When your process demands extreme and sustained heat, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are the definitive choice. They are best suited for high-temperature industrial applications where long-term operational stability and oxidation resistance are critical, such as in the manufacturing of glass, ceramics, and semiconductors, as well as in advanced metallurgy and materials research.
The decision to use MoSi2 elements is driven by a need for reliability in continuous, high-temperature environments. Their value is not just in the heat they produce, but in their ability to sustain it for extended periods, minimizing costly furnace downtime and ensuring consistent product quality.
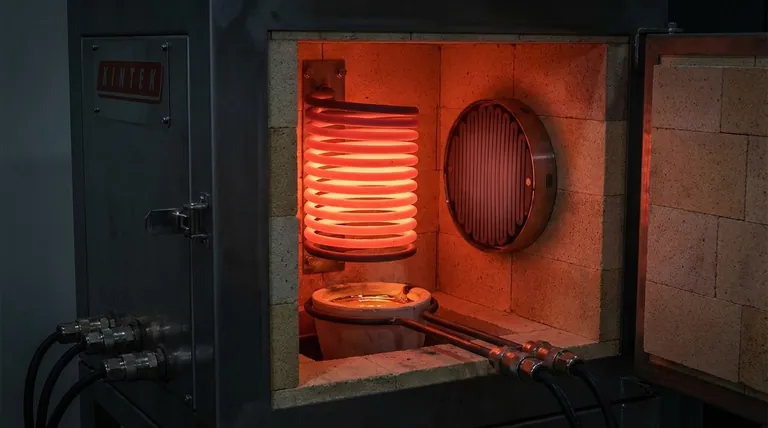

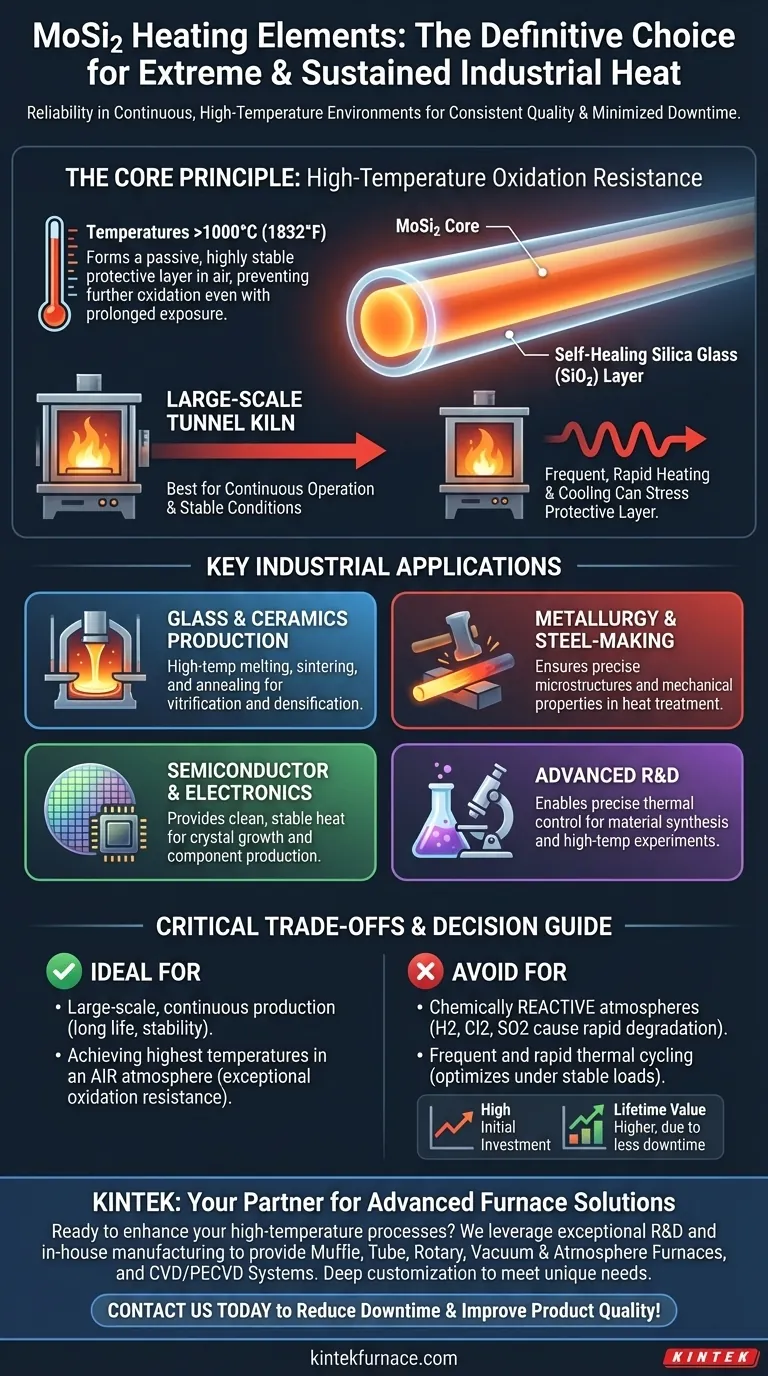
The Core Principle: High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance
The unique advantage of MoSi2 elements comes from their behavior at extreme temperatures. Understanding this principle is key to knowing where they fit best.
