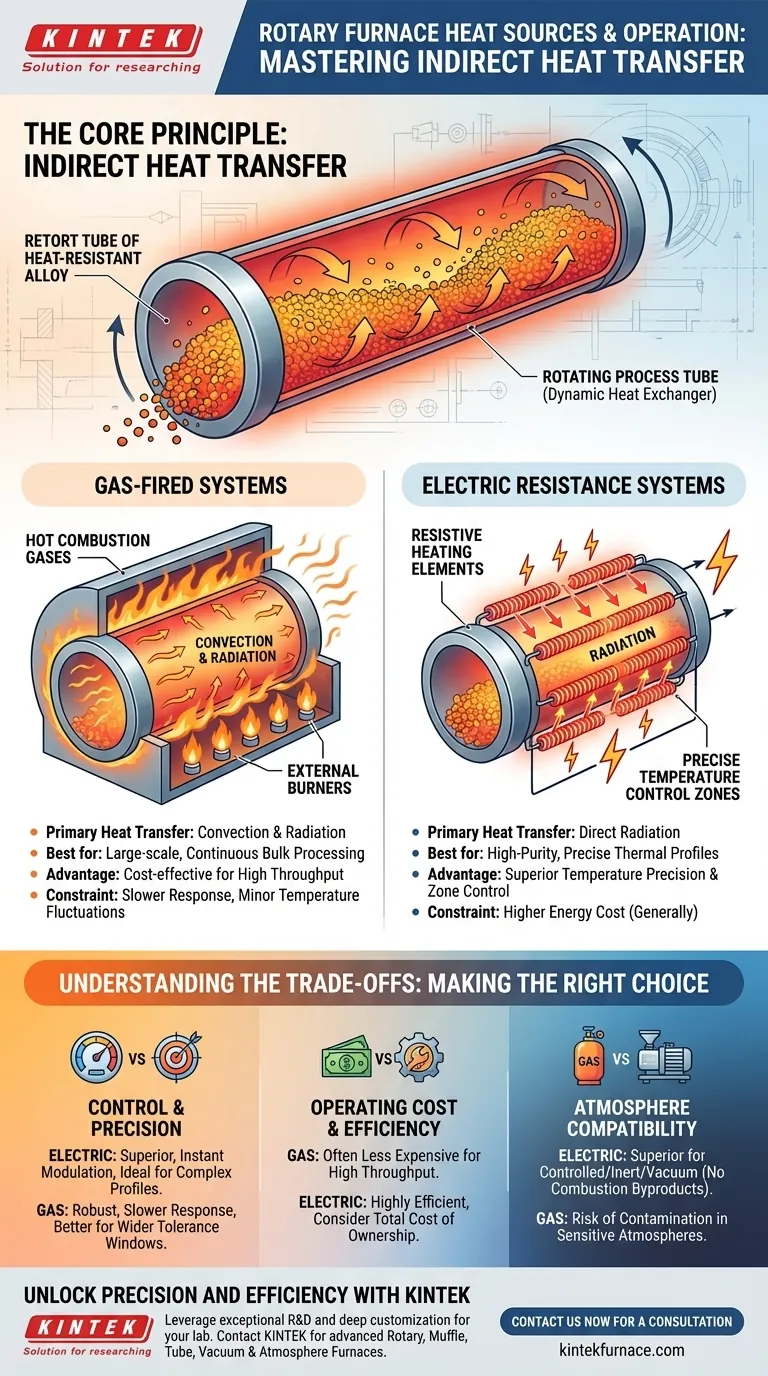
At their core, rotary furnaces utilize either gas-fired systems or electric resistance heating elements. Both types operate on the fundamental principle of indirect heat transfer, where the heat source is located outside the rotating process tube, ensuring the material inside is heated uniformly and without direct contact or contamination from the source itself.
The critical distinction in rotary furnace operation is not merely the choice between gas and electric, but its reliance on an indirect heating method. The external heat source warms the rotating tube, which then acts as a dynamic heat exchanger to uniformly process the material within it.
