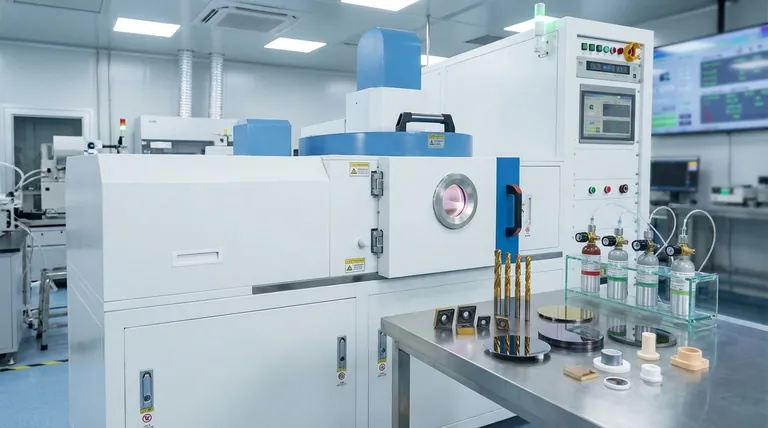
In practice, the most common CVD coatings are hard, ceramic materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbide (TiC), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3). These materials are chosen for their exceptional ability to protect surfaces from wear, corrosion, and high temperatures.
The key to understanding CVD materials is to distinguish between the final, solid coating material deposited on a surface and the volatile gas precursor chemicals used to create it. Mastering your process means mastering the relationship between these two components.
The Anatomy of a CVD Coating: Precursors vs. Final Material
The term "CVD materials" can be misleading. It's essential to separate the ingredients (precursors) from the final product (the film).
Understanding Precursor Gases
Precursors are the volatile chemical "ingredients" that are transported in a gas phase to the substrate surface. They are designed to react and decompose in a controlled way.
Common classes of precursors include halides (like Titanium Tetrachloride, TiCl4), hydrides (like Silane, SiH4), metal carbonyls, and various organometallics.
The choice of precursor is critical, as it dictates the reaction temperature, deposition rate, and potential impurities in the final film.
The Final Solid Film
When the precursor gases react on the hot substrate, they form a new, stable, and solid thin film. This is the functional coating.
These films typically fall into a few key categories:
- Nitrides (e.g., TiN)
- Carbides (e.g., TiC)
- Oxides (e.g., Al2O3, Silicon Dioxide)
- Semiconductors (e.g., Polysilicon)
- Pure Metals (e.g., Tungsten)
The final film's properties—not the precursor's—determine the performance of the coated part.
Common CVD Coating Materials and Their Purpose
Different materials are chosen to solve specific engineering problems across various industries, from aerospace to microelectronics.
Hard Coatings for Wear Resistance
Materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbide (TiC), and Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) are the workhorses for protecting cutting tools, molds, and mechanical components.
Their extreme hardness and low friction coefficient drastically extend the life of the underlying part.
Thermal and Chemical Barriers
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) is prized for its excellent thermal stability and chemical inertness. It is often used as an insulating layer in microelectronics or as a protective barrier against high-temperature corrosion.
There are different crystalline forms, like alpha and kappa alumina, which offer slightly different properties.
Films for Semiconductors and Electronics
The semiconductor industry is one of the largest users of CVD. The process is used to deposit a wide range of materials with extreme precision and purity.
This includes polycrystalline silicon, silicon dioxide (an insulator), and silicon nitride (a passivation layer), which are fundamental building blocks of modern microchips.
Optical and Decorative Coatings
CVD can be used to apply thin films to glass and other optics to modify their reflective or transmissive properties. The material choice depends entirely on the desired refractive index and wavelength performance.
Materials like TiN are also used for a decorative and durable gold-colored finish on items like watches and hardware.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing CVD is a strategic decision with distinct advantages and constraints. It is not always the right solution for every problem.
Key Advantage: Conformal Coverage
Because the coating is formed from a gas, it can uniformly coat highly complex, three-dimensional shapes. This is a significant advantage over line-of-sight processes like PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition).
Key Advantage: High Purity and Control
The chemical nature of the CVD process allows for the creation of exceptionally pure and dense films with precise control over their thickness and structure. This is why it is essential for semiconductor manufacturing.
Limitation: High Temperatures
Traditional CVD processes often require very high substrate temperatures (often >600°C) to drive the chemical reactions. This can damage or warp temperature-sensitive substrate materials like plastics or certain aluminum alloys.
Limitation: Precursor Safety and Handling
Many precursor gases are highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates significant investment in safety protocols, gas handling equipment, and exhaust treatment systems.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by the primary performance goal you need to achieve for your component.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear resistance: Your default choices are TiN, TiC, or multi-layered coatings involving TiCN for cutting tools and wear parts.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor fabrication: You will work with a well-defined set of precursors for silicon, silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, and various metals like tungsten.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or chemical insulation: Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) is a standard and highly effective barrier coating.
- If your primary focus is modifying optical properties: The material choice is vast and must be matched precisely to the target wavelength and desired refractive index, often using various oxides and nitrides.
Ultimately, effective material selection in CVD is an exercise in matching the known properties of a solid film to the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrides | TiN | High hardness, low friction | Cutting tools, wear parts |
| Carbides | TiC | Extreme hardness, wear resistance | Mechanical components |
| Carbonitrides | TiCN | Enhanced toughness, wear resistance | Multi-layered coatings |
| Oxides | Al2O3 | Thermal stability, chemical inertness | Microelectronics, corrosion barriers |
| Semiconductors | Polysilicon | Precision, purity | Semiconductor fabrication |
| Pure Metals | Tungsten | Conductive, durable | Electronics, interconnects |
Optimize Your CVD Coating Process with KINTEK Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're developing wear-resistant coatings, semiconductor films, or thermal barriers, our expertise ensures superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor our solutions to your specific CVD coating challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















