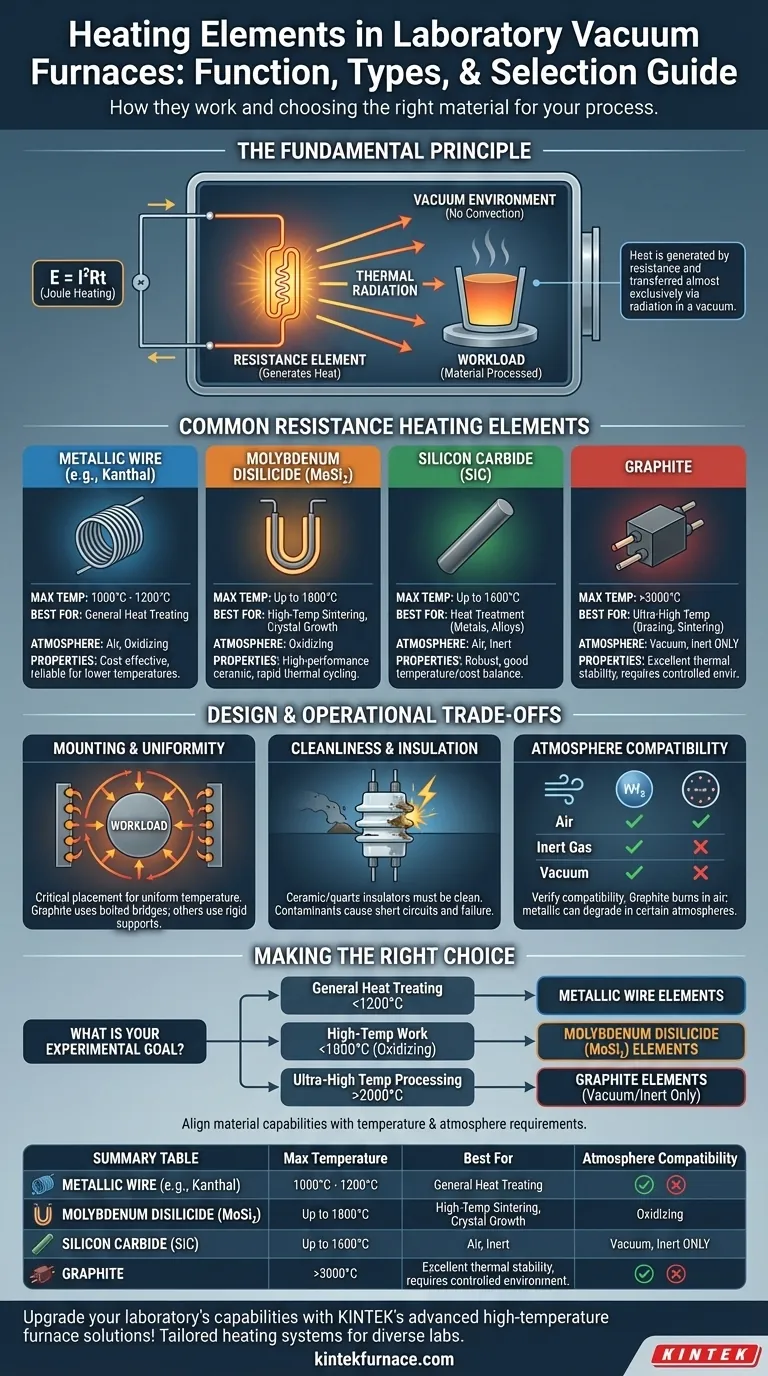
In laboratory vacuum furnaces, heating elements are typically made from metallic alloys, molybdenum disilicide, silicon carbide, or graphite. These elements function by resisting the flow of electrical current, which generates immense heat according to the principle of Joule heating. In the vacuum environment, this thermal energy is then transferred almost exclusively through radiation to the material being processed.
The choice of a heating element is not about finding the "best" one, but about selecting the right material for a specific application. This decision is a critical trade-off between the required maximum temperature, the process atmosphere, and the chemical compatibility with the workload.