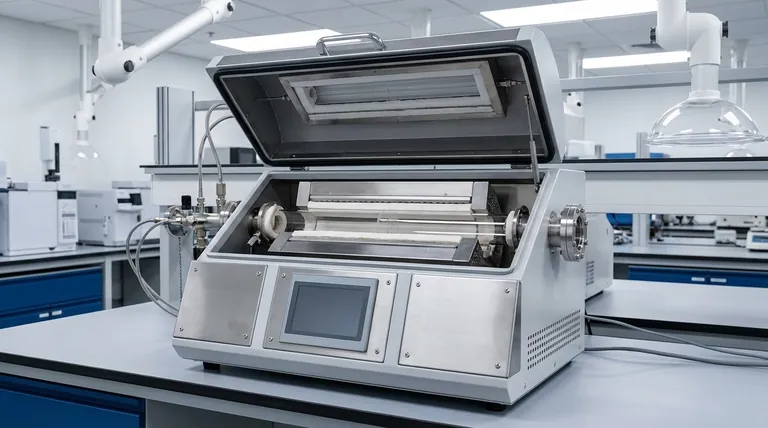

The Core Principle: Indirect Heat Transfer
The design of a rotary furnace is engineered to solve a fundamental challenge in materials processing: achieving perfect temperature uniformity across a batch of material, especially powders or granules.
Why Indirect Heating is Crucial
By placing the heat source outside the processing chamber, the system prevents any direct contact between the combustion byproducts (in gas systems) or heating elements and the material.
This separation is vital for high-purity applications and processes like calcination or oxidation, where the chemical integrity of the material and the surrounding atmosphere must be precisely controlled.
The Role of the Rotating Tube
The rotating tube or retort is the heart of the system. The external heating elements—either gas burners or electric coils—heat the outside surface of this tube.
The tube, typically made of a high-temperature alloy or ceramic, absorbs this thermal energy and transfers it via conduction to the material tumbling inside. It effectively becomes the heat source for the material.
How Rotation Ensures Uniformity
As the tube rotates, it continuously lifts and tumbles the material. This constant mixing ensures that every particle is repeatedly exposed to the hot inner wall of the tube.
This action eliminates temperature gradients and hot spots that are common in static furnaces, resulting in exceptionally uniform heat treatment.
A Closer Look at the Heat Sources
While both gas and electric systems achieve indirect heating, their operational characteristics differ.
Gas-Fired Systems
Gas-fired rotary furnaces use burners positioned along the length of the furnace shell to generate hot combustion gases.
These hot gases flow through the chamber outside the rotating process tube, transferring heat primarily through convection and radiation to the tube's external wall. They are often favored for large-scale, continuous processes where operational cost is a key factor.
Electric Resistance Heating Systems
Electric rotary furnaces use resistive heating elements, such as silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide, that are arranged around the process tube.
When an electric current passes through these elements, they heat up and radiate thermal energy directly onto the external surface of the tube. This method offers exceptionally precise temperature control, often managed by sophisticated computer systems across multiple heating zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gas vs. Electric
Choosing a heat source involves balancing control, cost, and process requirements. There is no single "best" option; the optimal choice depends entirely on the application.
Control and Precision
Electric systems offer superior temperature precision and zone control. The energy input can be modulated instantly and accurately, making them ideal for sensitive materials or complex heating profiles requiring specific ramps and soaks.
Gas systems, while robust, generally have slower response times and can introduce minor temperature fluctuations, making them better suited for bulk processes with wider tolerance windows.
Operating Cost and Efficiency
Gas is often a less expensive energy source than electricity, making gas-fired furnaces more cost-effective for high-throughput, continuous operations.
However, modern electric furnaces can be highly energy-efficient, especially when well-insulated. The total cost of ownership, including maintenance, should be considered.
Atmosphere Compatibility
For processes requiring a controlled or inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum, electric furnaces are almost always the superior choice.
Because there is no combustion, there is no risk of byproducts contaminating the process atmosphere inside the tube, ensuring process purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by your primary processing objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity materials and precise thermal profiles: An electric resistance furnace provides the unparalleled control and clean operating environment you need.
- If your primary focus is large-scale bulk material processing where throughput and operating cost are key drivers: A gas-fired furnace is typically the more pragmatic and economical solution.
- If your process requires a strictly controlled, inert, or vacuum atmosphere: An electric furnace is the only viable option to prevent atmospheric contamination.
Ultimately, understanding how the heat source interacts with the furnace's mechanical design empowers you to select the right tool for your specific material transformation goal.
Summary Table:
| Heat Source Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Gas-Fired Systems | Uses burners for convection/radiation heating; cost-effective for high throughput | Large-scale bulk processing where operational cost is a key driver |
| Electric Resistance Systems | Employs heating elements for precise temperature control; ideal for clean atmospheres | High-purity materials, precise thermal profiles, and inert/vacuum atmospheres |
Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Rotary Furnaces
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need the cost-effectiveness of gas-fired systems for bulk processing or the superior control of electric systems for sensitive materials, KINTEK has the expertise to deliver tailored solutions that enhance your material transformation processes. Don't let heating challenges hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your lab's performance and achieve your specific goals.
Contact us now for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