How MoSi2 Survives Extreme Heat
At temperatures above 1000°C (1832°F), a thin, self-healing layer of silica glass (SiO2) forms on the element's surface. This passive layer is highly stable and protects the underlying material from further oxidation, even with prolonged exposure to air.
The Importance of Continuous Operation
This protective layer is most effective under stable, continuous working conditions. For this reason, MoSi2 elements excel in large-scale furnaces like tunnel kilns that run for long, uninterrupted cycles. Frequent, rapid heating and cooling can stress the protective layer.
The Link to High-Value Manufacturing
Industries like aerospace and automotive require high-strength, defect-free materials. The stable, uniform heat provided by MoSi2 elements is crucial for the heat treatment and sintering processes that produce these advanced components, where process variation is unacceptable.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
MoSi2 elements are not a general-purpose solution; they are a specialized tool for demanding thermal processes.
Glass and Ceramics Production
These elements are widely used for melting, sintering, and annealing glass and advanced ceramics. Their ability to operate at temperatures needed to vitrify or densify materials makes them indispensable in this sector.
Metallurgy and Steel-Making
In metallurgy, MoSi2 elements are used in high-temperature heat-treating and forging furnaces. Their performance ensures that metals and alloys achieve their required microstructures and mechanical properties.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The production of semiconductor materials, electronic components, and crystals requires exceptionally pure and stable high-temperature environments. MoSi2 elements provide the clean, reliable heat needed for processes like crystal growth.
Advanced Research and Development
In laboratory and research settings, MoSi2-equipped furnaces are essential for synthesizing new materials and conducting high-temperature experiments where precise thermal control is paramount.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
To leverage MoSi2 elements effectively, you must also understand their operational limitations. Choosing them without acknowledging these factors can lead to premature failure.
The Absolute Need for the Right Atmosphere
MoSi2 elements are designed to operate in air or inert gas environments only. The protective silica layer is vulnerable to attack from chemically active gases.
Using them in atmospheres containing hydrogen (H2), chlorine (Cl2), or sulfur dioxide (SO2) will lead to rapid degradation and element failure.
Cost Profile: Initial Investment vs. Lifetime Value
MoSi2 elements typically have a higher initial purchase price compared to other element types. However, their long service life and the reliability they bring to continuous processes often result in a lower total cost of ownership by drastically reducing expensive production downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific operational goal is the most important factor in determining if MoSi2 is the correct technology for you.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous production: MoSi2 is an ideal choice due to its longevity and stability in furnaces that run for extended periods.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures in an air atmosphere: MoSi2's exceptional oxidation resistance makes it a premier technology for this purpose.
- If your process involves chemically reactive atmospheres: You must seek an alternative heating element technology, as MoSi2 will be damaged.
- If your operation requires frequent and rapid thermal cycling: You should carefully evaluate if MoSi2 is the best fit, as it performs optimally under more stable, continuous loads.
Ultimately, selecting MoSi2 is a strategic decision for processes where long-term thermal stability is the cornerstone of production value.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Glass & Ceramics Production | High-temperature melting, sintering, and annealing with uniform heat |
| Metallurgy & Steel-Making | Ensures precise microstructures and mechanical properties in heat treatment |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Provides clean, stable heat for crystal growth and component production |
| Advanced R&D | Enables precise thermal control for material synthesis and experiments |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable MoSi2 heating elements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can reduce downtime and improve product quality in your industrial applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















