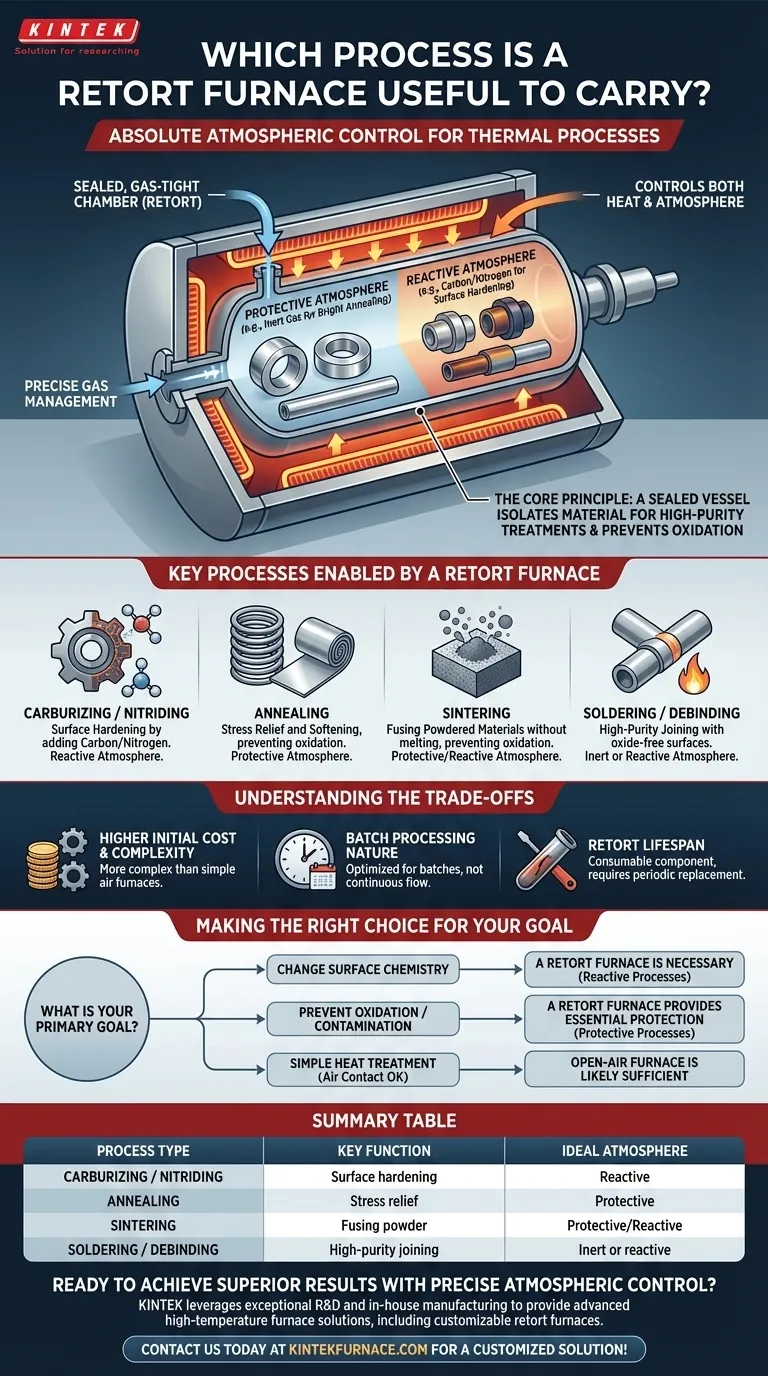
A standard furnace controls heat; a retort furnace controls both heat and atmosphere. Its defining feature is a sealed vessel—the retort—that isolates the material, enabling high-purity treatments that are impossible in an open-air system.
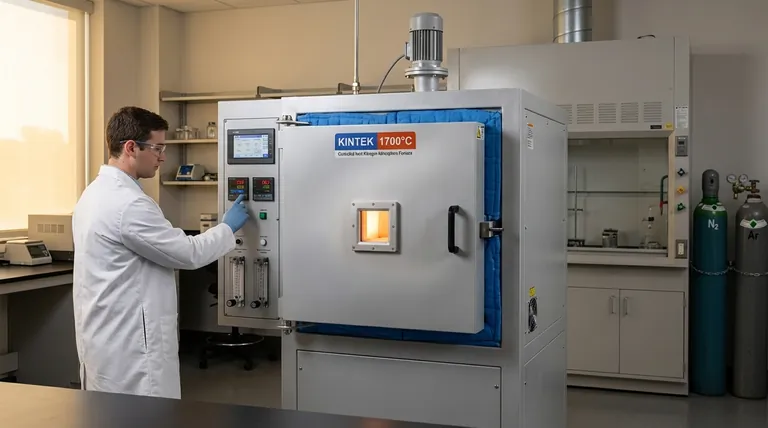

The Core Principle: Atmospheric Control
The primary reason to use a retort furnace is its ability to create a highly specific, controlled atmosphere around the parts being treated. This is achieved through its unique design.