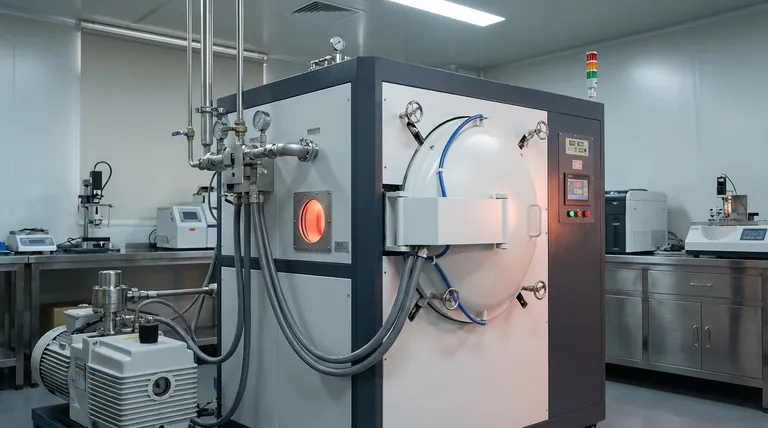

The Fundamental Principle: How Elements Work in a Vacuum
Understanding how heating elements function in a vacuum furnace requires grasping two core concepts: how heat is generated and how it is transferred.
From Electricity to Heat
The underlying principle for all resistance heating elements is Joule's First Law. When an electric current passes through a material with electrical resistance, electrical energy is converted into thermal energy.
The amount of heat produced is defined by the formula E = I²Rt. This means the heat generated is a function of the current (I), the material's resistance (R), and the time (t) the current is applied.
The Critical Role of Radiation
In a standard atmosphere, heat is transferred via conduction, convection, and radiation. However, in the near-perfect vacuum of a furnace, convection is virtually eliminated as there is no air to move the heat.
Therefore, heat transfer relies almost entirely on thermal radiation. The hot element emits electromagnetic waves that travel through the vacuum and are absorbed by the cooler objects in the furnace, raising their temperature.
A Breakdown of Common Resistance Heating Elements
Different materials are used as heating elements, each with distinct temperature ranges and properties that make them suitable for specific laboratory processes.
Metallic Wire Elements
These are often made from iron-chromium-aluminum alloys (like Kanthal) or nickel-chromium alloys. They are common in lower-temperature applications.
- Maximum Temperature: Typically 1000°C to 1200°C.
- Best For: General heat treating and processes where ultra-high temperatures are not required.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements
These are high-performance ceramic-based elements known for their ability to withstand very high temperatures and rapid thermal cycling.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to 1800°C.
- Best For: High-temperature sintering, crystal growth, and glass melting, particularly in oxidizing atmospheres.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements
SiC elements are robust and reliable, offering a good balance between temperature capability and cost. They are versatile for many high-temperature applications.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to 1600°C.
- Best For: A wide range of heat treatment processes for metals and alloys in both air and inert atmospheres.
Graphite Elements
Graphite is the material of choice for the highest temperature applications in controlled environments. It has excellent thermal stability but requires a specific atmosphere.
- Maximum Temperature: Can exceed 3000°C.
- Best For: Ultra-high temperature processes like brazing, sintering, and purification, but must be used in a vacuum or inert gas to prevent rapid oxidation.
Understanding the Design & Operational Trade-offs
The performance of a heating element is not just about the material itself, but also about the design and maintenance of the entire system.
Element Mounting and Temperature Uniformity
The placement of heating elements is critical for achieving a uniform temperature within the furnace's hot zone. They may be mounted radially around the workload or on the walls and door.
Elements made of graphite are often connected using bolted graphite bridges, while other types rely on rigid support structures to maintain their position and integrity at high temperatures.
The Importance of Cleanliness and Insulation
Heating elements are mounted using ceramic or quartz insulators. These insulators must be kept meticulously clean.
Contaminants like carbon dust or metallic vapors from the process can condense on the insulators, creating a conductive path. This can lead to a short circuit, causing element failure and costly downtime.
Atmosphere Compatibility
A material's suitability is heavily dependent on the process atmosphere. Metallic elements can operate in air, but graphite will rapidly burn away and be destroyed in an oxidizing atmosphere.
Conversely, some elements that excel in air may have their lifespan reduced in certain inert or reducing atmospheres. Always verify the element's compatibility with your specific process gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating element is a direct function of your experimental or production goals.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating below 1200°C: Metallic wire elements provide a reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work up to 1800°C in an oxidizing atmosphere: Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are the industry standard for performance and longevity.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing above 2000°C: Graphite elements are unmatched, provided you operate exclusively in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
By aligning the material's capabilities with your specific temperature and atmospheric requirements, you ensure an efficient, reliable, and successful heating process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature | Best For Applications | Atmosphere Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | 1000°C - 1200°C | General heat treating | Air, oxidizing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | High-temperature sintering, crystal growth | Oxidizing |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Heat treatment for metals and alloys | Air, inert |
| Graphite | Exceeds 3000°C | Ultra-high temp brazing, sintering | Vacuum, inert |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements and furnaces can optimize your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