The Sealed Retort Chamber
A retort is a gas-tight vessel, typically made of metal, that sits inside the furnace. The material being treated is placed inside this sealed chamber, completely separating it from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air.
This isolation is the furnace's key advantage. It prevents unwanted reactions, such as oxidation, that would otherwise occur when heating metals to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen.
Precise Gas Management
The sealed retort allows for the complete evacuation of air and the introduction of specific gases. This enables two fundamental types of processes:
- Protective Atmospheres: The chamber can be filled with an inert gas like Argon to prevent any chemical changes to the material's surface, crucial for processes like bright annealing.
- Reactive Atmospheres: The chamber can be filled with a reactive gas to intentionally alter the material's surface, such as introducing carbon for carburizing or nitrogen for nitriding.
Improved Efficiency and Quality
This sealed design directly leads to higher quality results and better efficiency. Because the atmosphere is contained, gas consumption is extremely low compared to other furnace types.
Furthermore, the sealed environment minimizes contamination, ensuring a cleaner, higher-quality end product with superior material properties.
Key Processes Enabled by a Retort Furnace
The ability to manipulate the atmosphere makes a retort furnace exceptionally versatile. It excels in applications where the environment is as critical as the temperature.
Surface Hardening (Carburizing & Nitriding)
These processes intentionally add elements to the surface of a metal to make it harder. A retort furnace provides the perfect environment to contain the carbon-rich or nitrogen-rich gases required for these surface chemistry modifications.
Stress Relief and Softening (Annealing)
When a metal is annealed to relieve internal stresses and increase its ductility, it becomes highly susceptible to oxidation. A retort furnace creates a protective, oxygen-free atmosphere, ensuring the part emerges clean and free of scale.
Fusing Powdered Materials (Sintering)
Sintering involves heating compacted powders (metal or ceramic) to just below their melting point, causing the particles to fuse. This requires a clean, controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation, which would inhibit the particles from bonding properly.
High-Purity Joining (Soldering & Debinding)
High-strength soldering or brazing requires perfectly clean, oxide-free surfaces for the filler metal to bond to. A retort furnace provides the inert or reactive atmosphere needed to prepare and join components without contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a retort furnace is a specialized piece of equipment. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The inclusion of a sealed retort, gas delivery systems, and vacuum pumps makes these furnaces more complex and expensive than simple air furnaces.
Batch Processing Nature
Most retort furnace designs are optimized for batch processing. While ideal for many applications, they may not be as suitable for high-volume, continuous-flow production lines where a tunnel furnace might be more efficient.
Retort Lifespan
The retort itself is subjected to extreme thermal cycling and potentially corrosive process gases. It is a consumable component that requires periodic inspection and will eventually need to be replaced, adding to the operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a retort furnace comes down to a single question: how critical is atmospheric control to your process outcome?
- If your primary focus is changing the surface chemistry of a part: A retort furnace is the necessary tool for reactive processes like carburizing and nitriding.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or contamination: A retort furnace provides the essential protective atmosphere for bright annealing, sintering, and high-purity brazing.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment where air contact is acceptable: A less complex and more cost-effective open-air furnace is likely sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, a retort furnace is the definitive solution when the integrity of the material's environment is just as critical as the temperature you apply to it.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Function | Ideal Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Carburizing / Nitriding | Surface hardening by adding carbon/nitrogen | Reactive (e.g., carbon-rich or nitrogen-rich gas) |
| Annealing | Stress relief and softening of metals | Protective (e.g., inert Argon to prevent oxidation) |
| Sintering | Fusing powdered materials without melting | Protective/Reactive (clean, controlled to prevent oxidation) |
| Soldering / Debinding | High-purity joining of components | Inert or reactive (oxide-free environment for bonding) |
Ready to achieve superior results with precise atmospheric control?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique thermal processing needs. Whether your goal is surface hardening, contamination-free annealing, or high-purity sintering, our retort furnaces—backed by strong deep customization capabilities—are engineered to deliver unmatched quality and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems can optimize your lab's performance.
Get in touch now for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios



















